CHE111-2 Atoms Molecules Ions
... Since molecules are too small for us to observe directly, we can use molecular models to observe them physically. In balland-stick models the atoms are represented by plastic or wooden balls with holes in them. Sticks or springs are used to represent chemical bonds. The angles of these bonds approx ...
... Since molecules are too small for us to observe directly, we can use molecular models to observe them physically. In balland-stick models the atoms are represented by plastic or wooden balls with holes in them. Sticks or springs are used to represent chemical bonds. The angles of these bonds approx ...
bond
... electron arrangement is the number of orbitals used by the central atom. Construct hybrid orbitals from atomic orbitals using the same number of atomic orbitals as hybrid orbitals required. Start with the s-orbital, then add p- and d-orbitals as needed to create the patterns listed in Table 9.5. Use ...
... electron arrangement is the number of orbitals used by the central atom. Construct hybrid orbitals from atomic orbitals using the same number of atomic orbitals as hybrid orbitals required. Start with the s-orbital, then add p- and d-orbitals as needed to create the patterns listed in Table 9.5. Use ...
ionic compound
... electrons in the orbits around the nucleus. A Fluorine atom (F: atomic # of 9) has 9 protons therefore 9 electrons in the orbits around the nucleus. ...
... electrons in the orbits around the nucleus. A Fluorine atom (F: atomic # of 9) has 9 protons therefore 9 electrons in the orbits around the nucleus. ...
How to Determine the Molecular Geometry for a Compound
... DO NOT count Lone Pair electrons on the atoms which are connected to the central atom. ONLY the lone pairs of electrons on the central atom count as E’s. 3. The total number of X’s and E’s determine the ELECTRON PAIR geometry. (There are only 5 basic electron pair geometries) ...
... DO NOT count Lone Pair electrons on the atoms which are connected to the central atom. ONLY the lone pairs of electrons on the central atom count as E’s. 3. The total number of X’s and E’s determine the ELECTRON PAIR geometry. (There are only 5 basic electron pair geometries) ...
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... Energy is quantized. Emission is due to specific transitions between ground and excited states. 18. Refer to the activity series in chapter 10. For the single replacement reactions below, write the half reactions. Label the reducing and oxidizing agents. Show the net ionic equation. If no reaction o ...
... Energy is quantized. Emission is due to specific transitions between ground and excited states. 18. Refer to the activity series in chapter 10. For the single replacement reactions below, write the half reactions. Label the reducing and oxidizing agents. Show the net ionic equation. If no reaction o ...
The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
... The topic that fascinated me the most in my Science lessons this year is the Periodic Table and its power of predicting the existence and properties of elements yet to be discovered. Dimitri Mendeleev placed the 65 known elements of his time into a grid table and observed gaps in the table. Based on ...
ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONS
... Recall that an element consists of atoms which have the same number of protons, and therefore, the same Atomic Number. Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. ...
... Recall that an element consists of atoms which have the same number of protons, and therefore, the same Atomic Number. Chemical properties of elements depend on the atomic number of the element. A complete Periodic Table lists the elements, their symbols and atomic numbers as well as atomic masses. ...
Tying some loose ends and introducing some new ones.
... located on the central atom are not necessarily “pure” atomic orbitals. Bonds involving elements in the second or higher row in the periodic table involve combinations of atomic orbitals that form “hybrid” orbitals as the bonds are being made. ...
... located on the central atom are not necessarily “pure” atomic orbitals. Bonds involving elements in the second or higher row in the periodic table involve combinations of atomic orbitals that form “hybrid” orbitals as the bonds are being made. ...
Molecular Orbital Theory
... • Suppose a male firefly is in a dark room with an open vial of female sex-attractant hormones. If we set up a camera to take pictures every time the firefly flashes and records the firefly’s location in the room we will find that most of it’s time is around the female, however, sometimes he flies f ...
... • Suppose a male firefly is in a dark room with an open vial of female sex-attractant hormones. If we set up a camera to take pictures every time the firefly flashes and records the firefly’s location in the room we will find that most of it’s time is around the female, however, sometimes he flies f ...
Module1 for YIC CHEM
... Do sample exercise 2.10 and practice exercise on p-59 Naming the inorganic compounds Inorganic compounds are formed consist of ionic compounds and molecular compounds. We know that ionic compounds are formed when metal ions (positive) and non-metal ions (negative) are combined. Positive Ions (cation ...
... Do sample exercise 2.10 and practice exercise on p-59 Naming the inorganic compounds Inorganic compounds are formed consist of ionic compounds and molecular compounds. We know that ionic compounds are formed when metal ions (positive) and non-metal ions (negative) are combined. Positive Ions (cation ...
