Chemistry of Life - Kania´s Science Page
... **If they have to choose, atoms would rather be stable (with a full “octet”) than neutral. ...
... **If they have to choose, atoms would rather be stable (with a full “octet”) than neutral. ...
Lecture Ch#9 Bonding - Seattle Central College
... that are then available to overlap and form covalent bonds with other atoms. • A hybrid atomic orbital is one of a set of equivalent orbitals about an atom created when specific atomic orbitals are mixed. ...
... that are then available to overlap and form covalent bonds with other atoms. • A hybrid atomic orbital is one of a set of equivalent orbitals about an atom created when specific atomic orbitals are mixed. ...
Summer Work
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
... 3. The number of protons in one atom of an element determines the atom’s __________________ , and the number of electrons determines ___________________ of an element. 4. The atomic number tells you the number of ______________________ in one atom of an element. It also tells you the number of _____ ...
chapters 1-4
... H and He most abundant in space, O and Si in earth crust, O and C in human bodies. Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
... H and He most abundant in space, O and Si in earth crust, O and C in human bodies. Atom – smallest building block; molecule – combination of two or more atoms. Can be an element or compound. ...
Final Exam Review Answers
... • In the periodic table, there is a periodic pattern in the physical and chemical properties of elements when they are arranged in order of • a. increasing atomic mass. • b. increasing electronegativity. • c. increasing atomic radius. • d. increasing atomic number. d. ...
... • In the periodic table, there is a periodic pattern in the physical and chemical properties of elements when they are arranged in order of • a. increasing atomic mass. • b. increasing electronegativity. • c. increasing atomic radius. • d. increasing atomic number. d. ...
Ch. 02 - HCC Learning Web
... Elements and Compounds • Matter is made up of elements • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elemen ...
... Elements and Compounds • Matter is made up of elements • An element is a substance that cannot be broken down to other substances by chemical reactions • A compound is a substance consisting of two or more elements in a fixed ratio • A compound has characteristics different from those of its elemen ...
Structure and Bonding
... Predicting the Structures of Simple Molecules from Their Formulas Commonly used in biology as a tissue preservative, formaldehyde, CH2O, contains a carbon-oxygen double bond. Draw the linebond structure of formaldehyde, and indicate the hybridization of the carbon atom. ...
... Predicting the Structures of Simple Molecules from Their Formulas Commonly used in biology as a tissue preservative, formaldehyde, CH2O, contains a carbon-oxygen double bond. Draw the linebond structure of formaldehyde, and indicate the hybridization of the carbon atom. ...
Packet
... d. all of the above. ____ 92. The diffusion of a gas is its tendency to a. move through other gases b. move away from other gases c. decompose d. do nothing ____ 93. According to kinetic molecular theory, a. the gas molecules themselves have a volume of zero. b. the gas molecules exert no attractive ...
... d. all of the above. ____ 92. The diffusion of a gas is its tendency to a. move through other gases b. move away from other gases c. decompose d. do nothing ____ 93. According to kinetic molecular theory, a. the gas molecules themselves have a volume of zero. b. the gas molecules exert no attractive ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... a. Number of atoms bonded to the central atom = 2. b. The molecule has a bond angle of 180O. c. It has a basic molecular formula of: AB2 (“A” is one element; “B” is the other element) For example: Be F2 2. Trigonal-Planer (3 point pyramid in one plane “flat”) a. Number of atoms bonded to the central ...
... a. Number of atoms bonded to the central atom = 2. b. The molecule has a bond angle of 180O. c. It has a basic molecular formula of: AB2 (“A” is one element; “B” is the other element) For example: Be F2 2. Trigonal-Planer (3 point pyramid in one plane “flat”) a. Number of atoms bonded to the central ...
(1) Dissolves, accompanied by evolution of flammable gas (2
... slowly and carefully to water Using models of chemical bonding and atomic or molecular structure, account for the differences in conductivity between the two samples in each of the following pairs. (a) Sucrose solution and silver nitrate solution (b) Solid silver nitrate and solid sodium metal (c) L ...
... slowly and carefully to water Using models of chemical bonding and atomic or molecular structure, account for the differences in conductivity between the two samples in each of the following pairs. (a) Sucrose solution and silver nitrate solution (b) Solid silver nitrate and solid sodium metal (c) L ...
Specific Objectives:
... 1. Explain the concept of quantized energy and its relationship to Classical and Quantum physics. 2. Explain and use Bohr's ideas of quantized energy levels (orbits) for electrons in atoms and relate this idea to the principal quantum number - n (shells) for an electron in an atom. 3. Discuss the pr ...
... 1. Explain the concept of quantized energy and its relationship to Classical and Quantum physics. 2. Explain and use Bohr's ideas of quantized energy levels (orbits) for electrons in atoms and relate this idea to the principal quantum number - n (shells) for an electron in an atom. 3. Discuss the pr ...
Theories of Covalent Bonding
... C and O are fairly similar in terms of electronegativity, with O more electronegative than C, so we saw some distortion but not a lot. What happens when the electronegativities are extremely different? HF ...
... C and O are fairly similar in terms of electronegativity, with O more electronegative than C, so we saw some distortion but not a lot. What happens when the electronegativities are extremely different? HF ...
Atomic Structure and Source of Charge Classwork 1. Which particle
... 1. Which particle of an atom carries a positive charge? Which carries the negative charge? 2. When a neutral atom captures a free electron, what is the net charge on the atom? What do we call this type of atom? 3. What is most of the atom composed of? 4. Is it possible to add 0.5e of charge to an ob ...
... 1. Which particle of an atom carries a positive charge? Which carries the negative charge? 2. When a neutral atom captures a free electron, what is the net charge on the atom? What do we call this type of atom? 3. What is most of the atom composed of? 4. Is it possible to add 0.5e of charge to an ob ...
Workshop #4 Answers
... A sample of nickel(II) phosphate, Ni3(PO4)2, weighs 114 g. How many moles are in this sample? 0.311 mol ...
... A sample of nickel(II) phosphate, Ni3(PO4)2, weighs 114 g. How many moles are in this sample? 0.311 mol ...
compound - Coal City Unit #1
... • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
... • most symbols come from their names • some symbols come from Latin or Greek names • some elem. named in honor of person or place they were discovered • ea. elem. has its own unique set of chem. and physical props. ...
Preview Sample 1
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
... 1. List several differences between ionic and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds occur when ions of opposite charge are mutually attracted. Acids and bases are examples of ionic compounds. Covalent bonds are strong chemical bonds that occur when atoms share electrons. Methane and sugar are examples of cova ...
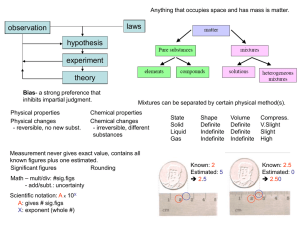
What is Matter?
... structure of its atoms. • The main feature used to distinguish the atoms of different kinds of elements is atomic number. – Atomic Number: the # of PROTONS in the nucleus of an atom. – It’s unique for each element. ...
... structure of its atoms. • The main feature used to distinguish the atoms of different kinds of elements is atomic number. – Atomic Number: the # of PROTONS in the nucleus of an atom. – It’s unique for each element. ...