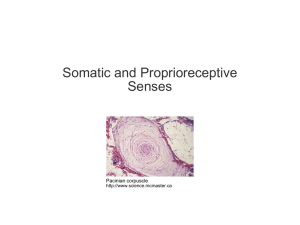
PDF+Links
... brain. However, there is in fact no substantial evidence that neuronal loss appears on a large scale as a universal effect throughout the whole brain. It is estimated that, in the cortex, very few neurons become lost with age (Cragg 1975; Pakkenberg & Gundensen, 1997; Peters et al., 1998), and that ...
... brain. However, there is in fact no substantial evidence that neuronal loss appears on a large scale as a universal effect throughout the whole brain. It is estimated that, in the cortex, very few neurons become lost with age (Cragg 1975; Pakkenberg & Gundensen, 1997; Peters et al., 1998), and that ...
Neurobiological Mechanisms Underlying Oestradiol Negative and
... positive-feedback response, or in the signal they receive (GABA versus another) to increase their activity during the surge. We favour the latter explanation because the increase in GnRH neurone activity occurs in the majority of GnRH neurones, and not just one-third of cells, suggesting that additi ...
... positive-feedback response, or in the signal they receive (GABA versus another) to increase their activity during the surge. We favour the latter explanation because the increase in GnRH neurone activity occurs in the majority of GnRH neurones, and not just one-third of cells, suggesting that additi ...
Program
and
Abstracts
from
the
Fifth
Annual
Canadian
Neuroscience
Meeting
May
29
–
June
1
2011
Quebec
City
Convention
Center
... splicing is important since imbalance in the ration 3R to 4R has been shown to lead to certain forms of tauopathies, and because hyperphosphorylation can induce aggregation in vitro, and is thought to induce aggregates formation in the brain. In this study we used both primary cultures and develo ...
... splicing is important since imbalance in the ration 3R to 4R has been shown to lead to certain forms of tauopathies, and because hyperphosphorylation can induce aggregation in vitro, and is thought to induce aggregates formation in the brain. In this study we used both primary cultures and develo ...
Neurons of the Central Complex of the Locust Schistocerca gregaria
... anesthetized by cooling and were waxed anterior uppermost to a metal holder. The heads of the locusts were immobilized by a wax–rosin mixture, and their legs were removed. For intracellular recordings from the central protocerebrum, a small window was cut into the head capsule between the two compou ...
... anesthetized by cooling and were waxed anterior uppermost to a metal holder. The heads of the locusts were immobilized by a wax–rosin mixture, and their legs were removed. For intracellular recordings from the central protocerebrum, a small window was cut into the head capsule between the two compou ...
Central mechanisms regulating coordinated cardiovascular and
... respiratory changes. As discussed in this review, several brain regions and pathways have major roles in subserving the cardiovascular and respiratory responses to threatening stimuli, which may vary from relatively mild acute arousing stimuli to more prolonged life-threatening stimuli. One key regi ...
... respiratory changes. As discussed in this review, several brain regions and pathways have major roles in subserving the cardiovascular and respiratory responses to threatening stimuli, which may vary from relatively mild acute arousing stimuli to more prolonged life-threatening stimuli. One key regi ...
Coexposure of Neonatal Mice to a Flame
... Epidemiological studies indicate that exposure to environmental pollutants during early human development can have deleterious effects on cognitive development. The interaction between environmental pollutants is suggested as one reason for the observed defective neurological development in children ...
... Epidemiological studies indicate that exposure to environmental pollutants during early human development can have deleterious effects on cognitive development. The interaction between environmental pollutants is suggested as one reason for the observed defective neurological development in children ...
Changes in Intracellular pH Associated with Glutamate Excitotoxicity
... to a pH, of 7.00 f 0.05 or an intracellular hydrogen ion concentration ([H+],) of 100 nM. Similar values for neuronal pH, in HEPES-buffered media have been reported previously (Nachshenand Drapeau, 1988; Koch and Barish, 1991; Raley-Susman et al., 1991). Following the establishmentof a stableresting ...
... to a pH, of 7.00 f 0.05 or an intracellular hydrogen ion concentration ([H+],) of 100 nM. Similar values for neuronal pH, in HEPES-buffered media have been reported previously (Nachshenand Drapeau, 1988; Koch and Barish, 1991; Raley-Susman et al., 1991). Following the establishmentof a stableresting ...
