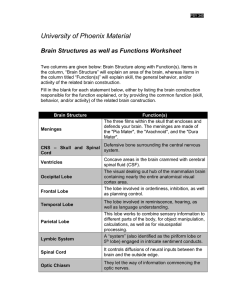
Chapter 2 figures 2.7 to 2.12
... Figure 2.9. (a) Image with 4 bands of differing brightness. A to D are locations marks. (b) Physical brightness levels of image in (a). (c) Perceptual brightness of image (a) "seen" by viewer resulting from lateral inhibition. (d) Conceptual diagram of how lateral inhibition can enhance borders bet ...
... Figure 2.9. (a) Image with 4 bands of differing brightness. A to D are locations marks. (b) Physical brightness levels of image in (a). (c) Perceptual brightness of image (a) "seen" by viewer resulting from lateral inhibition. (d) Conceptual diagram of how lateral inhibition can enhance borders bet ...
48.5, .6, .7
... • LTP can last days or weeks when memories are stored. • Post synaptic neurons possess two types of glutamate receptors – AMPA: part of ligand-gated ion channels; when glutamate binds to them, Na+ and K+ diffuse through channels – NMDA: both ligand gated and voltage gated that open only if glutamate ...
... • LTP can last days or weeks when memories are stored. • Post synaptic neurons possess two types of glutamate receptors – AMPA: part of ligand-gated ion channels; when glutamate binds to them, Na+ and K+ diffuse through channels – NMDA: both ligand gated and voltage gated that open only if glutamate ...
Nervous System
... metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
... metabolism. Lack of oxygen for more than 5 minutes can kill brain cells. • The brain requires glucose for metabolism. Lack of glucose for more than 15 minutes kills brain cells. • Neurons cannot undergo mitosis. ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... are arranged like rungs on a twisted ladder There are about 30,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions Genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
... are arranged like rungs on a twisted ladder There are about 30,000 genes that contain chemical instructions that equal about 300,000 pages of written instructions Genes program the development of individual parts into a complex body & brain ...
Time Zones
... 7. This is the mechanism that allows evolution to occur. It involves variety and adaptation! 8. This is the process where left over neurotransmitters or waste left over from devoured neurotransmitters travel back to the Terminal Button? 9. This principle is law that once a Soma “fires” it can’t not ...
... 7. This is the mechanism that allows evolution to occur. It involves variety and adaptation! 8. This is the process where left over neurotransmitters or waste left over from devoured neurotransmitters travel back to the Terminal Button? 9. This principle is law that once a Soma “fires” it can’t not ...
The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous
... • cerebral cortex – outer layer of cerebrum; gray matter made largely of cell bodies which lack myelin, located largely in the cerebral cortex; cerebral cortex consists mainly of nerve bodies located in a thin layer less than 3mm thick with axons projecting to interior of cortex; cortex deeply groov ...
... • cerebral cortex – outer layer of cerebrum; gray matter made largely of cell bodies which lack myelin, located largely in the cerebral cortex; cerebral cortex consists mainly of nerve bodies located in a thin layer less than 3mm thick with axons projecting to interior of cortex; cortex deeply groov ...
HP Authorized Customer
... Supplies the brain with nourishment (food) and oxygen. The main white substance area of dendrites as well as axons linking both hemispheres of the brain. It adds information from the two dissimilar halves of the cerebral cortex, main sensory as well as motor information. These 12 formations send and ...
... Supplies the brain with nourishment (food) and oxygen. The main white substance area of dendrites as well as axons linking both hemispheres of the brain. It adds information from the two dissimilar halves of the cerebral cortex, main sensory as well as motor information. These 12 formations send and ...
Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
... coordinating and executing both the voluntary and involuntary processes that maintain homeostasis ...
... coordinating and executing both the voluntary and involuntary processes that maintain homeostasis ...
Lesson 7:
... - memories - sense of smell 3. occipital lobe – visual info 4. parietal lobe – sensory info (temperature, pressure, touch, pain) Each side focus’s on certain tasks: Left side Right side Math, logic. Language creative (art and music) Gray matter – outer surface of the brain, grayish in color - contai ...
... - memories - sense of smell 3. occipital lobe – visual info 4. parietal lobe – sensory info (temperature, pressure, touch, pain) Each side focus’s on certain tasks: Left side Right side Math, logic. Language creative (art and music) Gray matter – outer surface of the brain, grayish in color - contai ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
... - Somatosensory cortex: area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations. - Association area: areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as ...
Grant Clay
... You should be able to answer the following questions: 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nat ...
... You should be able to answer the following questions: 1. Why is the cerebral cortex considered the part of the brain that makes people uniquely human? 2. How do we know what we know about the brain? 3. What are the major processes at work in the developing brain? 4. Is our behavior determined by nat ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... range of techniques scientists have used to learn about brain function, from procedures such as ablation, direct stimulation, EEG, CAT scans, PET scans, MRI, and fMRI. We also emphasize the brain’s role in the body’s nervous system, examining the anatomical and functional relationships of the centra ...
... range of techniques scientists have used to learn about brain function, from procedures such as ablation, direct stimulation, EEG, CAT scans, PET scans, MRI, and fMRI. We also emphasize the brain’s role in the body’s nervous system, examining the anatomical and functional relationships of the centra ...
BRAiNBAsED LEARNiNG - Slone Chiropractic
... to evaluate and treat many neurologic conditions such as Dyslexia, Autism, ADD/ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Treatment is designed to treat an area of the patient that is often overlooked… THE BRAIN. ...
... to evaluate and treat many neurologic conditions such as Dyslexia, Autism, ADD/ADHD and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Treatment is designed to treat an area of the patient that is often overlooked… THE BRAIN. ...
