this PowerPoint - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... The nerves from each side of the body cross over in this structure to opposite sides. ...
... The nerves from each side of the body cross over in this structure to opposite sides. ...
Sheep Brain Dissection - Milton
... 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callosum in each brain half. These cavities are the lateral ventricles that contain cerebrospinal fluid. 3. Return your attention to the mi ...
... 2. The corpus callosum had been connecting the two cerebral hemispheres and can now be clearly You may be able to see a hollow cavity just ventral to the corpus callosum in each brain half. These cavities are the lateral ventricles that contain cerebrospinal fluid. 3. Return your attention to the mi ...
Brain & Behavior
... recharge, so to speak • K(+) pumped out of cell, (-) charge restored • Refractory period – neuron cannot fire again during this process ...
... recharge, so to speak • K(+) pumped out of cell, (-) charge restored • Refractory period – neuron cannot fire again during this process ...
action potential
... Myelin Sheath •White fatty casing on axon •Acts as an electrical insulator •Not present on all cells •When present, increases the speed of neural signals down the axon ...
... Myelin Sheath •White fatty casing on axon •Acts as an electrical insulator •Not present on all cells •When present, increases the speed of neural signals down the axon ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? Class Objectives:
... The antidepressant drug Prozac works by slowing down the reuptake of serotonin into terminal buttons, thereby increasing brain levels of serotonin (Little, ...
... The antidepressant drug Prozac works by slowing down the reuptake of serotonin into terminal buttons, thereby increasing brain levels of serotonin (Little, ...
Structure of the Brain
... 1. Somatic nervous system (the sensory and motor neurons) 2. Autonomic nervous system (controls heart, digestion and organs) The autonomic nervous system has two divisions… 1. Sympathetic nervous system (prepares organism for activity, fight-flight etc.) 2. Parasympathetic nervous system (facilitate ...
... 1. Somatic nervous system (the sensory and motor neurons) 2. Autonomic nervous system (controls heart, digestion and organs) The autonomic nervous system has two divisions… 1. Sympathetic nervous system (prepares organism for activity, fight-flight etc.) 2. Parasympathetic nervous system (facilitate ...
Nervous System Notes PP
... Motor neurons in the PNS carry signals from the control center to the muscles, glands, and organs to regulate their functions. ...
... Motor neurons in the PNS carry signals from the control center to the muscles, glands, and organs to regulate their functions. ...
Brain Structures and their Functions
... efficient, because it can increase the surface area of the brain and the amount of neurons within it. We will discuss the relevance of the degree of cortical folding (or gyrencephalization) later. (Go here for more information about cortical folding) A deep furrow divides the cerebrum into two halve ...
... efficient, because it can increase the surface area of the brain and the amount of neurons within it. We will discuss the relevance of the degree of cortical folding (or gyrencephalization) later. (Go here for more information about cortical folding) A deep furrow divides the cerebrum into two halve ...
Copy Notes
... parietal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal l ...
... parietal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal l ...
awl review q answers
... In answering this, we can contextualize the issue by also revising some material from Chapter 2. Through sensory systems, the brain is informed of such things in the world as the presence of food and water. Through detectors within the body, it is informed of such internal states as dehydration, bod ...
... In answering this, we can contextualize the issue by also revising some material from Chapter 2. Through sensory systems, the brain is informed of such things in the world as the presence of food and water. Through detectors within the body, it is informed of such internal states as dehydration, bod ...
The Nervous System
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body ...
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body ...
Biology and Psychology - Austin Community College
... MIDBRAIN Consciousness Plays a role in vision & audition, coordinates basic movements with sensory information, vital to attention sleep & arousal. 1.Tegmentum motor movement ...
... MIDBRAIN Consciousness Plays a role in vision & audition, coordinates basic movements with sensory information, vital to attention sleep & arousal. 1.Tegmentum motor movement ...
