Unit #3 Atoms / Atomic Structure / Subatomic Particles
... atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
unit plan template
... Identify the names and symbols of common elements. Identify quarks as subatomic particles of matter. Describe the electron cloud model of the atom. Explain how electrons are arranged in an atom. Compute the atomic mass and mass number of an atom. Identify the components of isotopes. In ...
... Identify the names and symbols of common elements. Identify quarks as subatomic particles of matter. Describe the electron cloud model of the atom. Explain how electrons are arranged in an atom. Compute the atomic mass and mass number of an atom. Identify the components of isotopes. In ...
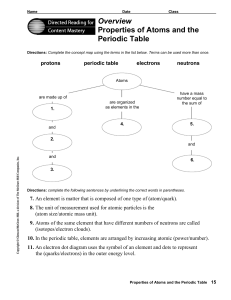
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
3. atomic structure
... nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
... nucleus where an electron is most likely to be found (probability of location) The exact path of an electron in this area is not known ...
Radioisotopes
... • Isotopes are any of the different types of atoms (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have di ...
... • Isotopes are any of the different types of atoms (Nuclides) of the same chemical element, each having a different atomic mass (mass number) • Isotopes of an element have nuclei with the same number of protons (the same atomic number) but different numbers of neutrons. • Therefore, isotopes have di ...
Introduction to the Atom PPT - all things chemistry with dr. cody
... Law of Constant Proportions ...
... Law of Constant Proportions ...
File - Mrs. Hale`s Science
... Cannot be grouped in a family because chemical properties very different from other elements Make up more than 90% of atoms in the universe Only makes up 1% of Earth’s mass Rarely found on Earth as pure element ~mostly combine with oxygen as wate ...
... Cannot be grouped in a family because chemical properties very different from other elements Make up more than 90% of atoms in the universe Only makes up 1% of Earth’s mass Rarely found on Earth as pure element ~mostly combine with oxygen as wate ...
GCSE Chemistry coursework: Research Study on `Francium and the
... model says that an atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that have circular orbits around the nucleus. This model was inspired by the workings of the solar system and says that electrons are kept attracted to the nucleus by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. [9] ...
... model says that an atom has a positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that have circular orbits around the nucleus. This model was inspired by the workings of the solar system and says that electrons are kept attracted to the nucleus by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. [9] ...
Lecture 1: Basic Concepts: Atoms and Bonding
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in mass. For example, 87Sr and 86Sr or 238U and 235U. Isotopes have similar chemical characteristics and are studied using a mass spectrograph or spectrometer. Most elements have at least two naturally occurring isotopes. • Isobars are nuclides ...
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in mass. For example, 87Sr and 86Sr or 238U and 235U. Isotopes have similar chemical characteristics and are studied using a mass spectrograph or spectrometer. Most elements have at least two naturally occurring isotopes. • Isobars are nuclides ...
The Periodic Table Notes
... Arranged by increasing atomic number A vertical column, known as a group contain elements with similar properties ...
... Arranged by increasing atomic number A vertical column, known as a group contain elements with similar properties ...
Chapter 5
... 5.5 Silver occurs as two isotopes with atomic masses 106.9041 amu and 108.9047 amu, respectively. The first isotope represents 51.82% and the second represents 48.18%. Determine the average atomic mass of silver. ...
... 5.5 Silver occurs as two isotopes with atomic masses 106.9041 amu and 108.9047 amu, respectively. The first isotope represents 51.82% and the second represents 48.18%. Determine the average atomic mass of silver. ...
Ch 2 Test Review part 2
... 7. An atom with _____ valence electrons is most stable. a. eight b. two c. four ...
... 7. An atom with _____ valence electrons is most stable. a. eight b. two c. four ...
The Periodic Table
... - As you move down the periodic table you add more space and make the atomic radius larger - As you move from the left to the right there is the same energy level (amount of space) but we add another proton and electron - This makes more attraction between these particles and contracts the atom ...
