D. Eisenhower Polio Myelitis: A Virus which caused Nerve cell
... Marrow where Red Blood Cells are produced. Bursa Sacs are located around the joints of the body and secrete Synovia Fluid which Lubricates the movements of the bones. Ligaments serve as connecting tissue holding ...
... Marrow where Red Blood Cells are produced. Bursa Sacs are located around the joints of the body and secrete Synovia Fluid which Lubricates the movements of the bones. Ligaments serve as connecting tissue holding ...
Unit 3A Notes
... when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. 6. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, we’re like robots. The brain is what makes us human. 400 trillion synapses “talk to one another” in our brains. 2. Neuro ...
... when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. 6. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, we’re like robots. The brain is what makes us human. 400 trillion synapses “talk to one another” in our brains. 2. Neuro ...
Nervous System - cloudfront.net
... EQ What are the different types of nervous systems in our body? ...
... EQ What are the different types of nervous systems in our body? ...
The expanded, most complex, and very important anterior part of the
... The anterior most part of the brain is called the fore brain. The main parts of the fore brain are the cerebrum and the diencephalons. The cerebrum is the largest, most prominent, and most important part of the entire brain. It consists of two large hemispheres called cerebral hemispheres. The two h ...
... The anterior most part of the brain is called the fore brain. The main parts of the fore brain are the cerebrum and the diencephalons. The cerebrum is the largest, most prominent, and most important part of the entire brain. It consists of two large hemispheres called cerebral hemispheres. The two h ...
Parts and Functions of a Nervous System
... A neuron consists of a ______________ and spreading branches that send or receive impulses to and from other cells. The cell body varies in shape. _______________ are short thread-like branches found in neurons. These are extensions of the cell body. There is only one ___________ and it is slender a ...
... A neuron consists of a ______________ and spreading branches that send or receive impulses to and from other cells. The cell body varies in shape. _______________ are short thread-like branches found in neurons. These are extensions of the cell body. There is only one ___________ and it is slender a ...
Brain - Amazon Web Services
... Originate from embryonic neural tube Filled with cerebrospinal fluid Identify : o Lateral ventricles o Third ventricle o Fourth ventricle Cerebrospinal fluid o Function: Support homeostatic environment for brain ...
... Originate from embryonic neural tube Filled with cerebrospinal fluid Identify : o Lateral ventricles o Third ventricle o Fourth ventricle Cerebrospinal fluid o Function: Support homeostatic environment for brain ...
Brain Basics
... So now we know that brains can be characterized in terms of their major visible anatomical features: a) Sulci (or fissures) and gyri can be used as boundaries for areas b) The brain has two hemispheres, connected by a massive bundle of neural tissue c) There are some other anatomically distinct area ...
... So now we know that brains can be characterized in terms of their major visible anatomical features: a) Sulci (or fissures) and gyri can be used as boundaries for areas b) The brain has two hemispheres, connected by a massive bundle of neural tissue c) There are some other anatomically distinct area ...
Right Brain and Left Brain Hemisphere
... hemisphere between the frontal and occipital lobes; it contains important sensory centers (located at the upper rear of the head). Pituitary Gland - a gland attached to the base of the brain (located between the Pons and the Corpus Callosum) that secretes hormones. Pons - the part of the brainstem t ...
... hemisphere between the frontal and occipital lobes; it contains important sensory centers (located at the upper rear of the head). Pituitary Gland - a gland attached to the base of the brain (located between the Pons and the Corpus Callosum) that secretes hormones. Pons - the part of the brainstem t ...
session1vocabulary
... Bundles of nerve fibers. (nerve fibers are axons and dendrites in parallel bundles covered in connective tissue. Sensory Neurons Picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment and converts each of the stimuli into a nerve impulse. a sensory neuron has to do with the 5 senses of the body. ...
... Bundles of nerve fibers. (nerve fibers are axons and dendrites in parallel bundles covered in connective tissue. Sensory Neurons Picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment and converts each of the stimuli into a nerve impulse. a sensory neuron has to do with the 5 senses of the body. ...
Essentials of Anatony and Physiology, 5e (Martini
... Depolarization during an action potential is caused by the … What is the difference between saltatory and continuous action potential propagation? How does myelin affect the speed of an action potential down a neuron? Know the sequence of events at a typical cholinergic synapse. Which neurotransmitt ...
