Dr. Ghassan The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): After studying
... There are two types of cholinergic receptors are nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. ● Nicotinic receptors are found on the cell bodies of all postganglionic neurons, both sympathetic and parasympathetic, in the ganglia of the ANS (and at neuromuscular junction). Acetylcholine released from the preg ...
... There are two types of cholinergic receptors are nicotinic and muscarinic receptors. ● Nicotinic receptors are found on the cell bodies of all postganglionic neurons, both sympathetic and parasympathetic, in the ganglia of the ANS (and at neuromuscular junction). Acetylcholine released from the preg ...
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT
... Local Control of Motor Neurons • Local control levels are relay points for instruc7ons coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjus7ng motor unit ac7vity to local condi7ons (obstacles to movem ...
... Local Control of Motor Neurons • Local control levels are relay points for instruc7ons coming from higher levels in the motor program • Adjus7ng motor unit ac7vity to local condi7ons (obstacles to movem ...
Sample Abstract
... 4. Short Description of what will be discussed during the presentation A body of clinical evidence has demonstrated that viral infections in the periphery exacerbate neurodegenerative conditions, e.g., multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, Alzheimer Disease (AD), and seizures. For example, peripher ...
... 4. Short Description of what will be discussed during the presentation A body of clinical evidence has demonstrated that viral infections in the periphery exacerbate neurodegenerative conditions, e.g., multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, Alzheimer Disease (AD), and seizures. For example, peripher ...
Nervous System - healthsciencesMBIT
... About 2 millionths of a centimeters in width Has protein molecules embedded in opposite synaptic knobs The receptors and neurotransmitters bind The binding can cause an impulse in the ...
... About 2 millionths of a centimeters in width Has protein molecules embedded in opposite synaptic knobs The receptors and neurotransmitters bind The binding can cause an impulse in the ...
the pattern of neurodegeneration in huntington`s disease
... adenosine A2a receptor binding in the caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus externus and an increase in GABAA receptor binding in the globus pallidus externus. Second, intermediate neuropathological grades (grades 1, 2) showed a further marked decrease of CB1 receptor binding in the caudate n ...
... adenosine A2a receptor binding in the caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus externus and an increase in GABAA receptor binding in the globus pallidus externus. Second, intermediate neuropathological grades (grades 1, 2) showed a further marked decrease of CB1 receptor binding in the caudate n ...
Chapter 23 - Anatomy Freaks
... in the medullary respiratory center that are responsible stopping inspiration. They also receive input from pontine group and stretch receptors in lungs. Inhibitory neurons activated and relaxation of respiratory muscles results in expiration. – Note: although the medullary neurons establish the bas ...
... in the medullary respiratory center that are responsible stopping inspiration. They also receive input from pontine group and stretch receptors in lungs. Inhibitory neurons activated and relaxation of respiratory muscles results in expiration. – Note: although the medullary neurons establish the bas ...
NEURAL REGULATION OF BREATHING Section 4, Part A
... A. Medulla isolated from cranial nerves and higher centers can drive respiratory muscles 1. rhythm appears "ataxic" B. Integration of neural centers 1. nucleus of the tractus solitarus (NTS) or dorsal resp. group a. appears to receive and integrate sensory information and to initiate motor response ...
... A. Medulla isolated from cranial nerves and higher centers can drive respiratory muscles 1. rhythm appears "ataxic" B. Integration of neural centers 1. nucleus of the tractus solitarus (NTS) or dorsal resp. group a. appears to receive and integrate sensory information and to initiate motor response ...
nervous system notes
... Cannabis. Marijuana – a hallucinogen – (from the dried leaves) and hashish (resin from the flowers). In low doses it is a depressant – impairs co-ordination, perception, timing and shortterm memory. It slows down motor activity and causes mild euphoria. It also causes disorientation, increased anx ...
... Cannabis. Marijuana – a hallucinogen – (from the dried leaves) and hashish (resin from the flowers). In low doses it is a depressant – impairs co-ordination, perception, timing and shortterm memory. It slows down motor activity and causes mild euphoria. It also causes disorientation, increased anx ...
lecture #6
... • NTs will cause either and excitatory or inhibitory response in the post-synaptic neuron • If the NT depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron = excitatory – change in membrane potential is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential ...
... • NTs will cause either and excitatory or inhibitory response in the post-synaptic neuron • If the NT depolarizes the postsynaptic neuron = excitatory – change in membrane potential is called an excitatory postsynaptic potential ...
Drugs and the Synapse
... with relaxation. • In greater amounts it impairs judgment and damages the liver and other organs. • Alcoholism/alcohol dependence is the continued use of alcohol despite medical or social harm even after one has decided to quit or decrease drinking. ...
... with relaxation. • In greater amounts it impairs judgment and damages the liver and other organs. • Alcoholism/alcohol dependence is the continued use of alcohol despite medical or social harm even after one has decided to quit or decrease drinking. ...
Notes - Scioly.org
... The following notes are based mainly off of Human Anatomy & Physiology 8th Edition by Marieb and Hoehn and Ross and Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness by Waugh and Grant. There may be other sources used (like my AP Bio notes), and *usually* will be correspondingly footnoted. Of cour ...
... The following notes are based mainly off of Human Anatomy & Physiology 8th Edition by Marieb and Hoehn and Ross and Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness by Waugh and Grant. There may be other sources used (like my AP Bio notes), and *usually* will be correspondingly footnoted. Of cour ...
教案编写基本格式与要求
... central and peripheral nervous systems. The peripheral nervous system includes the somatic and autonomic nervous systems which control voluntary and involuntary functions respectively. The ANS controls the vegetative functions of the body. These include functions like circulation, respiration, diges ...
