Endocrine System
... hormone oxytocin is released into the body, which stimulates further contractions. This results in contractions increasing in amplitude and frequency causing the release of more oxytocin. • Lactation also involves positive feedback in that the more the baby suckles, the more milk is produced, via a ...
... hormone oxytocin is released into the body, which stimulates further contractions. This results in contractions increasing in amplitude and frequency causing the release of more oxytocin. • Lactation also involves positive feedback in that the more the baby suckles, the more milk is produced, via a ...
Chapter 1: Animal Agriculture
... pregnancy and causes development of mammary lobule-alveolar system ...
... pregnancy and causes development of mammary lobule-alveolar system ...
chapter 18 study guide
... water soluble hormones bind to receptors on the plasma membrane activate one or several enzymes to catalyze reactions that produce physiologic responses permissive effect synergistic effect antagonistic effect ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND hGH – human growth hormone (somatotropin) stimulates several tiss ...
... water soluble hormones bind to receptors on the plasma membrane activate one or several enzymes to catalyze reactions that produce physiologic responses permissive effect synergistic effect antagonistic effect ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND hGH – human growth hormone (somatotropin) stimulates several tiss ...
CHAPTER 18 STUDY GUIDE
... water soluble hormones bind to receptors on the plasma membrane activate one or several enzymes to catalyze reactions that produce physiologic responses permissive effect synergistic effect antagonistic effect ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND hGH – human growth hormone (somatotropin) stimulates several tiss ...
... water soluble hormones bind to receptors on the plasma membrane activate one or several enzymes to catalyze reactions that produce physiologic responses permissive effect synergistic effect antagonistic effect ANTERIOR PITUITARY GLAND hGH – human growth hormone (somatotropin) stimulates several tiss ...
Hormone replacement therapy for pre
... • HRT after endometrial cancer (EMC) treatment is an uncertain subject with limited exploration among gynecologic cancer research. Because estrogen is a well-recognized etiologic factor of EMC, most physicians are probably reluctant to provide a replacement therapy, or limit its use to only a select ...
... • HRT after endometrial cancer (EMC) treatment is an uncertain subject with limited exploration among gynecologic cancer research. Because estrogen is a well-recognized etiologic factor of EMC, most physicians are probably reluctant to provide a replacement therapy, or limit its use to only a select ...
Endocrine Notes
... 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
... 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
Endocrine System
... 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
... 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
File
... HGH – makes muscle cells grow and divide & causes the liver to release Insulin Growth Factors (IGF) which makes bone and cartilage grow to support greater muscle mass. EPO – stimulates red blood cell production to increase oxygen transportation levels. ...
... HGH – makes muscle cells grow and divide & causes the liver to release Insulin Growth Factors (IGF) which makes bone and cartilage grow to support greater muscle mass. EPO – stimulates red blood cell production to increase oxygen transportation levels. ...
Chapter 11 Quiz
... 10. Which of the following is NOT one of the three stages in the response to stress? A. stage of exhaustion B. alarm reaction *C. stage of denial D. stage of resistance 11. A deficiency of dietary iodine would result in excessive TSH secretion. *A. True B. False 12. A(n) _____________ is an abnorma ...
... 10. Which of the following is NOT one of the three stages in the response to stress? A. stage of exhaustion B. alarm reaction *C. stage of denial D. stage of resistance 11. A deficiency of dietary iodine would result in excessive TSH secretion. *A. True B. False 12. A(n) _____________ is an abnorma ...
Photosynthesis Review Questions
... 12. What group of hormones released by the adrenal glands help to increase blood sugar levels? 13. What is Type 2 diabetes? How can it be managed/controlled? 14. What hormone causes an increase in blood calcium levels? a decrease in blood calcium levels? 15. Describe how a deficiency in iodine cause ...
... 12. What group of hormones released by the adrenal glands help to increase blood sugar levels? 13. What is Type 2 diabetes? How can it be managed/controlled? 14. What hormone causes an increase in blood calcium levels? a decrease in blood calcium levels? 15. Describe how a deficiency in iodine cause ...
Endocrine Gland Matching
... Endocrine Gland Matching - KEY Match the hormones to the gland which secretes them. ...
... Endocrine Gland Matching - KEY Match the hormones to the gland which secretes them. ...
Endocrine Lesson 2 Monday, March 12
... pituitary (adenohypophysis) • Produces hormones ADH and oxytocin that are stored in the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) ...
... pituitary (adenohypophysis) • Produces hormones ADH and oxytocin that are stored in the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) ...
The Endocrine system
... Adrenal glands 1. Located just above the kidney 2. Secretes many hormones ...
... Adrenal glands 1. Located just above the kidney 2. Secretes many hormones ...
The Endocrine Syetem
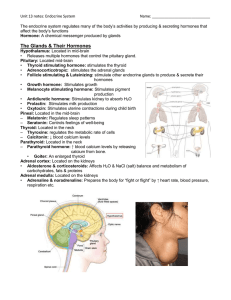
... - (thyroid-stimulating) Growth and secretion of the thyroid ACTH - (adenocorticotropic) Growth of Adrenal cortex and secretions FSH - (follicle stimulating) Growth and development of Ovarian Follicles - providers of ova (eggs), release of estrogen/progesterone LH - (Luteinizing) Control ovulat ...
