Functional and structural adaptation in the central nervous system
... • A critical period in developmental psychology and biology represents early stages in life during which a system is highly sensitive to environmental stimuli, affecting the way it develops ...
... • A critical period in developmental psychology and biology represents early stages in life during which a system is highly sensitive to environmental stimuli, affecting the way it develops ...
Memory Lecture
... Q: What part of the cortex? How would you determine what part of the cortex is in communication with the hippocampus? Long term storage of procedural memory is in other areas Fig. 31.8 ...
... Q: What part of the cortex? How would you determine what part of the cortex is in communication with the hippocampus? Long term storage of procedural memory is in other areas Fig. 31.8 ...
Media Release
... Scientists have shown how the brain anticipates all of the new situations that it may encounter in a lifetime by creating a special kind of neural network that is “pre-adapted” to face any eventuality. This emerges from a new neuroscience study published in PLOS Computational Biology. Enel et al at ...
... Scientists have shown how the brain anticipates all of the new situations that it may encounter in a lifetime by creating a special kind of neural network that is “pre-adapted” to face any eventuality. This emerges from a new neuroscience study published in PLOS Computational Biology. Enel et al at ...
Motor Cortex
... to the auditory cortex. There is also an auditory association area which lets us interpret and remember ...
... to the auditory cortex. There is also an auditory association area which lets us interpret and remember ...
The nervous system can be divided into several connected systems
... The thalamus receives sensory information and relays this information to the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex also sends information to the thalamus which then transmits this information to other areas of the brain and spinal cord. ...
... The thalamus receives sensory information and relays this information to the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex also sends information to the thalamus which then transmits this information to other areas of the brain and spinal cord. ...
Does the explanation account for a substantial quantity of behavior?
... for a substantial quantity of behavior? • Verifiable: Is the explanation testable? • Predictive Utility: Does the explanation provide reliable answers about what people are likely to do under certain circumstances? • Parsimonious: Is it the simplest explanation? ...
... for a substantial quantity of behavior? • Verifiable: Is the explanation testable? • Predictive Utility: Does the explanation provide reliable answers about what people are likely to do under certain circumstances? • Parsimonious: Is it the simplest explanation? ...
1 What Is Behavior? Statement of Logical Behaviorism (aka
... Note: Pain is always subjective. Each individual learns the application of the word through experiences related to injury in early life ... Experiences which resemble pain, e.g., pricking, but are not unpleasant, should not be called pain. Unpleasant abnormal experiences (dysaesthesia) may also be p ...
... Note: Pain is always subjective. Each individual learns the application of the word through experiences related to injury in early life ... Experiences which resemble pain, e.g., pricking, but are not unpleasant, should not be called pain. Unpleasant abnormal experiences (dysaesthesia) may also be p ...
ASAL USUL
... in correlation with the degree of injury to the brain. • The primary effect of cerebral palsy is impairment of : ...
... in correlation with the degree of injury to the brain. • The primary effect of cerebral palsy is impairment of : ...
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS
... top. A nerve in the body will have to send a message to the spinal cord, which then sends the message up to the brain. The brain then processes the message and interprets what to do with the information, sending instructions to the muscles. For example, when the bladder is full, the bladder’s nerves ...
... top. A nerve in the body will have to send a message to the spinal cord, which then sends the message up to the brain. The brain then processes the message and interprets what to do with the information, sending instructions to the muscles. For example, when the bladder is full, the bladder’s nerves ...
A nerve cell
... The levels of nerve growth factors continue to increase during regularly repeated exercise for several months. For nerve growth factors optimal effect is attained by training only every second day, but the perspective is lifelong, training works at all ages. Regardless of outset – physical condition ...
... The levels of nerve growth factors continue to increase during regularly repeated exercise for several months. For nerve growth factors optimal effect is attained by training only every second day, but the perspective is lifelong, training works at all ages. Regardless of outset – physical condition ...
CNS_notes
... Two pathways lead from peripheral sensory receptors (touch, temperature, pain, …) to cerebral cortex: spinothalamic and posterior (or dorsal) column pathways. For each pathway, know: where cell bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of bo ...
... Two pathways lead from peripheral sensory receptors (touch, temperature, pain, …) to cerebral cortex: spinothalamic and posterior (or dorsal) column pathways. For each pathway, know: where cell bodies/axons of 1st, 2nd, 3rd order neurons are/travel; what sensations are carried. Common features of bo ...
3680Lecture29 - U of L Class Index
... • Recall that the feed-forward sweep is not a single wave of information and that it doesn’t only go through V1 ...
... • Recall that the feed-forward sweep is not a single wave of information and that it doesn’t only go through V1 ...
chapter29_Neural Control(9
... • Different types of memories are stored and brought to mind by different mechanisms: • Skill memories (repetition of motor tasks) involve the cerebellum, and are highly persistent • Declarative memories (facts and impressions) involve the temporal lobe; inputs are screened by the amygdala, and some ...
... • Different types of memories are stored and brought to mind by different mechanisms: • Skill memories (repetition of motor tasks) involve the cerebellum, and are highly persistent • Declarative memories (facts and impressions) involve the temporal lobe; inputs are screened by the amygdala, and some ...
glossary of terms
... of acting by an individual or a group towards an object, event or situation. Cultural patterns Shared patterns of behavior, cognitive constructs, traits that are learned and show some continuity thro ...
