![Chapter41 Hormones Notes [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016605577_1-a7aad459db07937df65df4f3a411aef9-300x300.png)
Pituitary Gland
... 1.Which cells are target cells for hormone A? Explain why. 2.Which cells are target cells for hormone B? Explain why. ...
... 1.Which cells are target cells for hormone A? Explain why. 2.Which cells are target cells for hormone B? Explain why. ...
The Endocrine System - Mediapolis Community School
... • Growth hormone(GH)- stimulates cell growth in size and frequency. • Prolactin(PRL)- stimulates a woman’s milk production after the birth of an infant. • Thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH)- controls thyroid gland secretion. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH)- controls the manufacture and secretion o ...
... • Growth hormone(GH)- stimulates cell growth in size and frequency. • Prolactin(PRL)- stimulates a woman’s milk production after the birth of an infant. • Thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH)- controls thyroid gland secretion. • Adrenocorticotropic hormone(ACTH)- controls the manufacture and secretion o ...
Endocrine (regulatory) System
... Name three major local regulators that act on nearby target cells. (pgs. 947-948) Name three key molecules that play a role in the signal transduction pathway (typical reactions in the endocrine system). How is the anterior part of the pituitary gland different from the posterior part? Name the horm ...
... Name three major local regulators that act on nearby target cells. (pgs. 947-948) Name three key molecules that play a role in the signal transduction pathway (typical reactions in the endocrine system). How is the anterior part of the pituitary gland different from the posterior part? Name the horm ...
Endocrine System
... process feeds back on the system, shutting down the process. • Antagonistic feedback- one hormone has an opposite effect of another hormone on the system. • Positive feedback- the outcome of a process feeds back on the system, further stimulating the process. ...
... process feeds back on the system, shutting down the process. • Antagonistic feedback- one hormone has an opposite effect of another hormone on the system. • Positive feedback- the outcome of a process feeds back on the system, further stimulating the process. ...
Endocrine System - McCulloch Intermediate School
... production of hormones in the adrenal glands – 2 hormones stimulate all other sex hormones – Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Lutenizing hormone (LH) control the growth, development and functions of the gonads ...
... production of hormones in the adrenal glands – 2 hormones stimulate all other sex hormones – Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and Lutenizing hormone (LH) control the growth, development and functions of the gonads ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... Secretes 9 hormones that directly regulate body functions Controls the release of hormones by several other glands Divided into two parts: anterior and posterior pituitary Posterior: secretes antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin ADH-reabsorb water from kidneys Oxytocin- contraction of uterus, rel ...
... Secretes 9 hormones that directly regulate body functions Controls the release of hormones by several other glands Divided into two parts: anterior and posterior pituitary Posterior: secretes antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin ADH-reabsorb water from kidneys Oxytocin- contraction of uterus, rel ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... exert specific effects on tissues, organs or other glands located some distance away from the cells that secrete them. ...
... exert specific effects on tissues, organs or other glands located some distance away from the cells that secrete them. ...
The Endocrine System
... • These glands are associatd with the digestive system of the human body. They secrete digestive enzymes Produce Hormones Insulin – controls the storage of sugar in the liver and sugar breakdown in tissues Glucagon – converts glycogen to glucose and this process occurs when blood glucose concentrati ...
... • These glands are associatd with the digestive system of the human body. They secrete digestive enzymes Produce Hormones Insulin – controls the storage of sugar in the liver and sugar breakdown in tissues Glucagon – converts glycogen to glucose and this process occurs when blood glucose concentrati ...
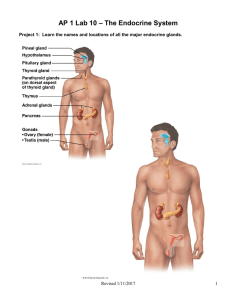
AP 1 Lab 10 – The Endocrine System
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
... Is called the "Master Gland" because it releases more Hs than any other and affects many other glands. _____________ Organ found adjacent to first part of the small intestine containing endocrine glands for control of blood sugar levels. _____________ This type of diabetes is caused by target tissue ...
The Hypothalamo-Pituitary- Adrenal Axis
... PL: prolactin TSH: thyroid stimulating hormone GH: growth hormone **Please see Figures 10.7-10.9 in text** ...
... PL: prolactin TSH: thyroid stimulating hormone GH: growth hormone **Please see Figures 10.7-10.9 in text** ...
Lab 1 Functional Anatomy of the Endocrine Glands
... ______________________ Parathyroid hormone ______________________ Estrogens and progesterone ______________________ Testosterone ______________________ Many releasing hormones (TRH, CRH, GHRH etc.) ______________________ FSH, LH, GH, ACTH, Prolactin, TSH, ______________________ T-cell stimulating ho ...