Lecture 4 - On the Evolution of Human Language
... defects in the grammatical processing of words difficulties understanding complex sentence structures inability to form intelligible speech defects in the ability to move the mouth and face not associated with speaking significantly reduced IQ ...
... defects in the grammatical processing of words difficulties understanding complex sentence structures inability to form intelligible speech defects in the ability to move the mouth and face not associated with speaking significantly reduced IQ ...
TECHNIQUES2001
... Radioactive substance emits positrons when its atoms disintegrate Positrons interact with electrons and produce photons of light Detectors measure the photons Functional but NO SPATIAL resolution ? = Baseline state - STATE of INTEREST ...
... Radioactive substance emits positrons when its atoms disintegrate Positrons interact with electrons and produce photons of light Detectors measure the photons Functional but NO SPATIAL resolution ? = Baseline state - STATE of INTEREST ...
AP Psychology
... 28. The association areas in the frontal lobe allow us to _____________________ 29. How might a lesion affect brain function? 30. What is an EEG and for what purpose is it used? 31. Describe each of the following neuroimaging techniques: a. CT--computerized tomography b. MRI--magnetic resonance imag ...
... 28. The association areas in the frontal lobe allow us to _____________________ 29. How might a lesion affect brain function? 30. What is an EEG and for what purpose is it used? 31. Describe each of the following neuroimaging techniques: a. CT--computerized tomography b. MRI--magnetic resonance imag ...
Imaging shows structural changes in mild traumatic brain injury
... majority were high-functioning people who were employed or in school at the time of evaluation. The researchers found that structural changes in the white matter correlate to observable cognitive deficits related to thinking, memory and attention. Patients with more severe injuries had greater white ...
... majority were high-functioning people who were employed or in school at the time of evaluation. The researchers found that structural changes in the white matter correlate to observable cognitive deficits related to thinking, memory and attention. Patients with more severe injuries had greater white ...
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... Roger Sperry received the Nobel Prize in physiology and medicine in 1981 for his experiments on split brain patients that provided strong evidence for lateralization of speech processing in the brain. Sperry's experiments showed, that the left hemisphere is responsible for the formation of speech wh ...
... Roger Sperry received the Nobel Prize in physiology and medicine in 1981 for his experiments on split brain patients that provided strong evidence for lateralization of speech processing in the brain. Sperry's experiments showed, that the left hemisphere is responsible for the formation of speech wh ...
______ 1
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
... _____________________ 3. The difference in electrical charge across a membrane _____________________ 4. Another name for a receiving neuron _____________________ 5. Another name for a transmitting neuron _____________________ 6. Is generated when a dendrite or cell body is stimulated _______________ ...
On the Brain of a Scientist: Albert Einstein
... to be concerned with "higher" neural functions. These regions do not directly receive primary sensory information, but rather, as their name implies, ,.associate,, or. analyze inputs from other brain regions. The associaiion-cortices are the last domains of the cortex to myerinate, indicating their ...
... to be concerned with "higher" neural functions. These regions do not directly receive primary sensory information, but rather, as their name implies, ,.associate,, or. analyze inputs from other brain regions. The associaiion-cortices are the last domains of the cortex to myerinate, indicating their ...
Characterization of GPR101 transcripts structure, expression and
... of the patients. Methods: We characterized GPR101 transcripts in vitro in human tissues by integrating 5’RACE and RNAseq, and we predicted the putative promoter region in silico. GPR101 expression was investigated at the mRNA and protein level in post-mortem human, rat, and zebrafish tissues, by qPC ...
... of the patients. Methods: We characterized GPR101 transcripts in vitro in human tissues by integrating 5’RACE and RNAseq, and we predicted the putative promoter region in silico. GPR101 expression was investigated at the mRNA and protein level in post-mortem human, rat, and zebrafish tissues, by qPC ...
Introduction to the brain and behaviour
... What purpose is served by the convolutions in the cerebral cortex of the brain? A. They allow more blood to flow to the neurons as the brain requires more oxygen and nutrients than other organs of the body. B. They provide some protection against injury by acting as a shock absorber if the brain is ...
... What purpose is served by the convolutions in the cerebral cortex of the brain? A. They allow more blood to flow to the neurons as the brain requires more oxygen and nutrients than other organs of the body. B. They provide some protection against injury by acting as a shock absorber if the brain is ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal buttons Nerve impulse triggers their release Over 50 have been identified Major ones are de ...
... of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal buttons Nerve impulse triggers their release Over 50 have been identified Major ones are de ...
Connectome

A connectome is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its ""wiring diagram"". More broadly, a connectome would include the mapping of all neural connections within an organism's nervous system.The production and study of connectomes, known as connectomics, may range in scale from a detailed map of the full set of neurons and synapses within part or all of the nervous system of an organism to a macro scale description of the functional and structural connectivity between all cortical areas and subcortical structures. The term ""connectome"" is used primarily in scientific efforts to capture, map, and understand the organization of neural interactions within the brain.Research has successfully constructed the full connectome of one animal: the roundworm C. elegans (White et al., 1986, Varshney et al., 2011). Partial connectomes of a mouse retina and mouse primary visual cortex have also been successfully constructed. Bock et al.'s complete 12TB data set is publicly available at Open Connectome Project.The ultimate goal of connectomics is to map the human brain. This effort is pursued by the Human Connectome Project, sponsored by the National Institutes of Health, whose focus is to build a network map of the human brain in healthy, living adults.




![The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005074380_1-b4c54e7cf592b472b621b12b4eff42cc-300x300.png)