Chapter 2. The Chemical Context of Life
... Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules Weak chemical bonds play important roles in chemistry of life A molecule’s biological function is related to its ...
... Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form molecules Weak chemical bonds play important roles in chemistry of life A molecule’s biological function is related to its ...
Chemistry I Final Review
... 14. Carbon-14 has a half life of 5700 years. How long will it take for a sample which contains 100. g of carbon -14 to decay to 12.5 g. ...
... 14. Carbon-14 has a half life of 5700 years. How long will it take for a sample which contains 100. g of carbon -14 to decay to 12.5 g. ...
Introduction to atoms
... __________________________________ _________________________________. – In some cases, an atom is also a molecule. Example: He, Ne, Ar. ...
... __________________________________ _________________________________. – In some cases, an atom is also a molecule. Example: He, Ne, Ar. ...
Atoms and Atomic Structure Learning Targets
... Define and explain what the atomic mass unit of an atom is. Identify the mass of each sub-atomic particle. Identify the electric charge of each sub-atomic particle. Identify the location of each sub-atomic particle in the atom. Describe the nucleus of an atom and what makes it up. Identify how to de ...
... Define and explain what the atomic mass unit of an atom is. Identify the mass of each sub-atomic particle. Identify the electric charge of each sub-atomic particle. Identify the location of each sub-atomic particle in the atom. Describe the nucleus of an atom and what makes it up. Identify how to de ...
MYP 10 PeriodicityWS
... 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (FI). 3.2.3. Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electronega ...
... 3.2.2 Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies, electronegativities and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs) and the halogens (FI). 3.2.3. Describe and explain the trends in atomic radii, ionic radii, first ionization energies and electronega ...
Atomic
... Fatty acids are long chains of CH2 units joined together. The fatty acids in saturated fats do not contain any double bonds between the CH2 units whereas the fatty acids in unsaturated fats contain some carbon-carbon double bonds. Saturated fats are found in butter, cheese, chocolate, beef, and coco ...
... Fatty acids are long chains of CH2 units joined together. The fatty acids in saturated fats do not contain any double bonds between the CH2 units whereas the fatty acids in unsaturated fats contain some carbon-carbon double bonds. Saturated fats are found in butter, cheese, chocolate, beef, and coco ...
Compound Name
... Bohr Diagrams (for first 20 elements) – orbitals/energy shells Lewis Diagrams (all Representative Elements) – valence electrons represented; ...
... Bohr Diagrams (for first 20 elements) – orbitals/energy shells Lewis Diagrams (all Representative Elements) – valence electrons represented; ...
Molecular Geometry VSEPR Theory
... Draw the electron dot structure Determine how many “things” and also the shape based on “things”? ...
... Draw the electron dot structure Determine how many “things” and also the shape based on “things”? ...
1 Atomic Mass
... Elements towards the right (anionic-like) of the periodic table substitutes the second half of its elemental name with ide. ...
... Elements towards the right (anionic-like) of the periodic table substitutes the second half of its elemental name with ide. ...
Hybridization and MO Theory PPT
... orbitals exist, the atomic orbitals are gone MO1 is lower in energy than the 1s orbitals they came from. ...
... orbitals exist, the atomic orbitals are gone MO1 is lower in energy than the 1s orbitals they came from. ...
Chapter-2-Human-Chemistry
... Energy “Currency” – Body’s energy carrier Supplier of energy for many of body’s reactions ...
... Energy “Currency” – Body’s energy carrier Supplier of energy for many of body’s reactions ...
Outline
... B. Balanced by atoms AND charge AND mass 1. Coefficients 2. implied “1” if nothing written a. like you to write it anyway for now 3. lowest whole number ratio C. How to balance 1. method on p137 or… 2. another way a. find biggest, ugliest molecule b. put a “1” down as its coefficient c. work your wa ...
... B. Balanced by atoms AND charge AND mass 1. Coefficients 2. implied “1” if nothing written a. like you to write it anyway for now 3. lowest whole number ratio C. How to balance 1. method on p137 or… 2. another way a. find biggest, ugliest molecule b. put a “1” down as its coefficient c. work your wa ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... Covalent Bonds • A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms • In a covalent bond, the shared electrons count as part of each atom’s valence shell – A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds – A single covalent bond, or single bond, is t ...
... Covalent Bonds • A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms • In a covalent bond, the shared electrons count as part of each atom’s valence shell – A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds – A single covalent bond, or single bond, is t ...
Chemistry of Life
... • Enzymes provide a site where the reactants can be brought together. • The reactants of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are known as Substrates. • The site in which the substrate binds on the enzyme is called the Active Site. • The enzyme remains UNCHANGED after a reaction. This allows one enzyme to c ...
... • Enzymes provide a site where the reactants can be brought together. • The reactants of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction are known as Substrates. • The site in which the substrate binds on the enzyme is called the Active Site. • The enzyme remains UNCHANGED after a reaction. This allows one enzyme to c ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide_S2014
... 30. Explain the main idea of the VSEPR Theory 31. For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis structure, name the number of lone and bond pairs, and give the name of the shape. a. BeCl2 b. AlCl3 c. CF4 d. H2O e. NH3 32. For each of the molecules in the previous question, draw the dipole mome ...
... 30. Explain the main idea of the VSEPR Theory 31. For each of the following molecules, draw the Lewis structure, name the number of lone and bond pairs, and give the name of the shape. a. BeCl2 b. AlCl3 c. CF4 d. H2O e. NH3 32. For each of the molecules in the previous question, draw the dipole mome ...
Atoms in Combination: The Chemical Bond
... Calcium and chlorine neutral-atom electron configurations (left), and their configurations after electrons have been transferred from the calcium to the chlorine atoms (right). ...
... Calcium and chlorine neutral-atom electron configurations (left), and their configurations after electrons have been transferred from the calcium to the chlorine atoms (right). ...
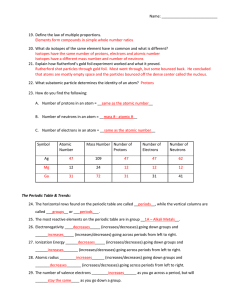
19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of n ...
... 19. Define the law of multiple proportions. Elements form compounds in simple whole number ratios 20. What do isotopes of the same element have in common and what is different? Isotopes have the same number of protons, electrons and atomic number Isotopes have a different mass number and number of n ...
Review Sheet for Chemistry* First Semester Final
... Na+ with OH– ___________ NH4+ with PO43– ______________ magnesium oxide____________ ...
... Na+ with OH– ___________ NH4+ with PO43– ______________ magnesium oxide____________ ...