... ______________________ Parathyroid hormone ______________________ Estrogens and progesterone ______________________ Testosterone ______________________ Many releasing hormones (TRH, CRH, GHRH etc.) ______________________ FSH, LH, GH, ACTH, Prolactin, TSH, ______________________ T-cell stimulating ho ...
I- Match Table A with Table B
... ( ) -The endocrine gland located at the base of the throat, just inferior to Adam's apple is a- pineal gland b- hypothalamus c- thyroid d- pituitary ( ) -The hormone that stimulates the contraction of smooth muscle in the uterus is: a- FSH b- LH c- oxytocin d- estrogen e- c+d ( ) -Nervousness, incr ...
... ( ) -The endocrine gland located at the base of the throat, just inferior to Adam's apple is a- pineal gland b- hypothalamus c- thyroid d- pituitary ( ) -The hormone that stimulates the contraction of smooth muscle in the uterus is: a- FSH b- LH c- oxytocin d- estrogen e- c+d ( ) -Nervousness, incr ...
Endocrine System Endocrine Glands
... - the release of hormones from the adenohypophysis is controlled by regulating hormones (or factors) from the hypothalamus via the blood supply ...
... - the release of hormones from the adenohypophysis is controlled by regulating hormones (or factors) from the hypothalamus via the blood supply ...
21 Endocrine Flashcards MtSAC
... 26. Adrenal medulla secretes which hormones? 27. Hypersecretion of cortisol and a round "moon" face and "buffalo hump" are characteristic of what disorder? 28. Hyposecretion of cortisol, increased blood acth levels, low blood volume and pressure, and increased skin pigmentation are characteristics o ...
... 26. Adrenal medulla secretes which hormones? 27. Hypersecretion of cortisol and a round "moon" face and "buffalo hump" are characteristic of what disorder? 28. Hyposecretion of cortisol, increased blood acth levels, low blood volume and pressure, and increased skin pigmentation are characteristics o ...
Chapter 9- Endocrine System
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs ...
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs ...
Endocrine System
... Tiny – size of a grape Base of brain Connected to hypothalamus Anterior / Posterior lobes Cranial cavity “Master Gland” ...
... Tiny – size of a grape Base of brain Connected to hypothalamus Anterior / Posterior lobes Cranial cavity “Master Gland” ...
Endocrine System
... The pancreas also has an exocrine function. Where are these products released? Describe the overlapping homeostatic mechanisms involving insulin and glucagon. ...
... The pancreas also has an exocrine function. Where are these products released? Describe the overlapping homeostatic mechanisms involving insulin and glucagon. ...
Female Reproductive System
... Anterior pituitary produces and stores: The anterior pituitary produces six major hormones, and the posterior pituitary stores two hormones originating in the hypothalamus. The pituitary's target endocrine glands are the thyroid, adrenal gland, and the gonads. Through these glands it Controls on t ...
... Anterior pituitary produces and stores: The anterior pituitary produces six major hormones, and the posterior pituitary stores two hormones originating in the hypothalamus. The pituitary's target endocrine glands are the thyroid, adrenal gland, and the gonads. Through these glands it Controls on t ...
Physio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioEx
... pregnancy, which will be a lot of work for her. She has to come to the lab for a blood glucose test every hour for four hours. If she fails that, goes to nutritionist, taught what foods she can eat; can’t have milk in the morning, although it is okay after lunch time. Milk has a high glycemic index ...
... pregnancy, which will be a lot of work for her. She has to come to the lab for a blood glucose test every hour for four hours. If she fails that, goes to nutritionist, taught what foods she can eat; can’t have milk in the morning, although it is okay after lunch time. Milk has a high glycemic index ...
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine
... grow and mature; it is also responsible for estrogen secretion. In men, the FSH hormone controls the growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm growth. Luteinizing hormone (LH) has separate functions for females and males. In females, it functions to mature the ovarian follicle and ovum, helps wit ...
... grow and mature; it is also responsible for estrogen secretion. In men, the FSH hormone controls the growth of the seminiferous tubules and sperm growth. Luteinizing hormone (LH) has separate functions for females and males. In females, it functions to mature the ovarian follicle and ovum, helps wit ...
Chp.18 Endocrine Glands
... • Gonadotropins: glycoprotein hormones that promote growth and function of the gonads • LH and FSH – Both hormones regulate production of gametes and reproductive hormones • Testosterone in males • Estrogen and progesterone in females ...
... • Gonadotropins: glycoprotein hormones that promote growth and function of the gonads • LH and FSH – Both hormones regulate production of gametes and reproductive hormones • Testosterone in males • Estrogen and progesterone in females ...
Endocrine System
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...