Growth Hormone
... • Bound to High Affinity Bound protein and Low Affinity Bound protein. • Binding compensates for irrating secretion rates. • Half life varies 6 to 20 minutes. • Somatomedins - produced by liver polypeptides - growth factors • Growth hormone increase IGF-I somatomedin • What is growth? • Uptake of Am ...
... • Bound to High Affinity Bound protein and Low Affinity Bound protein. • Binding compensates for irrating secretion rates. • Half life varies 6 to 20 minutes. • Somatomedins - produced by liver polypeptides - growth factors • Growth hormone increase IGF-I somatomedin • What is growth? • Uptake of Am ...
Document
... Receptor resembles growth hormone receptor Increases milk production Maintains corpus luteum Inhibits ovary ...
... Receptor resembles growth hormone receptor Increases milk production Maintains corpus luteum Inhibits ovary ...
iphy 3430 12-8
... Does not have target organ that secretes its own hormone. Controls growth after birth (via somatomedins) 1. Growth of bone 2. Growth of soft tissues 3. Stimulates protein synthesis (uptake of amino acids and inhibition of protein degredation) 4. Synergistic with thyroid hormone ...
... Does not have target organ that secretes its own hormone. Controls growth after birth (via somatomedins) 1. Growth of bone 2. Growth of soft tissues 3. Stimulates protein synthesis (uptake of amino acids and inhibition of protein degredation) 4. Synergistic with thyroid hormone ...
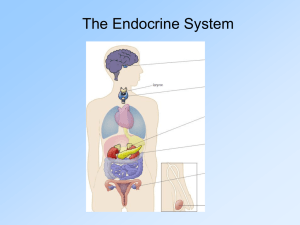
The Endocrine System
... •The endocrine system secretes hormones that stimulate growth and many kinds of reactions, such as activity levels and moods. •The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, the thyroid, the adrenals, the testes, and the ovaries. ...
... •The endocrine system secretes hormones that stimulate growth and many kinds of reactions, such as activity levels and moods. •The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, the thyroid, the adrenals, the testes, and the ovaries. ...
Endocrine System Notes
... D. Controls body’s reaction to stress – increase sugar levels/energy E. Also controls levels of salt and water in the body Islets of Langerhans A. Located throughout the Pancreas B. Hormone – Insulin C. Regulates amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood D. If gland does not operate correctly - Diabete ...
... D. Controls body’s reaction to stress – increase sugar levels/energy E. Also controls levels of salt and water in the body Islets of Langerhans A. Located throughout the Pancreas B. Hormone – Insulin C. Regulates amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood D. If gland does not operate correctly - Diabete ...
Calm Your Hormones or Everything You Should Know About
... • Hormones are all lipophilic • Subcu receptors get loaded over time, so rotate sites • If commercial cream, not compounded, be sure label says USP progesterone or it may lack enzyme for conversion • If exact dosing is required, do SL or injectible ...
... • Hormones are all lipophilic • Subcu receptors get loaded over time, so rotate sites • If commercial cream, not compounded, be sure label says USP progesterone or it may lack enzyme for conversion • If exact dosing is required, do SL or injectible ...
Ch. 3 S. 3
... testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone that play an important role in the development of primary and secondary sex characteristics and have psychological as well as biological effects. ...
... testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone that play an important role in the development of primary and secondary sex characteristics and have psychological as well as biological effects. ...
No Slide Title
... 2.Pancreatic islets secrete glucagons & insulin a. Glucagons – involved in carbohydrate metabolism; released when glucose level in blood is low * causes liver to convert glycogen into glucose and releases the glucose into the bloodstream b. Insulin – causes most of the body’s cells to take in glucos ...
... 2.Pancreatic islets secrete glucagons & insulin a. Glucagons – involved in carbohydrate metabolism; released when glucose level in blood is low * causes liver to convert glycogen into glucose and releases the glucose into the bloodstream b. Insulin – causes most of the body’s cells to take in glucos ...
Chapter 3 Section 3
... • Adrenal Gland – the outer layer of the adrenal gland, or cortex, secretes cortical steroids which increase resistance to stress and promote muscle development. They also release adrenaline and noradrenaline. • Testes and Ovaries – produce the hormones testosterone, estrogen, and ...
... • Adrenal Gland – the outer layer of the adrenal gland, or cortex, secretes cortical steroids which increase resistance to stress and promote muscle development. They also release adrenaline and noradrenaline. • Testes and Ovaries – produce the hormones testosterone, estrogen, and ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
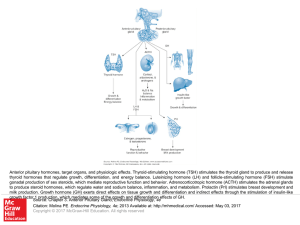
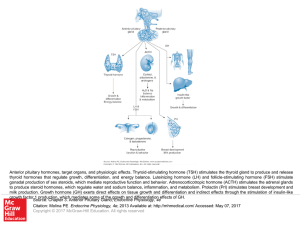
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
Slide ()
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
... Anterior pituitary hormones, target organs, and physiologic effects. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones that regulate growth, differentiation, and energy balance. Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimu ...
FEMALE HORMONES and their activity
... fibrocystic breast disease, PMS, mood swings, excessive bleeding, endometriosis, fibroids, infertility, and ovarian cysts. Peri-menopause is the time when hormone levels begin to shift in preparation for menopause. It is not so much the decrease in hormones that produces the uncomfortable symptoms a ...
... fibrocystic breast disease, PMS, mood swings, excessive bleeding, endometriosis, fibroids, infertility, and ovarian cysts. Peri-menopause is the time when hormone levels begin to shift in preparation for menopause. It is not so much the decrease in hormones that produces the uncomfortable symptoms a ...