... - (thyroid-stimulating) Growth and secretion of the thyroid ACTH - (adenocorticotropic) Growth of Adrenal cortex and secretions FSH - (follicle stimulating) Growth and development of Ovarian Follicles - providers of ova (eggs), release of estrogen/progesterone LH - (Luteinizing) Control ovulat ...
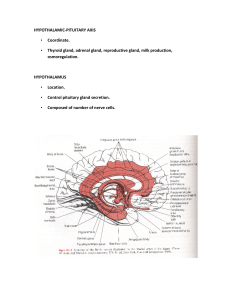
HYPOTHALAMIC-PITUITARY AXIS • Coordinate. • Thyroid gland
... HYPOTHALAMIC-HYPOPHYSIAL PORTAL SYSTEM ...
... HYPOTHALAMIC-HYPOPHYSIAL PORTAL SYSTEM ...
Endocrine SystemExam
... 9. This is the gland that regulates the levels of calcium in the bloodstream: a. A b. D c. C d. B 10. Testosterone is secreted by this gland: a. H b. G c. A d. F 11. The gland found in the brain that “connects” the nervous system and the endocrine system is called the: a. Parathyroid b. Thyroid c. ...
... 9. This is the gland that regulates the levels of calcium in the bloodstream: a. A b. D c. C d. B 10. Testosterone is secreted by this gland: a. H b. G c. A d. F 11. The gland found in the brain that “connects” the nervous system and the endocrine system is called the: a. Parathyroid b. Thyroid c. ...
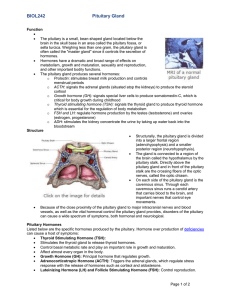
BIOL242pituitaryOCT2012
... Hormones have a dramatic and broad range of effects on metabolism, growth and maturation, sexuality and reproduction, and other important bodily functions. The pituitary gland produces several hormones: o Prolactin: stimulates breast milk production and controls menstrual periods o ACTH: signals ...
... Hormones have a dramatic and broad range of effects on metabolism, growth and maturation, sexuality and reproduction, and other important bodily functions. The pituitary gland produces several hormones: o Prolactin: stimulates breast milk production and controls menstrual periods o ACTH: signals ...
Lecture #20 Date ______
... – modified fatty acids secreted by placenta and immune system; also found in semen ...
... – modified fatty acids secreted by placenta and immune system; also found in semen ...
Endocrine System - TWHS 9th Grade Campus
... Pituitary Gland • Description- found at the base of skull • Hormones- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) • Diseases– Gigantism= too much HGH – Dwarfism= not enough HGH ...
... Pituitary Gland • Description- found at the base of skull • Hormones- Human Growth Hormone (HGH) • Diseases– Gigantism= too much HGH – Dwarfism= not enough HGH ...
TAKE HOME EXAM –URINARY SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE
... 11-12. The fallopian tubes connect the _____________________ to the ____________________. 13. The hormone _____________________ is released by the pituitary gland and stimulates labor. 14. ___________________ are defined as the finger-like projections on the fallopian tubes. 15. In males, sperm exit ...
... 11-12. The fallopian tubes connect the _____________________ to the ____________________. 13. The hormone _____________________ is released by the pituitary gland and stimulates labor. 14. ___________________ are defined as the finger-like projections on the fallopian tubes. 15. In males, sperm exit ...
File
... cells can respond to a hormone. Target cells have specific receptors that other cells do not have. ...
... cells can respond to a hormone. Target cells have specific receptors that other cells do not have. ...
Endocrine system powerpoint
... - (thyroid-stimulating) Growth and secretion of the thyroid ACTH - (adenocorticotropic) Growth of Adrenal cortex and secretions FSH - (follicle stimulating) Growth and development of Ovarian Follicles - providers of ova (eggs), release of estrogen/progesterone LH - (Luteinizing) Control ovulat ...
... - (thyroid-stimulating) Growth and secretion of the thyroid ACTH - (adenocorticotropic) Growth of Adrenal cortex and secretions FSH - (follicle stimulating) Growth and development of Ovarian Follicles - providers of ova (eggs), release of estrogen/progesterone LH - (Luteinizing) Control ovulat ...
Aim: How does the endocrine system work to maintain homeostasis?
... A gland makes a hormone and stores it until it is needed. When the hormone is needed the hormone is released into the blood stream. It will travel around the body in the blood until it finds its matching receptor molecule located on or in its target cell. The hormone binds to the receptor molecule a ...
... A gland makes a hormone and stores it until it is needed. When the hormone is needed the hormone is released into the blood stream. It will travel around the body in the blood until it finds its matching receptor molecule located on or in its target cell. The hormone binds to the receptor molecule a ...