CHAPTER 3, ATOMS: THE BUILDING BLOCKS OF MATTER
... Protons, neutrons, and electrons are often referred to as subatomic particles. Discovery of the Electron: 1897 by Joseph John Thomson via cathode-ray experiments The nuclear force is short-range proton-neutron, proton-proton, neutron-neutron force that holds nuclear particles together. ...
... Protons, neutrons, and electrons are often referred to as subatomic particles. Discovery of the Electron: 1897 by Joseph John Thomson via cathode-ray experiments The nuclear force is short-range proton-neutron, proton-proton, neutron-neutron force that holds nuclear particles together. ...
Unit2StudyGuide
... Which two particles have the same mass? What particles make up the nucleus? What particles are NOT in the nucleus? What particles make up the atomic mass? What particles have insignificant mass, but take up most of the space of an atom? Atoms of the same element but have a different mass are _______ ...
... Which two particles have the same mass? What particles make up the nucleus? What particles are NOT in the nucleus? What particles make up the atomic mass? What particles have insignificant mass, but take up most of the space of an atom? Atoms of the same element but have a different mass are _______ ...
5.1 Matter and Atoms
... The atomic mass – the avg. of an elements isotopes. Isotopes – When an element has a different # of neutrons than another atom of the same element. Mass Number – The sum of the protons and neutrons ...
... The atomic mass – the avg. of an elements isotopes. Isotopes – When an element has a different # of neutrons than another atom of the same element. Mass Number – The sum of the protons and neutrons ...
Basic Atomic Theory
... • The energy is therefore “quantized” – Only certain orbits with certain radii are possible – Orbits in between discrete value not possible ...
... • The energy is therefore “quantized” – Only certain orbits with certain radii are possible – Orbits in between discrete value not possible ...
Chapter Test on 4, 5 2016-2017 _____1. You ar
... 25. In a solution, the part that does the dissolving is called the ___________________ 26. In a solution, the part that gets dissolved is called the ________________________ 27. A mixture where the parts will settle after a while is a ______________________ 28. The atomic mass unit (amu) is the mass ...
... 25. In a solution, the part that does the dissolving is called the ___________________ 26. In a solution, the part that gets dissolved is called the ________________________ 27. A mixture where the parts will settle after a while is a ______________________ 28. The atomic mass unit (amu) is the mass ...
Atomic Structure - Chemistry-MYP
... • “Father of modern science” • Theorized that everything was composed of “atoms” which are indivisible and indestructible. • There are an infinite number of atoms and kinds of atoms. ...
... • “Father of modern science” • Theorized that everything was composed of “atoms” which are indivisible and indestructible. • There are an infinite number of atoms and kinds of atoms. ...
Review 2 - Solutions - Mayfield City Schools
... combine into compounds, they just change places. Dalton Who proposed the model of that atom that was like bread with raisins (electrons) stuck in it? - Thompson Who used light to figure out that atoms have distinct orbits? - Bohr ...
... combine into compounds, they just change places. Dalton Who proposed the model of that atom that was like bread with raisins (electrons) stuck in it? - Thompson Who used light to figure out that atoms have distinct orbits? - Bohr ...
The periodic table is the most significant tool that chemist use for
... Atomic size - The atomic radius increases going down a group. This can be explain by adding more and more energy level. As one moves left to right within a period , the radii of the atoms decrease. As more and more protons are added to the nucleus, the nuclear charge of the elements increases. This ...
... Atomic size - The atomic radius increases going down a group. This can be explain by adding more and more energy level. As one moves left to right within a period , the radii of the atoms decrease. As more and more protons are added to the nucleus, the nuclear charge of the elements increases. This ...
Periodic Table - Buford High School Chemistry
... Nonmetal of the second period and group 4A. The noble gas in period 3. This element has two more protons than phosphorus. The only nonmetal in group 1A. Metal in period 7 with two valence electrons. The element whose electron configuration ends with 3p1. The nonreactive element consisting of 4 energ ...
... Nonmetal of the second period and group 4A. The noble gas in period 3. This element has two more protons than phosphorus. The only nonmetal in group 1A. Metal in period 7 with two valence electrons. The element whose electron configuration ends with 3p1. The nonreactive element consisting of 4 energ ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... Studied radioactivity and figured out that the Becquerel rays were coming from atoms that were disintegrating. She coined the term, radioactivity. ...
... Studied radioactivity and figured out that the Becquerel rays were coming from atoms that were disintegrating. She coined the term, radioactivity. ...
Big History Chemistry Study Guide File
... mass and releasing energy in the process. 8. In nuclear _____________, radioactive elements such as ________________ break apart into smaller elements (“decay products”), also releasing energy. 9. The significance of Henry ___________________’s experiment with x-rays and atoms is that it found a num ...
... mass and releasing energy in the process. 8. In nuclear _____________, radioactive elements such as ________________ break apart into smaller elements (“decay products”), also releasing energy. 9. The significance of Henry ___________________’s experiment with x-rays and atoms is that it found a num ...
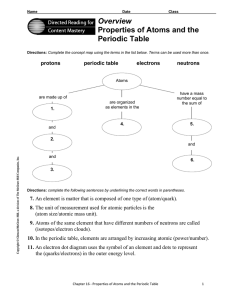
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
... 8. The unit of measurement used for atomic particles is the (atom size/atomic mass unit). 9. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called (isotopes/electron clouds). 10. In the periodic table, elements are arranged by increasing atomic (power/number). 11. An electron ...
Chapter 4: Atomic Structure
... smallest pieces we can. Eventually we will get to a particle that cannot be cut any further and still retain its physical properties. This would be one atom of lead ...
... smallest pieces we can. Eventually we will get to a particle that cannot be cut any further and still retain its physical properties. This would be one atom of lead ...
Chem 200 Dr. Saidane
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
... a) The Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that mass is neither destroyed nor created during ordinary chemical reactions. b) The Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by mass regardless of the size of the s ...
SCH3U Course Review
... increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
... increase with increasing atomic radii decrease with increasing nuclear charge decrease across a period from left to right increase across a period from left to right increase as you go down a family ...
Name Period
... 6. What does the atomic mass tell about the element above (silver)? 7. In what order did Mendeleev arrange the elements in the periodic table? (LOOK UP in text) 8. What can you predict about an element from its position in the periodic table? (other than atomic mass and atomic number) Vocabulary Fro ...
... 6. What does the atomic mass tell about the element above (silver)? 7. In what order did Mendeleev arrange the elements in the periodic table? (LOOK UP in text) 8. What can you predict about an element from its position in the periodic table? (other than atomic mass and atomic number) Vocabulary Fro ...
Atomic Structure - Peoria Public Schools
... Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and trans-uranium elements ...
... Ernest Rutherford: Existence of the nucleus, and its relative size Meitner & Fermi: Sustained nuclear fission Ernest Lawrence: The cyclotron and trans-uranium elements ...
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
Chapter 2 part 1
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...
... • Molecules form when two or more atoms bond together (example: O2) • Compounds form when two or more different elements bond together (H2O) • When a chemical reaction occurs, energy may be given off or absorbed. ...