Nervous System & Senses
... Messages jump across Drugs and the synapse alcohol disrupts like the an electrical communication current between neurons ...
... Messages jump across Drugs and the synapse alcohol disrupts like the an electrical communication current between neurons ...
1 2 The Advent of Modern Neuroscience
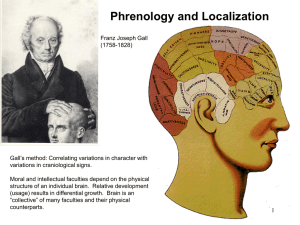
... of experimental ablation to establish a link between the cerebellum and coordination of movement, and the cerebrum and sensations in 1823. This opened up the way for the concept of localization of function. Flourens was also a vociferous critic of the pseudo-science of phrenology put forth by Franz ...
... of experimental ablation to establish a link between the cerebellum and coordination of movement, and the cerebrum and sensations in 1823. This opened up the way for the concept of localization of function. Flourens was also a vociferous critic of the pseudo-science of phrenology put forth by Franz ...
Module 6 PowerPoint
... We may soon be able to use computers to translate neural inputs into more commands and words than simply grabbing food. ...
... We may soon be able to use computers to translate neural inputs into more commands and words than simply grabbing food. ...
Module 6 Powerpoint
... We may soon be able to use computers to translate neural inputs into more commands and words than simply grabbing food. ...
... We may soon be able to use computers to translate neural inputs into more commands and words than simply grabbing food. ...
Document
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
... Lobes of the Brain & Functions: • Frontal = Top front, responsible for emotion and reasoning. • Parietal = Middle, and is the sensory center. • Occipital = Back, used for vision and reading. • Temporal = Lower sides, hearing and memory. ...
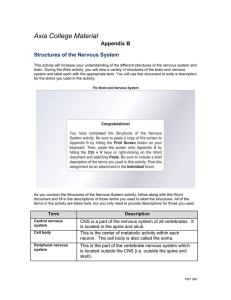
Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
... is located in the spine and skull. This is the center of metabolic activity within each neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine and skull). ...
... is located in the spine and skull. This is the center of metabolic activity within each neuron. The cell body is also called the soma. This is the part of the vertebrate nervous system which is located outside the CNS (i.e. outside the spine and skull). ...
Ch 3
... psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
... psychological functioning? 19. What is plasticity and for what mental function does it play a particularly important role? ...
Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of
... 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmi ...
... 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or-none response. D) dependent on neurotransmi ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... – How Does it Offer Protection? It bathes the brain and cushions from trauma. – How is it Formed? In a Dense capillary bed by called the CHOROID PLEXUS ...
... – How Does it Offer Protection? It bathes the brain and cushions from trauma. – How is it Formed? In a Dense capillary bed by called the CHOROID PLEXUS ...
Week 1a Lecture Notes
... Integration of synaptic inputs, synaptic and cellular plasticity Methods of cognitive neuroscience, functional neuroimaging, EEG, TMS, MEG Data analysis methods, neural coding, computational neuroscience ...
... Integration of synaptic inputs, synaptic and cellular plasticity Methods of cognitive neuroscience, functional neuroimaging, EEG, TMS, MEG Data analysis methods, neural coding, computational neuroscience ...
Copy Notes
... parietal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal l ...
... parietal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal l ...
Nervous System
... A group of neural pathways that connects parts of the thalmus & hypolthalmus & inner portions of the cerebrum “border” – to describe structures that bordered the basal regions of the cerebrum – but has come to describe all neuronal structures that control emotional behavior and motivational drives L ...
... A group of neural pathways that connects parts of the thalmus & hypolthalmus & inner portions of the cerebrum “border” – to describe structures that bordered the basal regions of the cerebrum – but has come to describe all neuronal structures that control emotional behavior and motivational drives L ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
... human brain. Recent estimates put it at about 86 billion. • About 100 trillion connections amongst these neurons. • Neurons have many of the same features as other cells – Nucleus – Cytoplasm – Cell membrane ...
notes - Other Places you want to go
... Colorless fluid that contains chemicals that have many functions Includes lymphocytes to fight infection Main function is to protect brain and spinal cord ***Know Figure 16.5 (see Brain handout to study)*** Functions of some parts of the brain: Cerebrum – deals with “higher-level” brain func ...
... Colorless fluid that contains chemicals that have many functions Includes lymphocytes to fight infection Main function is to protect brain and spinal cord ***Know Figure 16.5 (see Brain handout to study)*** Functions of some parts of the brain: Cerebrum – deals with “higher-level” brain func ...
Introduction to the Brain
... for carrying messages to and from the brain. Other cells, known as glia provide the support structure for the neurons. Neurons require oxygen to function, and begin to die within about 3 to 5 minutes without it. The neurons themselves are quite fragile and need extensive protection from being crushe ...
... for carrying messages to and from the brain. Other cells, known as glia provide the support structure for the neurons. Neurons require oxygen to function, and begin to die within about 3 to 5 minutes without it. The neurons themselves are quite fragile and need extensive protection from being crushe ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... of human brains because a reptile’s (who appear early on the evolutionary scale) entire brain resembles our brain stem. ...
... of human brains because a reptile’s (who appear early on the evolutionary scale) entire brain resembles our brain stem. ...
Inside the Human Brain - Hale
... emotion, and fear. The amygdala is both large and just beneath the surface of the front, medial part of the temporal lobe. ...
... emotion, and fear. The amygdala is both large and just beneath the surface of the front, medial part of the temporal lobe. ...
Neurons and the Brain
... young minds, work well in groups, and most important of all, your creativity. We will be focusing on neuroscience as we have deduced that the brain plays a very important role in explaining zombie behavior. Your goal will be to become a medications development specialist and create a cure for the zo ...
... young minds, work well in groups, and most important of all, your creativity. We will be focusing on neuroscience as we have deduced that the brain plays a very important role in explaining zombie behavior. Your goal will be to become a medications development specialist and create a cure for the zo ...
Unit 4: Neuroscience The Neuron Soma (cell body): Contains
... CAT) scans show structures within the brain but not functions of the brain. PET (positron emission tomography): visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose is being used while the brain performs certain tasks. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): technique that use ...
... CAT) scans show structures within the brain but not functions of the brain. PET (positron emission tomography): visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose is being used while the brain performs certain tasks. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): technique that use ...
GEOTRAN - Life Solutions Institute
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...
... In the human brain, there are more than several hundred million neurons. In these neurons ion currents flow. The ion currents produce the magnetic field. This magnetic field emerges out of the head through the brain, the scalp and the head. ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.