Streptococcus pneumoniae Senses a Human-like Sialic Acid
... Response to Neu5Ac Compared with Neu5Gc Because strain TIGR4 signals differentially in response to Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc, we performed qPCR to compare the transcription rates of all pneumococcal RRs in response to Neu5Ac or Neu5Gc in relation to no carbohydrates added. Of all known RRs, only CiaR was up ...
... Response to Neu5Ac Compared with Neu5Gc Because strain TIGR4 signals differentially in response to Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc, we performed qPCR to compare the transcription rates of all pneumococcal RRs in response to Neu5Ac or Neu5Gc in relation to no carbohydrates added. Of all known RRs, only CiaR was up ...
The physiological role of orexin/hypocretin neurons in the regulation
... neurons are located in the LHA. Prepro-orexin mRNA was shown to be upregulated under fasting conditions, indicating that these neurons somehow sense the animal’s energy balance (Sakurai et al., 1998). Recently, the forkhead box transcription factor Foxa2, a downstream target of insulin signaling, wa ...
... neurons are located in the LHA. Prepro-orexin mRNA was shown to be upregulated under fasting conditions, indicating that these neurons somehow sense the animal’s energy balance (Sakurai et al., 1998). Recently, the forkhead box transcription factor Foxa2, a downstream target of insulin signaling, wa ...
Program - Albion
... When we learn new information we use only a tiny fraction of the neurons in our brain for that particular memory trace. This sparse encoding makes it difficult to study the cellular and molecular changes associated with learning. In this lecture I will discuss recent results from our lab and oth ...
... When we learn new information we use only a tiny fraction of the neurons in our brain for that particular memory trace. This sparse encoding makes it difficult to study the cellular and molecular changes associated with learning. In this lecture I will discuss recent results from our lab and oth ...
Experimentally cross-wired lingual taste nerves can restore normal
... Oakley (36) was the first to address this question in a fascinating and innovative set of experiments using rats. He transected the chorda tympani nerve (CT), which normally innervates the anterior tongue (AT) taste buds, and formed a cross-anastomosis with the transected glossopharyngeal nerve (GL) ...
... Oakley (36) was the first to address this question in a fascinating and innovative set of experiments using rats. He transected the chorda tympani nerve (CT), which normally innervates the anterior tongue (AT) taste buds, and formed a cross-anastomosis with the transected glossopharyngeal nerve (GL) ...
Perception Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity: From Synapse to
... a level appropriate for LTD induction (38). Alternatively, a second coincidence detector independent of NMDAR is responsible for LTD at post-pre intervals. Karmarkar and Buonomano (51) suggest that the mGluR pathway, which is coupled to Ca2" influx through VDCCs, is a likely candidate for this secon ...
... a level appropriate for LTD induction (38). Alternatively, a second coincidence detector independent of NMDAR is responsible for LTD at post-pre intervals. Karmarkar and Buonomano (51) suggest that the mGluR pathway, which is coupled to Ca2" influx through VDCCs, is a likely candidate for this secon ...
Mechanism of acute and chronic pain
... • 2. Antidromic activation of nociceptive primary afferents further enhance the activity of the nociceptors by a positive feedback mechanism and elicit vascular effects. • 3. Synergistic actions and sensitization of nociceptors by the engagement of intracellular ...
... • 2. Antidromic activation of nociceptive primary afferents further enhance the activity of the nociceptors by a positive feedback mechanism and elicit vascular effects. • 3. Synergistic actions and sensitization of nociceptors by the engagement of intracellular ...
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Is a GABAA Receptor
... 0.1% Triton X-100. After the addition of 200 l of goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to agarose with 1% bovine serum albumin, the samples were carefully shaken for 16 hr at 4°C. The immunosorbent was removed by centrifugation, and the supernatant and pellets were assayed individually. To further isolat ...
... 0.1% Triton X-100. After the addition of 200 l of goat anti-mouse IgG conjugated to agarose with 1% bovine serum albumin, the samples were carefully shaken for 16 hr at 4°C. The immunosorbent was removed by centrifugation, and the supernatant and pellets were assayed individually. To further isolat ...
Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity: From Synapse to Perception
... GABAergic transmission in the slices from cocainetreated animal with diazepam eliminated LTP induction. By titrating the strength of GABAergic inputs with different doses of a GABAA antagonist, Liu et al. (60) concluded that a 30% reduction of GABAergic transmission in normal rat VTA can open the ga ...
... GABAergic transmission in the slices from cocainetreated animal with diazepam eliminated LTP induction. By titrating the strength of GABAergic inputs with different doses of a GABAA antagonist, Liu et al. (60) concluded that a 30% reduction of GABAergic transmission in normal rat VTA can open the ga ...
Enhanced intrinsic excitability and EPSP
... Running head: Environmental enrichment and hippocampal plasticity Keywords: Contextual fear learning; action potential threshold; theta-burst stimulation; miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents, after-hyperpolarization ...
... Running head: Environmental enrichment and hippocampal plasticity Keywords: Contextual fear learning; action potential threshold; theta-burst stimulation; miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents, after-hyperpolarization ...
Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy With Spontaneous
... to be determined, pending control or cure of diabetes, whether the initial adverse effects set in motion by derangements in glycemia are reversible. Neuropathy is unfortunately a common complication of patients with uncontrolled diabetes (4,5). At the point of clinical detection, significant impairm ...
... to be determined, pending control or cure of diabetes, whether the initial adverse effects set in motion by derangements in glycemia are reversible. Neuropathy is unfortunately a common complication of patients with uncontrolled diabetes (4,5). At the point of clinical detection, significant impairm ...
Cloning and Characterization of Human Urocortin
... CAMP accumulation from cells stably transfected with these receptors, and acts in vitro to releaseACTH from dispersedrat anterior pituitary cells. In addition, the CRF-binding protein binds humanurocortin with high affinity and can prevent urocortin-stimulated ACTH secretionin vitro. The inhibitory ...
... CAMP accumulation from cells stably transfected with these receptors, and acts in vitro to releaseACTH from dispersedrat anterior pituitary cells. In addition, the CRF-binding protein binds humanurocortin with high affinity and can prevent urocortin-stimulated ACTH secretionin vitro. The inhibitory ...
Is the Lateral Septum's Inhibitory Influence on the Amygdala Mediated... GABA-ergic Neurons? Mason Austin
... conclusions about the anxiety system as a whole. Before one can do that, one would have to subject the amygdala itself to a battery of tests to see whether it is necessary for anxiogenesis and whether it conforms to other models of anxiety. One approach in this pursuit has been to examine how electr ...
... conclusions about the anxiety system as a whole. Before one can do that, one would have to subject the amygdala itself to a battery of tests to see whether it is necessary for anxiogenesis and whether it conforms to other models of anxiety. One approach in this pursuit has been to examine how electr ...
Obesity and Appetite Control
... therefore, be important in confirming the long-term safety of GLP-1-based therapies. 2.4.2. Oxyntomodulin (OXM). OXM is a 37-amino acid peptide originally isolated from porcine jejunoileal cells and is found to show glucagon-like activity in the liver [82]. OXM is another product of the proglucagon ...
... therefore, be important in confirming the long-term safety of GLP-1-based therapies. 2.4.2. Oxyntomodulin (OXM). OXM is a 37-amino acid peptide originally isolated from porcine jejunoileal cells and is found to show glucagon-like activity in the liver [82]. OXM is another product of the proglucagon ...
Patterning and axon guidance of cranial motor neurons
... r1, r2 and r3 (in mice) or r2 and r3 (in chicks), the facial nucleus (nucleus VII; BM and VM neurons) lies in r4 and r5, the glossopharyngeal nucleus (nucleus IX; BM and VM neurons) lies in r6 (in mice) or r6 and r7 (in chicks), and the vagus nucleus (nucleus X; BM and VM neurons) and cranial access ...
... r1, r2 and r3 (in mice) or r2 and r3 (in chicks), the facial nucleus (nucleus VII; BM and VM neurons) lies in r4 and r5, the glossopharyngeal nucleus (nucleus IX; BM and VM neurons) lies in r6 (in mice) or r6 and r7 (in chicks), and the vagus nucleus (nucleus X; BM and VM neurons) and cranial access ...