leadership
... “You, your joys and your sorrows, your memories and your ambitions, your sense of personal Identity and free will are in fact are no more than a behavior of vast assembly of neurons and nerve cells” “You are nothing but a pack of Neuron” ...
... “You, your joys and your sorrows, your memories and your ambitions, your sense of personal Identity and free will are in fact are no more than a behavior of vast assembly of neurons and nerve cells” “You are nothing but a pack of Neuron” ...
The Biology of Behavior
... organs, process the signals, and send them to other neurons, muscles, or organs Sensory: respond to sensory organ input Motor: send signals to muscles to control movement Interneurons: the go-between of sensory and motor neurons ...
... organs, process the signals, and send them to other neurons, muscles, or organs Sensory: respond to sensory organ input Motor: send signals to muscles to control movement Interneurons: the go-between of sensory and motor neurons ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... of the body, and the right hemisphere controlling the left side of the body The sensory and motor cortex strips allocate space based on complexity and sensitivity ...
... of the body, and the right hemisphere controlling the left side of the body The sensory and motor cortex strips allocate space based on complexity and sensitivity ...
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
CHAPTER 21 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM and SENSES
... tell your brain about tactile sensations. There are several types of touch receptors, but they can be divided into two groups. • (1) mechanoreceptors that tell you about sensations of pushing, pulling or movement, – The mechanoreceptors contain the most types of ...
... tell your brain about tactile sensations. There are several types of touch receptors, but they can be divided into two groups. • (1) mechanoreceptors that tell you about sensations of pushing, pulling or movement, – The mechanoreceptors contain the most types of ...
Nerve Pathways Practice Sheet
... Fill-in-the-Blanks The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) ___________________ ...
... Fill-in-the-Blanks The nervous system is a connection of many different (1) _____________________ (nerve cells). These nerves form pathways that send messages all over the body, in many different directions. (2) ________ neurons detect specific kinds of environmental stimuli, (3) ___________________ ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 43. What is the major difference between gray matter and white matter in the CNS? Gray matter—contains mostly unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies White matter—consists of dense collections of myelinated fibers (tracts) 44. The __corpus callosum_____ connects the two hemispheres of the brain. 45. The ...
... 43. What is the major difference between gray matter and white matter in the CNS? Gray matter—contains mostly unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies White matter—consists of dense collections of myelinated fibers (tracts) 44. The __corpus callosum_____ connects the two hemispheres of the brain. 45. The ...
Endocrine System
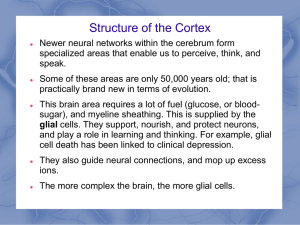
... – Outer layer of the forebrain; gives you the ability to learn and store complex and abstract information. ...
... – Outer layer of the forebrain; gives you the ability to learn and store complex and abstract information. ...
Quiz - Web Adventures
... b) Re-create Nobel Prize experiments c) Test how insulin binds to blood cells d) Understand how opioids work in the brain 6) Feelings of pleasure are triggered in the brain’s Reward Pathway by: a) Insulin b) Endogenous opioids c) NSAIDs d) Estrogen 7) Neurons transmit signals to other neurons across ...
... b) Re-create Nobel Prize experiments c) Test how insulin binds to blood cells d) Understand how opioids work in the brain 6) Feelings of pleasure are triggered in the brain’s Reward Pathway by: a) Insulin b) Endogenous opioids c) NSAIDs d) Estrogen 7) Neurons transmit signals to other neurons across ...
Nervous System Anatomy
... • made up of about 100 billion neurons • “the most complex living structure on the universe” Society for Neuroscience ...
... • made up of about 100 billion neurons • “the most complex living structure on the universe” Society for Neuroscience ...
Word version - World Book Encyclopedia
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
The Nervous System Activity Sheet
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
... World Book’s Building Blocks of Life Science The Nervous System Activity Sheet© ...
Unit 3ABC Reading and Study Guide
... What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmitters? What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? How does the endoc ...
