Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since
... Language and Symbolic Behavior Problem for Pavlov: how to account for language? Symbolic activity that involves a link between an arbitrary symbol and its referent. Pavlov proposed a two-part theory of language: First signal system: association between a signal (CS) and biologically meaningf ...
... Language and Symbolic Behavior Problem for Pavlov: how to account for language? Symbolic activity that involves a link between an arbitrary symbol and its referent. Pavlov proposed a two-part theory of language: First signal system: association between a signal (CS) and biologically meaningf ...
Brain Research Methods - RevisionforPsy3
... o Can be used for mapping brain areas, pinpoint/diagnose brain damage and to track patients recovery ie. From a stroke o Repetitive TMS (rTMS) used in procedures involving repeated (not necessarily rapid) delivery of a pulse causing area of brain to be inactive without unwanted side effects – used t ...
... o Can be used for mapping brain areas, pinpoint/diagnose brain damage and to track patients recovery ie. From a stroke o Repetitive TMS (rTMS) used in procedures involving repeated (not necessarily rapid) delivery of a pulse causing area of brain to be inactive without unwanted side effects – used t ...
Chap10aAlt
... The actual SSDR elicited depends on the situation as well as the species (flight, freezing, burying). ...
... The actual SSDR elicited depends on the situation as well as the species (flight, freezing, burying). ...
PsychScich04
... • Ventral stream appears to be specialized for the perception and recognition of objects • Dorsal stream seems to be specialized for spatial perception (determining where an object is) • These two processing streams are therefore known as the “what” stream and the “where” stream ...
... • Ventral stream appears to be specialized for the perception and recognition of objects • Dorsal stream seems to be specialized for spatial perception (determining where an object is) • These two processing streams are therefore known as the “what” stream and the “where” stream ...
Olfactory tubercle neurons exhibit slowphasic firing patterns during
... infusion pump. Infusions were followed by a 40 s schedule timeout during which responses had no programmed consequences. Before electrophysiological recordings, it was verified that animals had acquired SA behavior as evidenced by increases in both the number of responses and daily drug intake over ...
... infusion pump. Infusions were followed by a 40 s schedule timeout during which responses had no programmed consequences. Before electrophysiological recordings, it was verified that animals had acquired SA behavior as evidenced by increases in both the number of responses and daily drug intake over ...
AMD TC Newsletter Vol. 4, No. 2, October 2007
... process? Paterson et al. [1] says “Recent advances in cognitive neuroscience have allowed us to begin investigating the development of both structure and function in the infant brain. However, despite the rapid evolution of technology, surprisingly few studies have examined the intersection between ...
... process? Paterson et al. [1] says “Recent advances in cognitive neuroscience have allowed us to begin investigating the development of both structure and function in the infant brain. However, despite the rapid evolution of technology, surprisingly few studies have examined the intersection between ...
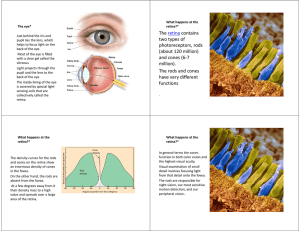
The retina contains two types of photoreceptors, rods (about 120
... fragmented information and integrate it so that we see an image, a colour, a face, a movement etc. • This occurs via two main neural streams that go to particular parts of the brain termed visual association areas where visual signals are further interpreted and given additional meaning • Each ...
... fragmented information and integrate it so that we see an image, a colour, a face, a movement etc. • This occurs via two main neural streams that go to particular parts of the brain termed visual association areas where visual signals are further interpreted and given additional meaning • Each ...
Behaviorism - pgt201e2009
... Watson took side within the Darwinian movement and adapted new approach to the development of the human mind. He was the first major psychologist to adopt the earlier theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children ...
... Watson took side within the Darwinian movement and adapted new approach to the development of the human mind. He was the first major psychologist to adopt the earlier theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children ...
2) Operant conditioning where there is reinforcement
... Watson took side within the Darwinian movement and adapted new approach to the development of the human mind. He was the first major psychologist to adopt the earlier theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children ...
... Watson took side within the Darwinian movement and adapted new approach to the development of the human mind. He was the first major psychologist to adopt the earlier theories of John Locke (1632-1704) who believed that knowledge came to the child only through experience and learning. The children ...
Operant Conditioning
... positively reinforced for this behavior when parents occasionally respond by giving in to a child’s demands. Result: stronger, more frequent ...
... positively reinforced for this behavior when parents occasionally respond by giving in to a child’s demands. Result: stronger, more frequent ...
God - Western Michigan University
... development of morality are in line with behavior analytic account – Evolution of altruism in different species • Moral behavior is necessary for the survival of the individual and the species ...
