IONS and Isotopes PPT
... Find how many protons or electrons in would have as a nuetral atom. Then what ever the charge is (i.e. positive) do the opposite of the charge (subtract) to the electrons only Cl+2 = 17 electrons -2 electrons = 15e ...
... Find how many protons or electrons in would have as a nuetral atom. Then what ever the charge is (i.e. positive) do the opposite of the charge (subtract) to the electrons only Cl+2 = 17 electrons -2 electrons = 15e ...
chapter_3_study_guide
... __________________ alpha particles. He found that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil but some were mysteriously deflected by something in the gold. Rutherford concluded there must be a ___________________ ____________________ in the center of the gold atoms that deflected the alpha pa ...
... __________________ alpha particles. He found that most alpha particles passed through the gold foil but some were mysteriously deflected by something in the gold. Rutherford concluded there must be a ___________________ ____________________ in the center of the gold atoms that deflected the alpha pa ...
Vocabulary
... form – oxidation number • It will always be with one form of cation and one form of anion. • Criss-cross • Subscripts indicate a ratio ...
... form – oxidation number • It will always be with one form of cation and one form of anion. • Criss-cross • Subscripts indicate a ratio ...
Page 201 - ClassZone
... Atoms are composed of three types of particles—protons, neutrons, and electrons. A proton is a positively charged particle. A neutron is an uncharged particle. The neutron has approximately the same mass as a proton. Protons and neutrons are grouped together in the atom’s center. This combination of ...
... Atoms are composed of three types of particles—protons, neutrons, and electrons. A proton is a positively charged particle. A neutron is an uncharged particle. The neutron has approximately the same mass as a proton. Protons and neutrons are grouped together in the atom’s center. This combination of ...
document
... (number of protons) In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised first periodic table based on atomic mass – however, some elements were out of order. In 1913, Henry G. J. Moseley arranged elements by atomic number and is what we use today. The periodic table is arranged by groups and periods Groups ...
... (number of protons) In the late 1800’s, Dmitri Mendeleev devised first periodic table based on atomic mass – however, some elements were out of order. In 1913, Henry G. J. Moseley arranged elements by atomic number and is what we use today. The periodic table is arranged by groups and periods Groups ...
niels bohr model
... motions Orbits are associated with definite energy or energy levels Said that electrons can only gain or lose energy by transferring to an allowed energy level ...
... motions Orbits are associated with definite energy or energy levels Said that electrons can only gain or lose energy by transferring to an allowed energy level ...
Bohr – Rutherford Diagrams
... maximum of 2 dots). Each dot represents 1 electron; if the atom contains more than 2 electrons, draw a second circle around the first one and draw small dots on this second energy level (up to a maximum of 8 dots). Each dot represents an electron; as appropriate, draw more energy level lines accordi ...
... maximum of 2 dots). Each dot represents 1 electron; if the atom contains more than 2 electrons, draw a second circle around the first one and draw small dots on this second energy level (up to a maximum of 8 dots). Each dot represents an electron; as appropriate, draw more energy level lines accordi ...
Atoms 8.8a Describe the structure and parts of an atoms. Verb
... Location of Subatomic Particles • Our model is not accurate (correct) – The electron cloud has many different shapes - The space between the nucleus and electron cloud is much greater ...
... Location of Subatomic Particles • Our model is not accurate (correct) – The electron cloud has many different shapes - The space between the nucleus and electron cloud is much greater ...
Atoms and Atomic Theory
... So what does it mean, and where does the 0.5 come from? Here is the explanation. The non integer values mean that there is more than one isotope of chlorine that exists in nature, in this case 35Cl and 37Cl. A quick calculation will tell you that these two species have the same number of protons and ...
... So what does it mean, and where does the 0.5 come from? Here is the explanation. The non integer values mean that there is more than one isotope of chlorine that exists in nature, in this case 35Cl and 37Cl. A quick calculation will tell you that these two species have the same number of protons and ...
Basics of Chemistry
... chemical behavior of an atom depends on number of electrons in its outermost shell ...
... chemical behavior of an atom depends on number of electrons in its outermost shell ...
The Periodic Table
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...
... 27. Draw lewis dot structures to represent number of valence electrons in an atom or ion 28. Use octet rule to predict how reactive or inert an element may be 7.2 Ionic Bonds and Ionic Compounds 29. Explain the electrical charge of an ionic compound 30. First learn logic of ionic bond formation, the ...
History of Atomic Theory
... the mass of an atom was about double the mass of its protons. However, it was James Chadwick that finally discovered that a neutral particle with about the same mass as a proton existed in the nucleus. This particle was called a neutron. This disproved Dalton’s 2nd Law that all atoms of the same ele ...