... What are neurons, and how do they transmit information? How do nerve cells communicate with other nerve cells? How do neurotransmitters influence behavior, and how do drugs and other chemicals affect neurotransmitters? What are the functions of the nervous system’s main divisions? How does the endoc ...
SNS—brain and spinal cord
... Afferent—towards the cell body, to the CNS, sensory Efferent—away from the cell body, motor neurons, from the CNS to cause some action. If myelin sheath is intact on the axon there is some repair. Grey matter—contains dendrites White matter—myelinated nerve fibers. Myelin sheeth—white li ...
... Afferent—towards the cell body, to the CNS, sensory Efferent—away from the cell body, motor neurons, from the CNS to cause some action. If myelin sheath is intact on the axon there is some repair. Grey matter—contains dendrites White matter—myelinated nerve fibers. Myelin sheeth—white li ...
neurotransmitters
... The Outer Nervous System is made of the nerves and the sense organs. Nerves ...
... The Outer Nervous System is made of the nerves and the sense organs. Nerves ...
1. Learning Depends on Integration of Brain Structures
... – The sooner children learn to coordinate the left-to-right movement of their eyes to follow the the words on a page while listening to stories and attempt to write their names, the earlier they while learn to read. ...
... – The sooner children learn to coordinate the left-to-right movement of their eyes to follow the the words on a page while listening to stories and attempt to write their names, the earlier they while learn to read. ...
nervous system
... that enters the eye Rods-Respond to dim light Cones-Respond to bright light and allow color vision Optic nerve-Exits back of the eye and runs along base of the brain to the thalamus ...
... that enters the eye Rods-Respond to dim light Cones-Respond to bright light and allow color vision Optic nerve-Exits back of the eye and runs along base of the brain to the thalamus ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
II. ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN NERVOUS
... sensory organ. Sensory receptors detect pressure, pain, heat, cold. 2. Smell - Response to a _chemical_____ stimulus. Sensory receptor cells are bathed in mucus and respond to different chemicals. 3. Taste - Response to a _chemical____stimulus. Sensory receptors called _taste buds____ are located on ...
... sensory organ. Sensory receptors detect pressure, pain, heat, cold. 2. Smell - Response to a _chemical_____ stimulus. Sensory receptor cells are bathed in mucus and respond to different chemicals. 3. Taste - Response to a _chemical____stimulus. Sensory receptors called _taste buds____ are located on ...
Nervous System Notes
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
... • Space between axon terminal of one neuron and dendrites of another. • Neurotransmitters in vesicles released in cleft either cause the cell to fire (excitatory) or not fire (inhibitory). ...
Nervous System Ch 35
... Brain has 4 main parts: •Cerebrum •Cerebellum •Brain stem •Hypothalmus ...
... Brain has 4 main parts: •Cerebrum •Cerebellum •Brain stem •Hypothalmus ...
The Nervous System
... • Acetylcholine- excitatory (arousal, attention, memory) • Dopamine- inhibitory (attention, learning, movement, pleasure) • Serotonin –inhibitory (anxiety, dreaming, eating, sleep, mood, pain) • Noradrenalin/Norepinephrineexcitatory (activity, alert, heart) ...
... • Acetylcholine- excitatory (arousal, attention, memory) • Dopamine- inhibitory (attention, learning, movement, pleasure) • Serotonin –inhibitory (anxiety, dreaming, eating, sleep, mood, pain) • Noradrenalin/Norepinephrineexcitatory (activity, alert, heart) ...
Unit 3A: Neural Processing and the Endocrine System Introduction
... it to not fire. When the excitatory signals outweigh the inhibitory signals by a certain amount, the neuron fires. This is called the threshold. How neurons communicate 1. A synapse is the place where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrites of another. There is a very slight gap in between (the “ ...
... it to not fire. When the excitatory signals outweigh the inhibitory signals by a certain amount, the neuron fires. This is called the threshold. How neurons communicate 1. A synapse is the place where the axon of one neuron meets the dendrites of another. There is a very slight gap in between (the “ ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.