... development of morality are in line with behavior analytic account – Evolution of altruism in different species • Moral behavior is necessary for the survival of the individual and the species ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Action Potential: neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ...
... Action Potential: neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ...
Human Biology
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
... to develop, while pathways that are not used are eventually destroyed. This is why we become better at certain tasks when we practice them more often. ...
Disorders of the Nervous System
... So how is the nerve message continued along the axon/dendrite route??? ...
... So how is the nerve message continued along the axon/dendrite route??? ...
Human Economic Choice as Costly Information Processing
... larger neural activation, and less experience on the part of the subject making choices will induce larger activation. We provide experimental evidence that is consistent with these predictions. ...
... larger neural activation, and less experience on the part of the subject making choices will induce larger activation. We provide experimental evidence that is consistent with these predictions. ...
Classical Conditioning
... form of learning Called S-R-R theory S= Stimulus R= Response R(2nd one)= Reinforcement Classical Conditioning does NOT use reinforcement at all!!!!! ...
... form of learning Called S-R-R theory S= Stimulus R= Response R(2nd one)= Reinforcement Classical Conditioning does NOT use reinforcement at all!!!!! ...
Applying Learning
... stimulus (e.g. a spider), that are ranked from least fearful to most fearful. The patient works their way up starting at the least unpleasant and practicing their relaxation technique as they go. When they feel comfortable with this (they are no longer afraid) they move on to the next stage in the h ...
... stimulus (e.g. a spider), that are ranked from least fearful to most fearful. The patient works their way up starting at the least unpleasant and practicing their relaxation technique as they go. When they feel comfortable with this (they are no longer afraid) they move on to the next stage in the h ...
Name - appsychologykta
... did not take into account internal thoughts and feelings did not take into account overt physical behaviors did not take into account accumulated experiences focused primarily on childhood experiences focused primarily on the unconscious ...
... did not take into account internal thoughts and feelings did not take into account overt physical behaviors did not take into account accumulated experiences focused primarily on childhood experiences focused primarily on the unconscious ...
Chapter 17: Nervous System - Johnston Community College
... Excitatory signals have a depolarizing effect, and inhibitory signals have a hyperpolarizing effect on the postsynaptic membrane. Integration is the summing up of these excitatory and inhibitory signals. ...
... Excitatory signals have a depolarizing effect, and inhibitory signals have a hyperpolarizing effect on the postsynaptic membrane. Integration is the summing up of these excitatory and inhibitory signals. ...
full text - Ghent University Academic Bibliography
... remains a challenge, interdisciplinary collaboration has yielded considerable educationally-relevant information about learning mechanisms that could not have been acquired solely through behavioural methods. (Hardiman e.a., 2012, p. 137) ...
... remains a challenge, interdisciplinary collaboration has yielded considerable educationally-relevant information about learning mechanisms that could not have been acquired solely through behavioural methods. (Hardiman e.a., 2012, p. 137) ...
What is Your Reaction Time?
... transmission of nerve impulses. Unlike any other cell in the body, neurons consist of a central cell body as well as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. Scientists estimate there are more than 100 billion neurons in the brain. Neurotransmitter: A chem ...
... transmission of nerve impulses. Unlike any other cell in the body, neurons consist of a central cell body as well as several threadlike "arms" called axons and dendrites, which transmit nerve impulses. Scientists estimate there are more than 100 billion neurons in the brain. Neurotransmitter: A chem ...
This Week in The Journal Cellular/Molecular The N-Terminal Portion of A 
... Perimenstrual-Like Hormonal Regulation of Extrasynaptic ␦-Containing GABAA Receptors Mediating Tonic Inhibition and Neurosteroid Sensitivity Chase Matthew Carver, Xin Wu, Omkaram Gangisetty, and Doodipala Samba Reddy Department of Neuroscience and Experimental Therapeutics, College of Medicine, Texa ...
... Perimenstrual-Like Hormonal Regulation of Extrasynaptic ␦-Containing GABAA Receptors Mediating Tonic Inhibition and Neurosteroid Sensitivity Chase Matthew Carver, Xin Wu, Omkaram Gangisetty, and Doodipala Samba Reddy Department of Neuroscience and Experimental Therapeutics, College of Medicine, Texa ...
Learning Notes
... B. Principles of Reinforcement - any event/consequence that strengthens the behavior it follows. 1. Positive Reinforcement - adding a desirable stimulus; giving a reward; praise, money, food 2. Negative Reinforcement - removing an aversive stimulus; fastening seatbelt, taking aspirin 3. Primary Rei ...
... B. Principles of Reinforcement - any event/consequence that strengthens the behavior it follows. 1. Positive Reinforcement - adding a desirable stimulus; giving a reward; praise, money, food 2. Negative Reinforcement - removing an aversive stimulus; fastening seatbelt, taking aspirin 3. Primary Rei ...