File
... Niels Bohr (1913): e– can possess only certain amounts of energy, and can therefore be only ...
... Niels Bohr (1913): e– can possess only certain amounts of energy, and can therefore be only ...
File
... their proportion by mass will always be the same. Example: H2O is always made up of 2 atoms of H and one atom of O. The ratio of O to H in water is always 16:2 or ...
... their proportion by mass will always be the same. Example: H2O is always made up of 2 atoms of H and one atom of O. The ratio of O to H in water is always 16:2 or ...
Electron and Molecular Geometries
... ▪ Thus, total no. of electrons surrounding iodine atom is: 7 + 4 + 1 = 12, i.e. in 6 pairs. ▪ Since iodine has 6 pairs of electrons but only 4 bonds, there must be 2 lone pairs as well as 4 bonding pairs. ...
... ▪ Thus, total no. of electrons surrounding iodine atom is: 7 + 4 + 1 = 12, i.e. in 6 pairs. ▪ Since iodine has 6 pairs of electrons but only 4 bonds, there must be 2 lone pairs as well as 4 bonding pairs. ...
Chapter 10 The Periodic Law
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
... 10-7. The Periodic Table The Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev formulated the periodic law about 1869 which states that when elements are listed in order of atomic number, elements with similar chemical and physical properties appear at regular intervals. The periodic table is a listing of the eleme ...
Atomic Theory Practice Test
... ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms results from the attraction between electrons and a. Lewis structures. c. van der Waals forces. b. ...
... ____ 18. The electrons involved in the formation of a chemical bond are called a. dipoles. c. Lewis electrons. b. s electrons. d. valence electrons. ____ 19. In a chemical bond, the link between atoms results from the attraction between electrons and a. Lewis structures. c. van der Waals forces. b. ...
Chemistry Essay - Properties of atoms 21.8Kb
... unknown properties (Hinchlife, 2011, p.14). Elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their atomic structure which is a systematic increasing the number of atoms. The elements display other characteristics and trends that distinguish them from others which is their chemical, physical ...
... unknown properties (Hinchlife, 2011, p.14). Elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their atomic structure which is a systematic increasing the number of atoms. The elements display other characteristics and trends that distinguish them from others which is their chemical, physical ...
Bonding II
... • According to valence bond theory, bonding takes place between atoms when their atomic or hybrid orbitals interact – “overlap” • To interact, the orbitals must either be aligned along the axis between the atoms, or • The orbitals must be parallel to each other and perpendicular to the interatomic a ...
... • According to valence bond theory, bonding takes place between atoms when their atomic or hybrid orbitals interact – “overlap” • To interact, the orbitals must either be aligned along the axis between the atoms, or • The orbitals must be parallel to each other and perpendicular to the interatomic a ...
AP Chemistry Chapter 8 Answers
... For example, consider ClF3 (28 valence electrons): The central Cl atom is surrounded by 5 electron pairs, which requires a trigonal bypyramid geometry. Since there are 3 bonded atoms and 2 lone pairs of electrons about Cl, we describe the molecular structure of ClF3 as T-shaped with predicted bond a ...
... For example, consider ClF3 (28 valence electrons): The central Cl atom is surrounded by 5 electron pairs, which requires a trigonal bypyramid geometry. Since there are 3 bonded atoms and 2 lone pairs of electrons about Cl, we describe the molecular structure of ClF3 as T-shaped with predicted bond a ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... Different elements contain different numbers of subatomic particles Hydrogen has 1 proton, 0 neutrons, and 1 electron Lithium has 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons ...
... Different elements contain different numbers of subatomic particles Hydrogen has 1 proton, 0 neutrons, and 1 electron Lithium has 3 protons, 4 neutrons, and 3 electrons ...
Molecules Interactive - Avon Community School Corporation
... these electrons and completes this octet, or set of eight, by interacting with other atoms. Note: The exception to this is that hydrogen and helium want 2 electrons in the outer shell. • Atoms form chemical bonds in an attempt to fill their outer shells. If an atom already has a full outer shell, it ...
... these electrons and completes this octet, or set of eight, by interacting with other atoms. Note: The exception to this is that hydrogen and helium want 2 electrons in the outer shell. • Atoms form chemical bonds in an attempt to fill their outer shells. If an atom already has a full outer shell, it ...
Carbohydrates
... these electrons and completes this octet, or set of eight, by interacting with other atoms. Note: The exception to this is that hydrogen and helium want 2 electrons in the outer shell. • Atoms form chemical bonds in an attempt to fill their outer shells. If an atom already has a full outer shell, it ...
... these electrons and completes this octet, or set of eight, by interacting with other atoms. Note: The exception to this is that hydrogen and helium want 2 electrons in the outer shell. • Atoms form chemical bonds in an attempt to fill their outer shells. If an atom already has a full outer shell, it ...
