Atom Structure and Isotopes
... Videoclip #2 Questions 1) What is the atomic number? number of protons in the nucleus 2) What are isotopes? Atoms with the same number of protons, but a DIFFERENT number of neutrons. 3) How many protons and neutrons are in the following carbon isotopes? Carbon-12 Carbon-13 Carbon-14 ...
... Videoclip #2 Questions 1) What is the atomic number? number of protons in the nucleus 2) What are isotopes? Atoms with the same number of protons, but a DIFFERENT number of neutrons. 3) How many protons and neutrons are in the following carbon isotopes? Carbon-12 Carbon-13 Carbon-14 ...
400 Chem periodic table
... energy level, the higher nuclear charge (from the additional protons in the nucleus) attracts the all of outer electrons more strongly. Thus the energy required to remove an electron becomes larger across the period (left to right). ...
... energy level, the higher nuclear charge (from the additional protons in the nucleus) attracts the all of outer electrons more strongly. Thus the energy required to remove an electron becomes larger across the period (left to right). ...
MatterPP4
... What are elements? On Earth, matter usually can be found as a solid, liquid, or gas. ...
... What are elements? On Earth, matter usually can be found as a solid, liquid, or gas. ...
Slide 1
... Atoms of the same element are identical Can combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another by a chemical reaction ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical Can combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another by a chemical reaction ...
In 1908 Ernest Rutherford fired a stream of positively
... From his information, Rutherford proposed that an atom had a small, dense, positively charged center that he named the nucleus. ...
... From his information, Rutherford proposed that an atom had a small, dense, positively charged center that he named the nucleus. ...
Me, Myself, I, Chlorine BY: Ethan. BP:2
... family is called the halogen family. I was named after the greek word for greenish yellowish witch is chloros. I’m a guy who likes to attach to thing and never let go. Its all because I'm missing something that I really want a electron. You see I only have 17 but I think 18 would really suit me bett ...
... family is called the halogen family. I was named after the greek word for greenish yellowish witch is chloros. I’m a guy who likes to attach to thing and never let go. Its all because I'm missing something that I really want a electron. You see I only have 17 but I think 18 would really suit me bett ...
Atomic Structure Scientists
... • Compounds consist of atoms of different elements combined together. • Compounds have constant composition because they contain a fixed ratio of atoms. • Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of combinations of those atoms. ...
... • Compounds consist of atoms of different elements combined together. • Compounds have constant composition because they contain a fixed ratio of atoms. • Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of combinations of those atoms. ...
Chapter 12 The Periodic Table
... The mass of individual atoms is so small that the numbers are difficult to work with. To make calculations easier, scientists use the atomic mass unit (amu). The atomic mass of any element is the average mass (in amu) of an atom of each element. ...
... The mass of individual atoms is so small that the numbers are difficult to work with. To make calculations easier, scientists use the atomic mass unit (amu). The atomic mass of any element is the average mass (in amu) of an atom of each element. ...
Nature of Matter
... that consists entirely of one type of atom. -Over 100 elements are known, but only about 24 are found in living organisms. -Elements are represented by symbols, Ex : C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, etc. -An element’s atomic number = # protons in an atom of the element. ...
... that consists entirely of one type of atom. -Over 100 elements are known, but only about 24 are found in living organisms. -Elements are represented by symbols, Ex : C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, etc. -An element’s atomic number = # protons in an atom of the element. ...
Activity 17 Follow-up
... all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
... all the known isotopes of the element •The element which appears on the periodic table is the isotope which is most abundant ...
ATOMS
... symbol that tells how many atoms of an element there are in the compound. It means “written below”. • For example: H20 (2 is the subscript) There are 2 atoms of hydrogen (H) and 1 atom of oxygen (O). This makes up 1 molecule of water. ...
... symbol that tells how many atoms of an element there are in the compound. It means “written below”. • For example: H20 (2 is the subscript) There are 2 atoms of hydrogen (H) and 1 atom of oxygen (O). This makes up 1 molecule of water. ...
Test 4
... Calculate the amount of heat lost or gained when there is a temperature change. Calculate the amount of heat lost or gained when the amount of reactant or product is given. Hess’ Law problems = where you add up reactions to get the H of an overall reaction. Heat = (specific heat)(mass)T T = Tfina ...
... Calculate the amount of heat lost or gained when there is a temperature change. Calculate the amount of heat lost or gained when the amount of reactant or product is given. Hess’ Law problems = where you add up reactions to get the H of an overall reaction. Heat = (specific heat)(mass)T T = Tfina ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
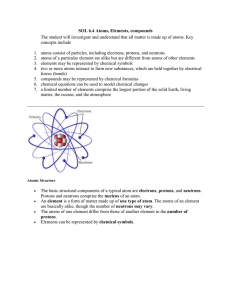
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Periodic Trends Name: Part 1: Summary of the Periodic Trends
... 8. In the following pairs of elements, which one has the larger atomic radius? a. Cs or Fr b. Sn or Pb c. Ag or Cd 9. In the following pairs of elements, which one has the larger 1st ionization energy? a. Cs or Ba b. Sb or Bi c. Au or Hg ...
... 8. In the following pairs of elements, which one has the larger atomic radius? a. Cs or Fr b. Sn or Pb c. Ag or Cd 9. In the following pairs of elements, which one has the larger 1st ionization energy? a. Cs or Ba b. Sb or Bi c. Au or Hg ...
Unit #3 - Wikispaces
... 9) Rutherford's Atomic Theorya) Ernest Rutherford (1871 - 1937 = 66 yrs. old). English physicist. b) Rutherford's experiment concluded that most of the atom must consist of space without the nucleus. The nucleus must occupy a very, very, small portion of the volume of an atom. This nucleus contains ...
... 9) Rutherford's Atomic Theorya) Ernest Rutherford (1871 - 1937 = 66 yrs. old). English physicist. b) Rutherford's experiment concluded that most of the atom must consist of space without the nucleus. The nucleus must occupy a very, very, small portion of the volume of an atom. This nucleus contains ...
Elements PPT
... and we’re not making any more elements Where they are located in the system effects the system, how do we get the stuff we need and how do we ensure that we have enough. ...
... and we’re not making any more elements Where they are located in the system effects the system, how do we get the stuff we need and how do we ensure that we have enough. ...
Atomic Number, Mass Number, and Isotopes
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
... ATOMS: All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons: the number of protons determines the identity of the atom. For example, a carbon atom always has six protons. If it has seven protons, it’s nitrogen, not carbon. The number of protons is called the atomic number (Z). ISOTOPES: Alt ...
Physical Science
... History of the Periodic Table The periodic table was discovered by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 1800s. He arranged the elements in order by their atomic masses. The first periodic table was written on paper!! p.554 In 1913, Henry Moseley rearranged the periodic table by their atomic numbers instead ...
... History of the Periodic Table The periodic table was discovered by Dmitri Mendeleev in the late 1800s. He arranged the elements in order by their atomic masses. The first periodic table was written on paper!! p.554 In 1913, Henry Moseley rearranged the periodic table by their atomic numbers instead ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... Mass number (A) = # protons + # neutrons Atomic number (Z) = # protons ...
... Mass number (A) = # protons + # neutrons Atomic number (Z) = # protons ...
Lecture 2
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...