Central Nervous System
... presynaptic terminal cause voltagegated Ca2+ channels to open 2. Calcium ions diffuse into the cell and cause synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters 3. Neurotransmitters diffuse from the presynaptic terminal across the synaptic cleft 4. Neurotransmitters combine with their receptor sites and ...
... presynaptic terminal cause voltagegated Ca2+ channels to open 2. Calcium ions diffuse into the cell and cause synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters 3. Neurotransmitters diffuse from the presynaptic terminal across the synaptic cleft 4. Neurotransmitters combine with their receptor sites and ...
OPIATES
... that lasts only briefly and is followed by a few hours of a relaxed, contented state. This excessive release of dopamine and stimulation of the reward system can lead to addiction. ...
... that lasts only briefly and is followed by a few hours of a relaxed, contented state. This excessive release of dopamine and stimulation of the reward system can lead to addiction. ...
Opiates: The Brain`s Response To Drugs
... that lasts only briefly and is followed by a few hours of a relaxed, contented state. This excessive release of dopamine and stimulation of the reward system can lead to addiction. ...
... that lasts only briefly and is followed by a few hours of a relaxed, contented state. This excessive release of dopamine and stimulation of the reward system can lead to addiction. ...
Introduction to Psychology - Shoreline School District
... the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body ...
... the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body ...
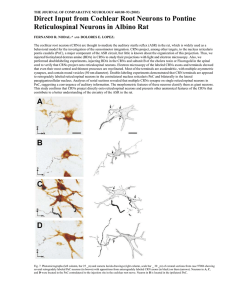
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003)
... The cochlear root neurons (CRNs) are thought to mediate the auditory startle reflex (ASR) in the rat, which is widely used as a behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis (PnC), a major compone ...
... The cochlear root neurons (CRNs) are thought to mediate the auditory startle reflex (ASR) in the rat, which is widely used as a behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis (PnC), a major compone ...
Respiratory Regulation - Warner Pacific College
... a feedback that ”switches off” the respirator ramp and stop further inspiration ○ can also increase the rate of respiration Not activated until tidal volume increases Can appear to be a protective mechanism for preventing lung inflation ...
... a feedback that ”switches off” the respirator ramp and stop further inspiration ○ can also increase the rate of respiration Not activated until tidal volume increases Can appear to be a protective mechanism for preventing lung inflation ...
Module 3 - socialscienceteacher
... STRUCTURE OF THE BRAIN 2. Neurons – Transmit messages to other neurons as well as the rest of the body – Are responsible for all psychological activities either physical or mental: 1. physical: beating of heart, voluntary movement, sweating, pain etc. 2. mental: emotions, intelligence, language, ...
... STRUCTURE OF THE BRAIN 2. Neurons – Transmit messages to other neurons as well as the rest of the body – Are responsible for all psychological activities either physical or mental: 1. physical: beating of heart, voluntary movement, sweating, pain etc. 2. mental: emotions, intelligence, language, ...
LTP
... • "when an axon of cell A ... excite a cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A's efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased" (Hebb, 1949) • Cells that fire together, wire together ...
... • "when an axon of cell A ... excite a cell B and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that A's efficiency, as one of the cells firing B, is increased" (Hebb, 1949) • Cells that fire together, wire together ...
The Nervous System
... Explain how the nervous system functions as the central control system of the body. Identify factors that may lead to disorders of the nervous system. http://thekidshouldseethis.com/post/21915392227 ...
... Explain how the nervous system functions as the central control system of the body. Identify factors that may lead to disorders of the nervous system. http://thekidshouldseethis.com/post/21915392227 ...
Specialized Neurotransmitters Dopamine
... alertness, and plays an important regulatory role in long-term memory and learning. It also protects endorphins from being broken down prematurely. • Optimal levels of this transmitter can stimulate a sense of wellbeing or even create a euphoric effect in stressful situations . . . • Yet excess nore ...
... alertness, and plays an important regulatory role in long-term memory and learning. It also protects endorphins from being broken down prematurely. • Optimal levels of this transmitter can stimulate a sense of wellbeing or even create a euphoric effect in stressful situations . . . • Yet excess nore ...
Choline Esters
... Release of transmitter occurs when voltagesensitive calcium channels in the terminal membrane are opened, allowing an influx of calcium. The resulting increase in intracellular calcium causes fusion of vesicles with the surface membrane and exocytotic expulsion of acetylcholine and cotransmitters in ...
... Release of transmitter occurs when voltagesensitive calcium channels in the terminal membrane are opened, allowing an influx of calcium. The resulting increase in intracellular calcium causes fusion of vesicles with the surface membrane and exocytotic expulsion of acetylcholine and cotransmitters in ...
16-1 INTRODUCTION The ANS regulates many important functions
... B. Stimulation of the effector organ results in excitation or inhibition. C. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for unconscious control of its effector organs. However it can be influenced by conscious functions (e.g., biofeedback, emotions). ANATOMY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. The A ...
