Neurons
... Signaling by another neuron or a sensory event may initiate an action potential. During an action potential there is a transitory change in the polarity of the electrical charge across the cell membrane. The membrane then alters its permeability to the charged ions, and the charge across the cell ...
... Signaling by another neuron or a sensory event may initiate an action potential. During an action potential there is a transitory change in the polarity of the electrical charge across the cell membrane. The membrane then alters its permeability to the charged ions, and the charge across the cell ...
Shedding Light on the Role of Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine in
... neurons to support instrumental responding in the absence of food reward using a procedure similar to electrical intracranial self-stimulation. In this paradigm, active-lever presses were followed only by optical stimulation of the VTA. ChR2 mice did not develop a preference for the active lever (Ad ...
... neurons to support instrumental responding in the absence of food reward using a procedure similar to electrical intracranial self-stimulation. In this paradigm, active-lever presses were followed only by optical stimulation of the VTA. ChR2 mice did not develop a preference for the active lever (Ad ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... In more complex invertebrates, such as annelids and arthropods, behavior is regulated by more complicated brains and ventral nerve cords containing segmentally arranged clusters of neurons called ganglia. ...
... In more complex invertebrates, such as annelids and arthropods, behavior is regulated by more complicated brains and ventral nerve cords containing segmentally arranged clusters of neurons called ganglia. ...
Axia College Material Appendix C Brain Response of Behavior Part I
... commonly referred to as the “little brain”. The brains “relay station” for information is the thalamus. Located beneath the thalamus is the hypothalamus. This is the area of the brain which has immense impact on an individuals’ motivation and emotional responses. Desire for food, drink, and even se ...
... commonly referred to as the “little brain”. The brains “relay station” for information is the thalamus. Located beneath the thalamus is the hypothalamus. This is the area of the brain which has immense impact on an individuals’ motivation and emotional responses. Desire for food, drink, and even se ...
ASCENDING TRACTS
... • Sensory systems allow us to detect, analyze and respond to our environment • “ascending pathways” • Carry information from sensory receptors to the brain • Conscious: reach cerebral cortex • Unconscious: do not reach cerebral cortex • Sensations from body reach the opposite side of the brain ...
... • Sensory systems allow us to detect, analyze and respond to our environment • “ascending pathways” • Carry information from sensory receptors to the brain • Conscious: reach cerebral cortex • Unconscious: do not reach cerebral cortex • Sensations from body reach the opposite side of the brain ...
Chapter 14 - apsubiology.org
... Cholinergic fibers/neurons tend to cause relatively short-lived effects due to the rapid hydrolysis of acetylcholine by cholinesterase in the synapse Adrenergic fibers/neurons tend to cause relatively longer-lived effects due to the slower degradation of norepinephrine by catechol-omethyltransfera ...
... Cholinergic fibers/neurons tend to cause relatively short-lived effects due to the rapid hydrolysis of acetylcholine by cholinesterase in the synapse Adrenergic fibers/neurons tend to cause relatively longer-lived effects due to the slower degradation of norepinephrine by catechol-omethyltransfera ...
Central Nervous System
... - has four lobes that receive and store information and are responsible for giving signals for voluntary movement. ...
... - has four lobes that receive and store information and are responsible for giving signals for voluntary movement. ...
Function of prostaglandins
... They cause mobilization of intracellular calcium, vasoconstriction, and contraction of smooth muscles. They also decreases production of cAMP in platelets and cause platelets aggregation,thus promoting the formation of blood clots (thrombi) ( opposite effect to PGI. This limit formation to site of v ...
... They cause mobilization of intracellular calcium, vasoconstriction, and contraction of smooth muscles. They also decreases production of cAMP in platelets and cause platelets aggregation,thus promoting the formation of blood clots (thrombi) ( opposite effect to PGI. This limit formation to site of v ...
Stochastic fluctuations of the synaptic function
... variability of the postsynaptic response observed in hippocampal neurons should be extended to all the neurons of brain, it would constitute a strong biological constraint for all the theories about superior brain functions and, in particular, for the theories on brain neural code. The relatively re ...
... variability of the postsynaptic response observed in hippocampal neurons should be extended to all the neurons of brain, it would constitute a strong biological constraint for all the theories about superior brain functions and, in particular, for the theories on brain neural code. The relatively re ...
The Nervous System - Valhalla High School
... There are two main divisions of the nervous system. 1. The central nervous system (CNS): Consists of your brain and spinal column. 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS): Consists of all the nerves that branch away from the central nervous system. (This is further divided into the somatic and auto ...
... There are two main divisions of the nervous system. 1. The central nervous system (CNS): Consists of your brain and spinal column. 2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS): Consists of all the nerves that branch away from the central nervous system. (This is further divided into the somatic and auto ...
Nervous Systems - Groupfusion.net
... opening voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. – Ca2+ ions diffuse into presynaptic neuron ...
... opening voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. – Ca2+ ions diffuse into presynaptic neuron ...
Itch neurons play a role in managing pain
... not separate. They can receive signals from itch fibers and also pain fibers," says study coauthor and neuroscientist at Johns Hopkins University Xinzhong Dong. These neurons, called the GRP neurons, are a way station for pain and itch signals on their way to the brain. ...
... not separate. They can receive signals from itch fibers and also pain fibers," says study coauthor and neuroscientist at Johns Hopkins University Xinzhong Dong. These neurons, called the GRP neurons, are a way station for pain and itch signals on their way to the brain. ...