The Body and the Brain
... The nervous system regulates our internal functions. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central nervous system and all the parts of the body. Neurons - or nerve cells – run throu ...
... The nervous system regulates our internal functions. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central nervous system and all the parts of the body. Neurons - or nerve cells – run throu ...
test yourself
... Part of the brain located at the top end of the spinal cord that controls breathing and other involuntary functions. Membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Part of the brain between the hypothalamus and the pons that regulates visual, auditory, and rightening reflexes. Soft, white, fatty ma ...
... Part of the brain located at the top end of the spinal cord that controls breathing and other involuntary functions. Membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Part of the brain between the hypothalamus and the pons that regulates visual, auditory, and rightening reflexes. Soft, white, fatty ma ...
Ch on Drugs and Prep for Test
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...
... * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills ...
Document
... All information to and from our body passes through the brain stem on the way to or from the brain. ...
... All information to and from our body passes through the brain stem on the way to or from the brain. ...
hendrick
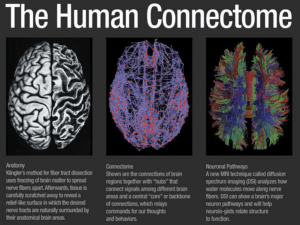
... identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 = 74 bits per connection, or 518,000 bits (65 kilobytes) per neuron. Multiplying by 86 billion neurons gives a total of 5.59 petabytes (PB) of information. That’s just for the basic connectivity map: a record of which neurons are connected to which. More i ...
... identify the two neurons would take 37 + 37 = 74 bits per connection, or 518,000 bits (65 kilobytes) per neuron. Multiplying by 86 billion neurons gives a total of 5.59 petabytes (PB) of information. That’s just for the basic connectivity map: a record of which neurons are connected to which. More i ...
Ch 3
... 21. What are glial cells and what do they form around brain and spinal cord axons? 22. What are the two main building blocks of the nervous system? 23. What does it take to produce thoughts, sensations and feelings? 24. What is the central nervous system? In your response, discuss its components, fu ...
... 21. What are glial cells and what do they form around brain and spinal cord axons? 22. What are the two main building blocks of the nervous system? 23. What does it take to produce thoughts, sensations and feelings? 24. What is the central nervous system? In your response, discuss its components, fu ...
Chapter 3: The Nervous System
... •In the PNS, it is the NT released at synapses on skeletal muscles and is also found in the cell bodies of the autonomic nervous system. •In the brain, it appears to be involved in learning/memory, attention as well as sleeping and dreaming. ...
... •In the PNS, it is the NT released at synapses on skeletal muscles and is also found in the cell bodies of the autonomic nervous system. •In the brain, it appears to be involved in learning/memory, attention as well as sleeping and dreaming. ...
COURSE: 7065
... Cerebellum---controls muscular coordination, balance, and posture Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works N ...
... Cerebellum---controls muscular coordination, balance, and posture Pituitary gland---releases hormones that control metabolism and sexual development Spinal cord---controls simple reflexes that do not involve the brain Thalamus---controls the way emotions are expressed How the brain works N ...
Module 6 The Cerebral Cortex and Our Divided Brain
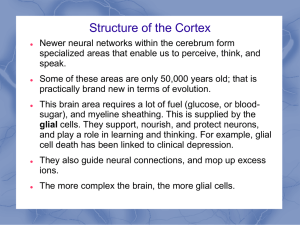
... specialized areas that enable us to perceive, think, and speak. Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They suppor ...
... specialized areas that enable us to perceive, think, and speak. Some of these areas are only 50,000 years old; that is practically brand new in terms of evolution. This brain area requires a lot of fuel (glucose, or bloodsugar), and myeline sheathing. This is supplied by the glial cells. They suppor ...
the brain - Cloudfront.net
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
... 4. The more you repeat something the more brain space is dedicated to it. For example, in musicians the part of the brain that controls fingers used to play an instrument is up to 130% larger than in a non-musician. ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.