... - As you move down the periodic table you add more space and make the atomic radius larger - As you move from the left to the right there is the same energy level (amount of space) but we add another proton and electron - This makes more attraction between these particles and contracts the atom ...
History of the Atomic Theory
... Charge of electron 1.592 x 10-19 coulomb Oil drop experiment: suspended an oil drop between two charged plates. ...
... Charge of electron 1.592 x 10-19 coulomb Oil drop experiment: suspended an oil drop between two charged plates. ...
Chapter 4 Review
... atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. An element has an atomic number of 76. What is the number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom of this element? How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? ...
... atoms of the same element have the same _____. Know Dalton’s Atomic Theory. An element has an atomic number of 76. What is the number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom of this element? How is the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom calculated? ...
Worksheet: Development of Atomic Theory
... Short Answer and Fill in the Blanks: 1. What must models and theories do in order to remain valid? a. b. 2. The "gold-foil" experiment had the following results: ____________ of the alpha particles were deflected, ______________ of the alpha particles were reflected, and _____________ of the alpha p ...
... Short Answer and Fill in the Blanks: 1. What must models and theories do in order to remain valid? a. b. 2. The "gold-foil" experiment had the following results: ____________ of the alpha particles were deflected, ______________ of the alpha particles were reflected, and _____________ of the alpha p ...
Structure of Atoms Study Guide
... 7. An atom has 17 protons. Which atom is it? (Hint, use the periodic table on page 154 in the Intro to Matter book). How many electrons does it have? ...
... 7. An atom has 17 protons. Which atom is it? (Hint, use the periodic table on page 154 in the Intro to Matter book). How many electrons does it have? ...
Periodic TABLE: Tables: PT, Table S
... group have the same number of valence electrons (helium is an exception) and therefore similar chemical properties. 3.1aaThe succession of elements within the same group demonstrates characteristic trends: differences in atomic radius, ionic radius, electronegativity, first ionization energy, metall ...
... group have the same number of valence electrons (helium is an exception) and therefore similar chemical properties. 3.1aaThe succession of elements within the same group demonstrates characteristic trends: differences in atomic radius, ionic radius, electronegativity, first ionization energy, metall ...
Name
... 16. Where are the metallic elements located on the periodic table? Are there more elements which are considered metallic or non-metallic? ...
... 16. Where are the metallic elements located on the periodic table? Are there more elements which are considered metallic or non-metallic? ...
10-2 Intensive Chemistry Review for Chapters 3
... transition metals, main group elements, metalloids, active metals, non-metals, rare earth metals, alkali metals, halogens, noble gases, alkaline earth metals, hydrogen. 25. Why is hydrogen often considered to be in a family by itself? 26. List several common characteristics of metals, compared to no ...
... transition metals, main group elements, metalloids, active metals, non-metals, rare earth metals, alkali metals, halogens, noble gases, alkaline earth metals, hydrogen. 25. Why is hydrogen often considered to be in a family by itself? 26. List several common characteristics of metals, compared to no ...
Unit 3 Note Outline
... The stability of a nucleus depends on its neutron-to-proton ratio. Elements with atomic #s less than ...
... The stability of a nucleus depends on its neutron-to-proton ratio. Elements with atomic #s less than ...
J.J. Thomson and the Cathode Ray Tube 1897
... • Electrons have orbits about the nucleus (planetary theory) • Electrons could only exist at given energy levels • An energy level is where an electron is likely to be moving • Energy levels were like steps on a ladder – An electron can only be at any given step at any given time ...
... • Electrons have orbits about the nucleus (planetary theory) • Electrons could only exist at given energy levels • An energy level is where an electron is likely to be moving • Energy levels were like steps on a ladder – An electron can only be at any given step at any given time ...
Chapter 4 Review “Atomic Structure
... atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. What does the number 84 represent in the name krypton-84? ...
... atoms are neutral, with the number of protons equaling the ___. Isotopes of the same element have different _____. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in 16O. What does the number 84 represent in the name krypton-84? ...