... Depolarization during an action potential is caused by the … What is the difference between saltatory and continuous action potential propagation? How does myelin affect the speed of an action potential down a neuron? Know the sequence of events at a typical cholinergic synapse. Which neurotransmitt ...
Upon completion of the dissection, complete the following
... 9. Why is the cerebellum also called the arbor vitae? (2 pts.) To some it resembles a tree and bush as a result arbor vitae ( the tree of life ) 10. Give the function of each of the following: (14 pts.) Hypothalamus—links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary glad, Hippocampus ...
... 9. Why is the cerebellum also called the arbor vitae? (2 pts.) To some it resembles a tree and bush as a result arbor vitae ( the tree of life ) 10. Give the function of each of the following: (14 pts.) Hypothalamus—links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary glad, Hippocampus ...
The nervous system
... The nervous system has three main functions, sensory input, integration of data and motor output. Sensory input is when the body gathers information or data, by way of neurons, glia and synapses. The nervous system is composed of excitable nerve cells and synapses connecting the cells to one anothe ...
... The nervous system has three main functions, sensory input, integration of data and motor output. Sensory input is when the body gathers information or data, by way of neurons, glia and synapses. The nervous system is composed of excitable nerve cells and synapses connecting the cells to one anothe ...
What is the Nervous System?
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
... 2. Motor Neurons - project axons out from the central nervous system to control muscles ...
Major Brain Structures and Functions
... receives info from all senses (except smell) and routes them to higher brain regions; “gateway” to the cortex; also involved in sleep (helps us tune out during deep sleep) ...
... receives info from all senses (except smell) and routes them to higher brain regions; “gateway” to the cortex; also involved in sleep (helps us tune out during deep sleep) ...
intro to psych brain and behavior
... Autonomic Nervous System: glands and organs; “automatic functions” ...
... Autonomic Nervous System: glands and organs; “automatic functions” ...
Interbrain and Brainstem
... • Pons = “bridge” of the brainstem. Controls Breathing. • Medulla Oblongata = The lowest part of the brain stem – Merges into the spinal cord – Contains important control centers ...
... • Pons = “bridge” of the brainstem. Controls Breathing. • Medulla Oblongata = The lowest part of the brain stem – Merges into the spinal cord – Contains important control centers ...
Document
... • _____________________________ – _______________- specialized for the transition of impulses from one part of the body to another. •Neurons _______________ _______________ –Cannot be replaced. If outside the brain and spinal cord may slowly grow back. Structure of a Neuron _______________ take in i ...
... • _____________________________ – _______________- specialized for the transition of impulses from one part of the body to another. •Neurons _______________ _______________ –Cannot be replaced. If outside the brain and spinal cord may slowly grow back. Structure of a Neuron _______________ take in i ...
AP Psychology
... 17. The central nervous system is made up of the spinal cord and brain. Explain the pathway from sensory receptor to reflex. 18. Define the brainstem and describe the following parts: a. medulla b. reticular formation 19. Why is the thalamus often thought to be part of the brainstem, and what is its ...
... 17. The central nervous system is made up of the spinal cord and brain. Explain the pathway from sensory receptor to reflex. 18. Define the brainstem and describe the following parts: a. medulla b. reticular formation 19. Why is the thalamus often thought to be part of the brainstem, and what is its ...
Biology and Behaviour
... accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
... accept that the brain controls it, we must understand the brain The nervous system is built out of neurons or nerve cells, and glial cells, which are sort of the glue Glial cells do other support functions too ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell bod ...
... 2. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. 3. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". However, neurons differ from other cells in the body in some ways such as: 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell bod ...
Evolutionary Psychology: Understanding Human Nature
... Endocrine System: the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. - Hormones: chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues - Adrenal Glands: a pair of endocrine ...
... Endocrine System: the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. - Hormones: chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands travel through the bloodstream and affect other tissues - Adrenal Glands: a pair of endocrine ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
... Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
File - Mr. Greenwood Science
... The interneuron then sends an impulse to a motor neuron. The motor neuron then signals its muscle to act. This whole pathway is called an Arc Reflex ...
... The interneuron then sends an impulse to a motor neuron. The motor neuron then signals its muscle to act. This whole pathway is called an Arc Reflex ...
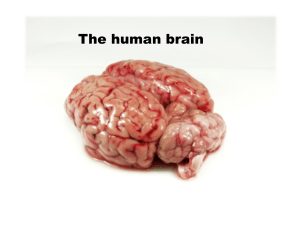
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.