... central and peripheral nervous systems. The peripheral nervous system includes the somatic and autonomic nervous systems which control voluntary and involuntary functions respectively. The ANS controls the vegetative functions of the body. These include functions like circulation, respiration, diges ...
Insights into schizophrenia using positron emission tomography
... noted greater [18F]fluorodopa uptake in the dorsal anterior cingulate in patients during performance on the Stroop task in comparison with normal controls.2 These findings may highlight the important role of the anterior cingulate dopamine function in suppression of attention processes and response ...
... noted greater [18F]fluorodopa uptake in the dorsal anterior cingulate in patients during performance on the Stroop task in comparison with normal controls.2 These findings may highlight the important role of the anterior cingulate dopamine function in suppression of attention processes and response ...
Biology 2121 – Lecture Sheet – ANS 1. The autonomic nervous sy
... 28. The nerves that leave the sacral area via the ventral rami are called the __________________ nerves and join to form the __________________ plexus. 29. The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons can be found in this portion of the spinal cord: _____________. They exit via the _____ ...
... 28. The nerves that leave the sacral area via the ventral rami are called the __________________ nerves and join to form the __________________ plexus. 29. The cell bodies of the sympathetic preganglionic neurons can be found in this portion of the spinal cord: _____________. They exit via the _____ ...
Nervous System Intro
... released by many PNS neurons (and some in the CNS). Ach is excitatory at the NMJ but inhibitory at other synapses. ...
... released by many PNS neurons (and some in the CNS). Ach is excitatory at the NMJ but inhibitory at other synapses. ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... version,please visit the website to access more. www.officeconvert.com ...
... version,please visit the website to access more. www.officeconvert.com ...
Kuliah4-anatomi2
... muscular walls of the viscera. However, some of these preganglionic neurons pass right on through this second ganglion and into the adrenal medulla. Here they synapse with the highlymodified postganglionic cells that make up the secretory portion of the adrenal medulla. ...
... muscular walls of the viscera. However, some of these preganglionic neurons pass right on through this second ganglion and into the adrenal medulla. Here they synapse with the highlymodified postganglionic cells that make up the secretory portion of the adrenal medulla. ...
Dr. Cam Perkins - BIOL 2210
... • stimulation of receptor causes local change in its receptor potential • a graded electrical current is generated that reflects intensity of stimulation • if receptor is part of a neuron, the membrane potential may generate an action potential • if receptor is not part of a neuron, the receptor pot ...
... • stimulation of receptor causes local change in its receptor potential • a graded electrical current is generated that reflects intensity of stimulation • if receptor is part of a neuron, the membrane potential may generate an action potential • if receptor is not part of a neuron, the receptor pot ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I
... PP. A neurilemma is a portion of a Schwann cell outside of the myelin sheath. QQ. A node of Ranvier is a narrow gap between myelin sheaths. RR. Myelinated axons have myelin sheaths. SS. Unmyelinated axons have no myelin sheaths. TT. White matter is composed of myelinated axons. UU. Gray matter is c ...
... PP. A neurilemma is a portion of a Schwann cell outside of the myelin sheath. QQ. A node of Ranvier is a narrow gap between myelin sheaths. RR. Myelinated axons have myelin sheaths. SS. Unmyelinated axons have no myelin sheaths. TT. White matter is composed of myelinated axons. UU. Gray matter is c ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... The midbrain is part of the brainstem. Nerve fibers that control voluntary motor function pass from the forebrain through the midbrain. The midbrain also participates in hearing and eye reflexes and regulates consciousness. The forebrain consists of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebrum. The thal ...
... The midbrain is part of the brainstem. Nerve fibers that control voluntary motor function pass from the forebrain through the midbrain. The midbrain also participates in hearing and eye reflexes and regulates consciousness. The forebrain consists of the thalamus, hypothalamus, and cerebrum. The thal ...
Lecture 1 st week
... Copyright: Hall, J. E., & Guyton, A. C. (2006). Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier. ...
... Copyright: Hall, J. E., & Guyton, A. C. (2006). Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier. ...
Investigating Nervous and Sensory Systems
... activities of the nervous and endocrine systems are directed or regulated by genetic information and learning. In this laboratory you will study three levels of components of the mammalian nervous system: the structural unit of the nervous system, the neuron, or nerve cell; several sensory receptors ...
... activities of the nervous and endocrine systems are directed or regulated by genetic information and learning. In this laboratory you will study three levels of components of the mammalian nervous system: the structural unit of the nervous system, the neuron, or nerve cell; several sensory receptors ...
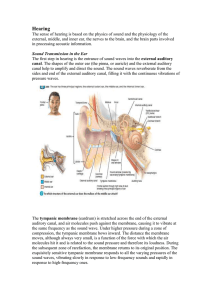
Ear
... inner ear must be amplified. This is achieved by a movable chain of three small bones, the malleus, incus, and stapes; these bones act as a piston and couple the motions of the tympanic membrane to the oval window, a membrane covered opening separating the middle and inner ear. The total force of a ...
... inner ear must be amplified. This is achieved by a movable chain of three small bones, the malleus, incus, and stapes; these bones act as a piston and couple the motions of the tympanic membrane to the oval window, a membrane covered opening separating the middle and inner ear. The total force of a ...
Neurotransmitters
... evidence is mixed as to whether neurotransmitter release (firing) is increased. Even with increased neurotransmitter release, it is unclear whether this will result in a long-term increase in neurotransmitter signal strength, since the nervous system can adapt to changes such as increased neurotrans ...
... evidence is mixed as to whether neurotransmitter release (firing) is increased. Even with increased neurotransmitter release, it is unclear whether this will result in a long-term increase in neurotransmitter signal strength, since the nervous system can adapt to changes such as increased neurotrans ...