... B. Stimulation of the effector organ results in excitation or inhibition. C. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for unconscious control of its effector organs. However it can be influenced by conscious functions (e.g., biofeedback, emotions). ANATOMY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. The A ...
Physiology of Behavior
... resistance pushes the endolymph against the cupula, causing it to bend, until the fluid begins to move at the same speed as the head. If the head rotation is then stopped, the endolymph, still circulating through the canal, pushes the cupula the other way. Angular acceleration is thus translated int ...
... resistance pushes the endolymph against the cupula, causing it to bend, until the fluid begins to move at the same speed as the head. If the head rotation is then stopped, the endolymph, still circulating through the canal, pushes the cupula the other way. Angular acceleration is thus translated int ...
16-1 INTRODUCTION The ANS regulates many important functions
... B. Stimulation of the effector organ results in excitation or inhibition. C. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for unconscious control of its effector organs. However it can be influenced by conscious functions (e.g., biofeedback, emotions). ANATOMY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. The A ...
... B. Stimulation of the effector organ results in excitation or inhibition. C. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for unconscious control of its effector organs. However it can be influenced by conscious functions (e.g., biofeedback, emotions). ANATOMY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. The A ...
Stages in Neuromuscular Synapse Elimination
... Rudimentary Ocular Dominance Columns Develop in the Absence of Visual Inputs • Columns in layer 4a of primary visual cortex with appropriate eye-specific inputs are present before the critical period for ocular dominance column plasticitiy. •Columns develop in the absence of visual system input and ...
... Rudimentary Ocular Dominance Columns Develop in the Absence of Visual Inputs • Columns in layer 4a of primary visual cortex with appropriate eye-specific inputs are present before the critical period for ocular dominance column plasticitiy. •Columns develop in the absence of visual system input and ...
Reflex arc ppt - bananateachersworld
... blunt pencil about 1 cm apart. 2. The blindfolded student has to say whether it was one point or two points that touched them. 3. Place a cross on the hand for each point felt. Results: Map the density of sensory receptors by drawing it into your book. Conclusion: Are the receptors in groups? Or ran ...
... blunt pencil about 1 cm apart. 2. The blindfolded student has to say whether it was one point or two points that touched them. 3. Place a cross on the hand for each point felt. Results: Map the density of sensory receptors by drawing it into your book. Conclusion: Are the receptors in groups? Or ran ...
Human Vision: Electrophysiology and Psychophysics
... but also the underlying brain architecture and physiology that solves this problem. ...
... but also the underlying brain architecture and physiology that solves this problem. ...
Serotonin, also known as 5-HT (5
... found at the synapses of certain neurons. That is, it is released by the tip of one stimulated neuron, and recognized by an adjacent neuron, causing it to fire and so on. In this way, the nerve impulse is propagated throughout the nervous system. Note that after a nerve fires at a synapse, the neuro ...
... found at the synapses of certain neurons. That is, it is released by the tip of one stimulated neuron, and recognized by an adjacent neuron, causing it to fire and so on. In this way, the nerve impulse is propagated throughout the nervous system. Note that after a nerve fires at a synapse, the neuro ...
Name: Block: Date
... The largest portion of the human brain is the CEREBRUM. The PARASYMPATHETIC nervous system causes the heartbeat to slow down. The drug amphetamine has a chemical structure similar to the neurotransmitter EPINEPHRINE. The cerebral cortex can be mapped. There are SENSORY areas that receive impulses fr ...
... The largest portion of the human brain is the CEREBRUM. The PARASYMPATHETIC nervous system causes the heartbeat to slow down. The drug amphetamine has a chemical structure similar to the neurotransmitter EPINEPHRINE. The cerebral cortex can be mapped. There are SENSORY areas that receive impulses fr ...
Initiation of the arousal response
... of moderate to high levels of Cortisol-involved arousal, such that excitatory MR’s are fully occupied, and GR’s are only partly occupied. Since GR and MR are also colocalized in the PFC, very high or very low levels of cortisol are correlated with less effective inhibitory functions such as attentio ...
... of moderate to high levels of Cortisol-involved arousal, such that excitatory MR’s are fully occupied, and GR’s are only partly occupied. Since GR and MR are also colocalized in the PFC, very high or very low levels of cortisol are correlated with less effective inhibitory functions such as attentio ...
Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse
... Nerve pathways are our information super highways. They are made up of cells called ...
... Nerve pathways are our information super highways. They are made up of cells called ...
9d. Know the functions of the nervous system and the role of
... The __________________ ________________ controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses throughout the body. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord. Motor neurons carry im ...
... The __________________ ________________ controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. Neurons transmit electrochemical impulses throughout the body. Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs to the spinal cord. Motor neurons carry im ...
Thalamus & Hypothalamus
... sexual activity, food & water intake, aggression • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
... sexual activity, food & water intake, aggression • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...