... the mass of an atom was about double the mass of its protons. However, it was James Chadwick that finally discovered that a neutral particle with about the same mass as a proton existed in the nucleus. This particle was called a neutron. This disproved Dalton’s 2nd Law that all atoms of the same ele ...
ps ch 4 rev 2015ans
... 27. Explain in detail the Thomson model of the atom and why it was important to the understanding of the atom as we know it today. The Thompson model was based on the idea of Plum Pudding or a chocolate chip cookie. The pudding was the positively charged substance and inside of that scattered around ...
... 27. Explain in detail the Thomson model of the atom and why it was important to the understanding of the atom as we know it today. The Thompson model was based on the idea of Plum Pudding or a chocolate chip cookie. The pudding was the positively charged substance and inside of that scattered around ...
creator of the atomic theory
... moved in paths at certain distances around the nucleus, called orbitals. Higher orbitals have more energy. When electrons move down orbitals, light (photons) is emitted. ...
... moved in paths at certain distances around the nucleus, called orbitals. Higher orbitals have more energy. When electrons move down orbitals, light (photons) is emitted. ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... together to make it easier to predict the properties of an element based on its location. How is the Periodic Table organized? ◦ Based on the number of protons, or atomic number, an element has in the nucleus of an atom. ...
... together to make it easier to predict the properties of an element based on its location. How is the Periodic Table organized? ◦ Based on the number of protons, or atomic number, an element has in the nucleus of an atom. ...
Development of the Atomic Model
... • In a reaction the mass you start with is the mass you end with. ...
... • In a reaction the mass you start with is the mass you end with. ...
Bohr Models and Lewis Dot Structures
... • Periods go from left to • Groups go up and down right ...
... • Periods go from left to • Groups go up and down right ...
Chapter 2: The Composition and Structure of the Atom • 2.1 Matter
... o Electrons exist in fixed energy levels surrounding the nucleus. The quantization of energy. o Promotion of an electron occurs as it absorbs energy. The excited state. o Energy is released as the electron travels back to lower levels. Relaxation. o Orbit – what Bohr called the fixed energy levels. ...
... o Electrons exist in fixed energy levels surrounding the nucleus. The quantization of energy. o Promotion of an electron occurs as it absorbs energy. The excited state. o Energy is released as the electron travels back to lower levels. Relaxation. o Orbit – what Bohr called the fixed energy levels. ...
Year 11 Chemistry Balancing Equations
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
... Looking over your electron configurations, are there any elements above that have similar valence electron configurations to those of other elements? If so, list below the elements that are similar (in terms of valence electrons) and state the similarity for each of the groups. ...
the Atom
... Isotopes: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Most elements occur naturally with varying numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numb ...
... Isotopes: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. Most elements occur naturally with varying numbers of neutrons. Atoms of the same element that have a different number of neutrons in the nucleus are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass numb ...
What is matter? - Waterford Public Schools
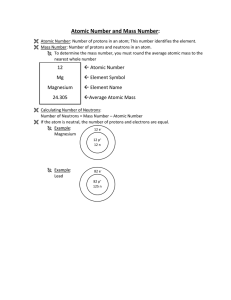
... an element if the abundance of each isotope for that element is known Average Atomic Mass % natural abundance ...
... an element if the abundance of each isotope for that element is known Average Atomic Mass % natural abundance ...
Atomic Theory - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... • Planetary model • Proposed electrons have a set amount of energy putting them in different energy levels, or orbits around the nucleus. • Electrons can change energy levels; higher energy levels are further from the nucleus. electron ...
... • Planetary model • Proposed electrons have a set amount of energy putting them in different energy levels, or orbits around the nucleus. • Electrons can change energy levels; higher energy levels are further from the nucleus. electron ...
Lesson x- Review W14 answers
... Rutherford -atoms are mostly empty space (where electrons are) with a dense positive centre (nucleus) -used the gold foil experiment to discover the nucleus; most particles went through, few bounced back Bohr -atoms have a dense nucleus surround by shells (energy levels) of electrons -discovered ele ...
... Rutherford -atoms are mostly empty space (where electrons are) with a dense positive centre (nucleus) -used the gold foil experiment to discover the nucleus; most particles went through, few bounced back Bohr -atoms have a dense nucleus surround by shells (energy levels) of electrons -discovered ele ...
Chapter 2 Lect. 1
... 1. Becquerel (1896) discovered that uranium produced an image on photographic film in the absence of light 2. This spontaneous emission of radiation was called radioactivity 3. Three types of radioactive emission were eventually discovered a. Gamma rays (g) = high energy light wave b. Beta particles ...
... 1. Becquerel (1896) discovered that uranium produced an image on photographic film in the absence of light 2. This spontaneous emission of radiation was called radioactivity 3. Three types of radioactive emission were eventually discovered a. Gamma rays (g) = high energy light wave b. Beta particles ...