... of acting by an individual or a group towards an object, event or situation. Cultural patterns Shared patterns of behavior, cognitive constructs, traits that are learned and show some continuity thro ...
Negative Reinforcement - Methacton School District
... Cognitive Learning – involves mental process and may involve observation and imitation • Cognitive Map – mental picture of a place ...
... Cognitive Learning – involves mental process and may involve observation and imitation • Cognitive Map – mental picture of a place ...
USC Brain Project Specific Aims
... Once in equilibrium, one may increase a non-maximal stimulus s2 so that it becomes larger than the previously largest stimulus s1, yet not switch activity to the corresponding element. In neural networks with loops - an internal state resists dependence on input: buildup of excitation and inhibition ...
... Once in equilibrium, one may increase a non-maximal stimulus s2 so that it becomes larger than the previously largest stimulus s1, yet not switch activity to the corresponding element. In neural networks with loops - an internal state resists dependence on input: buildup of excitation and inhibition ...
Perspectives and Careers
... in human behavior. ◦ Believed that people become anxious and unhappy if they are prevented from selfactualization. ...
... in human behavior. ◦ Believed that people become anxious and unhappy if they are prevented from selfactualization. ...
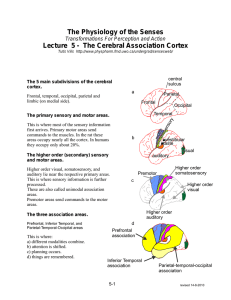
The Cerebral Association Cortex
... Evidence for: Some lesions do impair the recognition of faces selectively. Some cells are activated only by a particular face. Evidence against: Brain cell death is common, yet the memory loss observed is a general fuzziness in remembering faces, not an absolute loss of one face and not of another. ...
... Evidence for: Some lesions do impair the recognition of faces selectively. Some cells are activated only by a particular face. Evidence against: Brain cell death is common, yet the memory loss observed is a general fuzziness in remembering faces, not an absolute loss of one face and not of another. ...
Cognitive Learning - Scott County Schools
... Helplessness: condition in which repeated attempts to control a situation fail, resulting in the belief that the situation is uncontrollable. Ex. If a person gets rewarded for nothing, they do not learn to work ...
... Helplessness: condition in which repeated attempts to control a situation fail, resulting in the belief that the situation is uncontrollable. Ex. If a person gets rewarded for nothing, they do not learn to work ...
Social Studies Standards Infused 2015
... guide for instruction. It is not intended to be a state-mandated curriculum for how and when content is taught. The outline is not a list of required items, and so, was developed with the understanding that content often overlaps. Because of this overlap, it may seem as if important ideas, people, p ...
... guide for instruction. It is not intended to be a state-mandated curriculum for how and when content is taught. The outline is not a list of required items, and so, was developed with the understanding that content often overlaps. Because of this overlap, it may seem as if important ideas, people, p ...
Biopsychology – Paper 2
... Cerebral Cortex, which is involved in a variety of higher cognitive (conscious thought), emotional, sensory, and motor (movement) functions is more developed in humans than any other animal. It is what we see when we picture a human brain, the gray matter with a multitude of folds making up the oute ...
... Cerebral Cortex, which is involved in a variety of higher cognitive (conscious thought), emotional, sensory, and motor (movement) functions is more developed in humans than any other animal. It is what we see when we picture a human brain, the gray matter with a multitude of folds making up the oute ...
Neural correlates of thought suppression
... between two of the task conditions. Within a functional run, there were eight alternating 30 s epochs. In two of the functional runs, subjects alternated between the SUPPRESS and FREE-THOUGHT tasks. In the remaining two runs they alternated between the CLEAR and FREE-THOUGHT tasks. Cue words to indi ...
... between two of the task conditions. Within a functional run, there were eight alternating 30 s epochs. In two of the functional runs, subjects alternated between the SUPPRESS and FREE-THOUGHT tasks. In the remaining two runs they alternated between the CLEAR and FREE-THOUGHT tasks. Cue words to indi ...
425 Terms You Ought to Know for the AP Exam
... the role of what they feel are proper for the situation Cognitive Dissonance – people change their behavior to avoid looking bad, ie person is against gay rights then becomes gay, he will change attitude to gay rights activist Asch – conformity – tendency to go along with the views and actions of ...
... the role of what they feel are proper for the situation Cognitive Dissonance – people change their behavior to avoid looking bad, ie person is against gay rights then becomes gay, he will change attitude to gay rights activist Asch – conformity – tendency to go along with the views and actions of ...
AAAS Summary
... similar neurotoxic phenomenon occurs in the developing human brain following exposure to such drugs. This is a very difficult question to answer conclusively, because if a similar phenomenon did occur in humans the manifestations, except in extreme cases, would be subtle and would only become eviden ...
... similar neurotoxic phenomenon occurs in the developing human brain following exposure to such drugs. This is a very difficult question to answer conclusively, because if a similar phenomenon did occur in humans the manifestations, except in extreme cases, would be subtle and would only become eviden ...