General Chemistry
... represents a large charge density. A hydrogen bond results when this strong positive charge density attracts a lone pair of electrons on another heteroatom, which becomes the hydrogen-bond acceptor. The most ubiquitous, and perhaps simplest, example of a hydrogen bond is found between water molecule ...
... represents a large charge density. A hydrogen bond results when this strong positive charge density attracts a lone pair of electrons on another heteroatom, which becomes the hydrogen-bond acceptor. The most ubiquitous, and perhaps simplest, example of a hydrogen bond is found between water molecule ...
Unit 4
... ● Atoms are made up of 3 subatomic particles; protons, neutrons, and electrons. ● The history of atomic development shaped the way scientists have constructed the current model of the atom. ...
... ● Atoms are made up of 3 subatomic particles; protons, neutrons, and electrons. ● The history of atomic development shaped the way scientists have constructed the current model of the atom. ...
T1 Final Study Guide - District 196 e
... *** This study guide is a place to get you started preparing for your final. The final is not limited to only things mentioned on this review, it can be anything we have done over the course of the trimester. We will also be having some review time during class as well. *** ...
... *** This study guide is a place to get you started preparing for your final. The final is not limited to only things mentioned on this review, it can be anything we have done over the course of the trimester. We will also be having some review time during class as well. *** ...
Science Olympiad
... (A) ionization energy decreases due to increases shielding effect. (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ioni ...
... (A) ionization energy decreases due to increases shielding effect. (B) atomic radius decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (C) electronegativity decreases due to an increase in atomic radius. (D) electron affinity decreases due to an increase in effective nuclear charge. (E) ioni ...
Chapter 4 The Structure of Matter
... − (4) the reason why the melting and boiling points of quartz is so high – (a) melting point 1700oC – (b) boiling point 2230oC ...
... − (4) the reason why the melting and boiling points of quartz is so high – (a) melting point 1700oC – (b) boiling point 2230oC ...
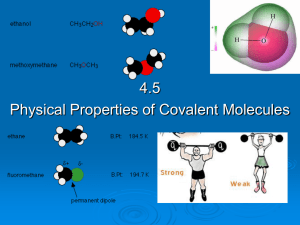
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... Glycerol (HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH) has high and water (H2O) has low viscosity. The more viscous fluid flows more slowly because the intermolecular forces between the molecules are stronger increasing the attraction the molecules have for one another. Viscosity increases with temperature. ...
... Glycerol (HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH) has high and water (H2O) has low viscosity. The more viscous fluid flows more slowly because the intermolecular forces between the molecules are stronger increasing the attraction the molecules have for one another. Viscosity increases with temperature. ...
Exam 3B - TAMU Chemistry
... (3) Each multiple choice question is actually 2 questions on your scanning sheet. If you are sure of an answer, put the same answer down for both questions for 5 pts. If you cannot decide between two answers, put your best answer down for the first (odd) question and the other answer down for the se ...
... (3) Each multiple choice question is actually 2 questions on your scanning sheet. If you are sure of an answer, put the same answer down for both questions for 5 pts. If you cannot decide between two answers, put your best answer down for the first (odd) question and the other answer down for the se ...
Atoms-Molecules-Ions-office98
... 12 protons; # neutrons = 24 - 12 neutral atom has 12 electrons Ion contains 10 electrons: symbol? ...
... 12 protons; # neutrons = 24 - 12 neutral atom has 12 electrons Ion contains 10 electrons: symbol? ...
chapter-2 - HCC Learning Web
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
... • The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by the distribution of electrons in electron shells • The periodic table of the elements shows the electron distribution for each element ...
CHAPTER 2: THE ATOMS AND MOLECULES OF ANCIENT EARTH
... b. Reduction of CO2 by H2 forms H2CO, which is used as a building block to form organic compounds (compounds containing at least one C–C bond). (Fig. 2.13) B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is k ...
... b. Reduction of CO2 by H2 forms H2CO, which is used as a building block to form organic compounds (compounds containing at least one C–C bond). (Fig. 2.13) B. For carbon to be reduced, early atmosphere must have contained CH 4, H2, and NH3 (molecules that can give up electrons). 1. Volcanic ash is k ...
Elements, mixtures and compounds lecture
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
30.09.2013 1 Chapter 2 Atoms and Molecules Warning!! Chapter
... • Ions with more protons than electrons are called cations. • net positive charge • Ions with more electrons that protons are called anions. • net negative charge • A monatomic ion is derived from a single atom. • A polyatomic ion is derived from a group of atoms with an overall charge. ...
... • Ions with more protons than electrons are called cations. • net positive charge • Ions with more electrons that protons are called anions. • net negative charge • A monatomic ion is derived from a single atom. • A polyatomic ion is derived from a group of atoms with an overall charge. ...