Chemistry NYOS Dr. McPhee December 2015 Learning Objectives
... Draw partial charges correctly for a polar covalent bond List the three most important inter-molecular forces (IMFs) Identify if a molecule is capable of forming a hydrogen bond Identify from a Lewis structure if a molecule participates in dipole-dipole interactions Explain the origin of the London ...
... Draw partial charges correctly for a polar covalent bond List the three most important inter-molecular forces (IMFs) Identify if a molecule is capable of forming a hydrogen bond Identify from a Lewis structure if a molecule participates in dipole-dipole interactions Explain the origin of the London ...
Bonding and Molecular Structure - PART 1
... bond angles associated with it that you must memorize (see Table 9.1). These “ideal” bond angles may be distorted by certain conditions as ...
... bond angles associated with it that you must memorize (see Table 9.1). These “ideal” bond angles may be distorted by certain conditions as ...
Unit 2
... 60. A chemical bond resulting from the sharing of electrons between two atoms is called a(n) _____ A. Lewis structure. B. ionic bond. C. orbital bond. D. covalent bond. 61. The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as _ A. ions. B. e ...
... 60. A chemical bond resulting from the sharing of electrons between two atoms is called a(n) _____ A. Lewis structure. B. ionic bond. C. orbital bond. D. covalent bond. 61. The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as _ A. ions. B. e ...
A = 27
... #32) Al+3 has lost 3 electrons (each + charge represents a lost electron). The neutral atom has 13 protons, thus there are 13 electrons in the neutral atom. If three e- were lost 10, are remaining. ANS-4 #33 The excited state must have the same # of electrons as the neutral atom, however one or more ...
... #32) Al+3 has lost 3 electrons (each + charge represents a lost electron). The neutral atom has 13 protons, thus there are 13 electrons in the neutral atom. If three e- were lost 10, are remaining. ANS-4 #33 The excited state must have the same # of electrons as the neutral atom, however one or more ...
The periodic table
... • Valence shell = The outermost shell of e- . • The first e- orbital only holds 2. • All of the others we will consider hold UP TO 8. • (There are energy levels that hold more than 8 e- , but you’ll get to that in chemistry). ...
... • Valence shell = The outermost shell of e- . • The first e- orbital only holds 2. • All of the others we will consider hold UP TO 8. • (There are energy levels that hold more than 8 e- , but you’ll get to that in chemistry). ...
Fundamentals Fall Final Review
... 20. Isotopes of a given element have the same number of __________, but different number of ____________. 21. Know how to calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom when given its isotope mass and atomic number. As an example: Iron (Fe) has an atomic number of 26. An isotope ...
... 20. Isotopes of a given element have the same number of __________, but different number of ____________. 21. Know how to calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom when given its isotope mass and atomic number. As an example: Iron (Fe) has an atomic number of 26. An isotope ...
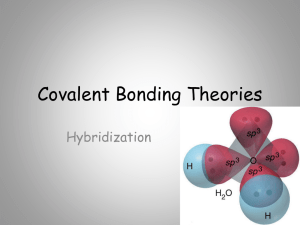
AP HYBRIDIZATION
... orbitals for bonding is called hybridization. These four new orbitals are called sp3 orbitals because they are formed from one 2s and three 2p orbitals (how clever). We say that the carbon atom undergoes sp3 hybridization or is sp3 hybridized. In fact, whenever the electron geometry is tetrahedral, ...
... orbitals for bonding is called hybridization. These four new orbitals are called sp3 orbitals because they are formed from one 2s and three 2p orbitals (how clever). We say that the carbon atom undergoes sp3 hybridization or is sp3 hybridized. In fact, whenever the electron geometry is tetrahedral, ...
Electrons - biospaces
... explanations called hypotheses. Deductive logic is used to make predictions. Experiments are designed to test the predictions. Controlled experiments manipulate the variable that is predicted to cause differences between groups. ...
... explanations called hypotheses. Deductive logic is used to make predictions. Experiments are designed to test the predictions. Controlled experiments manipulate the variable that is predicted to cause differences between groups. ...
CHEMONE Directions: Select the letter of the best
... a. space where electrons are unlikely to be found in an atom b. space which may contain electron, protons and/or neutrons c. the space in an atom where an electron is most likely to be found d. small, walled spheres that contain electrons e. a single space within an atom that contains all electrons ...
... a. space where electrons are unlikely to be found in an atom b. space which may contain electron, protons and/or neutrons c. the space in an atom where an electron is most likely to be found d. small, walled spheres that contain electrons e. a single space within an atom that contains all electrons ...