PDF only
... the cerebellum showed immunostaining for EP1. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to consistently characterize the expression of the EP1 receptor in different areas of the rat brain. It is important to mention that compared to all of the other brain regions examined, levels of EP1 ...
... the cerebellum showed immunostaining for EP1. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to consistently characterize the expression of the EP1 receptor in different areas of the rat brain. It is important to mention that compared to all of the other brain regions examined, levels of EP1 ...
Nervous Tissue - Chiropractor Manhattan | Chiropractor New
... Absolute refractory period – a second action potential cannot be initiated, even with a very strong stimulus. Relative refractory period – an action potential can be initiated, but only with a larger than normal stimulus. ...
... Absolute refractory period – a second action potential cannot be initiated, even with a very strong stimulus. Relative refractory period – an action potential can be initiated, but only with a larger than normal stimulus. ...
Physiology – Excitable Tissue – 11th May 2010
... 29. When skeletal muscle contracts, which of the following is true? a. calcium is released and this initiates contraction by binding Troponin T b. there is always a decrease in the length of the muscle c. if it is an isotonic contraction, work is done d. the initiating event is acetylcholine binding ...
... 29. When skeletal muscle contracts, which of the following is true? a. calcium is released and this initiates contraction by binding Troponin T b. there is always a decrease in the length of the muscle c. if it is an isotonic contraction, work is done d. the initiating event is acetylcholine binding ...
Nervous System - IB BiologyMr. Van Roekel Salem High School
... • What are the cells used in the nervous system called? Name two different types of these cells. • Neurons • Sensory neurons send signals from sensory receptors all over the body to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons sends signals from the central nervous system to effectors (muscles and gl ...
... • What are the cells used in the nervous system called? Name two different types of these cells. • Neurons • Sensory neurons send signals from sensory receptors all over the body to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons sends signals from the central nervous system to effectors (muscles and gl ...
Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems
... • Learning - ability to acquire knowledge or skills • Memory - storage of knowledge gained or skills developed over time • Plasticity - changes in the nervous system that are reflected in behavioral changes to stimuli (i.e. learning and memory) – Changes may include altered cell synthesis of protein ...
... • Learning - ability to acquire knowledge or skills • Memory - storage of knowledge gained or skills developed over time • Plasticity - changes in the nervous system that are reflected in behavioral changes to stimuli (i.e. learning and memory) – Changes may include altered cell synthesis of protein ...
Document
... In this way, sodium and potassium do not have to undergo exchanges along the entire length of the axon Sodium and potassium pumps and channels are active only at each NODE OF RANVIER. This is where the axon can actually exchange ions with the ...
... In this way, sodium and potassium do not have to undergo exchanges along the entire length of the axon Sodium and potassium pumps and channels are active only at each NODE OF RANVIER. This is where the axon can actually exchange ions with the ...
NMDA and AMPA Receptors: Development and Status Epilepticus
... D are expressed in cortical and hippocampal interneurons but not in principal cells (Watanabe et al. 1992, Monyer et al. 1994, Wenzel et al. 1997). NR3A and NR3B subunits Unlike NR2 subunits, which bind glutamate NR3A form a glycine binding structure (Yao et al. 2008, Henson et al. 2010). NR3A conta ...
... D are expressed in cortical and hippocampal interneurons but not in principal cells (Watanabe et al. 1992, Monyer et al. 1994, Wenzel et al. 1997). NR3A and NR3B subunits Unlike NR2 subunits, which bind glutamate NR3A form a glycine binding structure (Yao et al. 2008, Henson et al. 2010). NR3A conta ...
Lect16
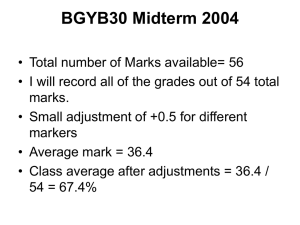
... • If you want your test remarked – Compare your grade to posted marking scheme – Tests will be entirely remarked /56 – Your test must NOT leave the office – All requests submitted by 1pm Nov 18 ...
... • If you want your test remarked – Compare your grade to posted marking scheme – Tests will be entirely remarked /56 – Your test must NOT leave the office – All requests submitted by 1pm Nov 18 ...
Modulation of Synaptic Transmission to Second
... EGTA, 2 mM Mg2ATP, and 0.3 mM Na3GTP. The pH was adjusted to 7.3 with KOH. With this pipette solution, the junction potential was 15.5 mV at 24°C (3.6 mV for KCl-based pipette solution) and was not corrected in subsequent analysis. The pipette resistance ranged from 3 to 6 M⍀. A seal resistance of a ...
... EGTA, 2 mM Mg2ATP, and 0.3 mM Na3GTP. The pH was adjusted to 7.3 with KOH. With this pipette solution, the junction potential was 15.5 mV at 24°C (3.6 mV for KCl-based pipette solution) and was not corrected in subsequent analysis. The pipette resistance ranged from 3 to 6 M⍀. A seal resistance of a ...
Mood & Nuerotransmitters - Center for Optimal Health
... found in the brain and central nervous system. Serotonin helps to regulate appetite, sleep, memory, learning, temperature, mood, behavior, muscle contraction, cardiovascular function and hormone balance. ...
... found in the brain and central nervous system. Serotonin helps to regulate appetite, sleep, memory, learning, temperature, mood, behavior, muscle contraction, cardiovascular function and hormone balance. ...
Biology and behavior
... Nervous System: Consists of all the nerve cells. It is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication system. ...
... Nervous System: Consists of all the nerve cells. It is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication system. ...