p-Block Elements, Part 1
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
The Chemical Earth
... separate atoms joined by a covalent bond is referred to as the bond energy. Ionic bonds are formed by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charge ions. The energy required to break ionic bonds is referred to as the lattice energy. ...
... separate atoms joined by a covalent bond is referred to as the bond energy. Ionic bonds are formed by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charge ions. The energy required to break ionic bonds is referred to as the lattice energy. ...
Resource for Final Exam Prep
... For active metals: metal + water metal hydroxide + H2(g) Metal oxide + water metal hydroxide (aq) [basic solution] metal oxide + acid salt + H2O Nonmetal oxide + water acid (aq) [an acidic solution] Non-metal oxide + base salt + H2O Carbonate or bicarbonate + acid salt + CO2 + H2O Chapte ...
... For active metals: metal + water metal hydroxide + H2(g) Metal oxide + water metal hydroxide (aq) [basic solution] metal oxide + acid salt + H2O Nonmetal oxide + water acid (aq) [an acidic solution] Non-metal oxide + base salt + H2O Carbonate or bicarbonate + acid salt + CO2 + H2O Chapte ...
Na 2 O - s3.amazonaws.com
... 2Na + O2 → 2Na2O Notice that the 2 on the right hand side is "distributed" to both the Na2 and the O. Currently the left hand side of the equation has 2 Na's and 2O's. The right hand side has 4 Na's total and 2 O's. Again, this is a problem, there must be an equal amount of each chemical on both sid ...
... 2Na + O2 → 2Na2O Notice that the 2 on the right hand side is "distributed" to both the Na2 and the O. Currently the left hand side of the equation has 2 Na's and 2O's. The right hand side has 4 Na's total and 2 O's. Again, this is a problem, there must be an equal amount of each chemical on both sid ...
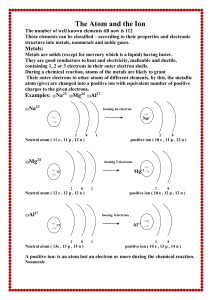
The Atom and the Ion
... The number of well known elements till now is 112 Those elements can be classified – according to their properties and electronic structure into metals, nonmetals and noble gases. ...
... The number of well known elements till now is 112 Those elements can be classified – according to their properties and electronic structure into metals, nonmetals and noble gases. ...
Midterm Review 2017
... 33) Which electron-dot symbol correctly represents an atom of its given element? ...
... 33) Which electron-dot symbol correctly represents an atom of its given element? ...
04 Biochemistry
... • e- like to be in pairs, but fill single e- first before pairing them up. • Octet rule = an atom in 2nd energy level always likes to have 8 e- on the outermost energy level. • When bonds form between two atoms, only the unpaired valence e- from the two atoms pair up. ...
... • e- like to be in pairs, but fill single e- first before pairing them up. • Octet rule = an atom in 2nd energy level always likes to have 8 e- on the outermost energy level. • When bonds form between two atoms, only the unpaired valence e- from the two atoms pair up. ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... The only way to form a compound from elements is by a chemical reaction. Example: Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas react to synthesize water. 2H2 + O2 2H2O The only way to separate a compound into its elements is by a chemical reaction that breaks the chemical bonds, forming new substances. (Example: w ...
... The only way to form a compound from elements is by a chemical reaction. Example: Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas react to synthesize water. 2H2 + O2 2H2O The only way to separate a compound into its elements is by a chemical reaction that breaks the chemical bonds, forming new substances. (Example: w ...
What do we call a substance with more than one kind of atom
... 43. As a nonmetal becomes an ion, its radius _________ 44. The ______________ are the family that contain the most reactive metals. 45. Examine the following electron configuration for element X and use it to answer the questions below 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d2 a. In which period is element X? ...
... 43. As a nonmetal becomes an ion, its radius _________ 44. The ______________ are the family that contain the most reactive metals. 45. Examine the following electron configuration for element X and use it to answer the questions below 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s24d2 a. In which period is element X? ...
Atom
... when two or more atoms share electrons to form a molecule. • If the electrons are shared equally = nonpolar bond. • If electrons are NOT shared equally = polar bond. – Ex. H2O (hydrogen bonds) – Who does it remind you of? ...
... when two or more atoms share electrons to form a molecule. • If the electrons are shared equally = nonpolar bond. • If electrons are NOT shared equally = polar bond. – Ex. H2O (hydrogen bonds) – Who does it remind you of? ...
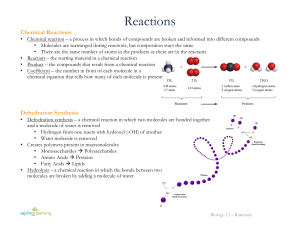
Reactions
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
... • Chemical reaction – a process in which bonds of compounds are broken and reformed into different compounds • Molecules are rearranged during reactions, but composition stays the same • There are the same number of atoms in the products as there are in the reactants • Reactant – the starting materi ...
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding
... b) Draw the Lewis electron dot structure for each atom. (Use the method in which the electrons are spread to all four sides of an imaginary square before being paired.) For the sake of keeping the drawing as neat as possible, direct single electrons on adjacent atoms towards each other. c) Draw a li ...
... b) Draw the Lewis electron dot structure for each atom. (Use the method in which the electrons are spread to all four sides of an imaginary square before being paired.) For the sake of keeping the drawing as neat as possible, direct single electrons on adjacent atoms towards each other. c) Draw a li ...
Unit - III - E
... Steric attraction occurs when molecules have shapes or geometries that are optimized for interaction with one another. In these cases molecules will react with each other most often in specific arrangements. Chain crossing — A random coil can't change from one conformation to a closely related shap ...
... Steric attraction occurs when molecules have shapes or geometries that are optimized for interaction with one another. In these cases molecules will react with each other most often in specific arrangements. Chain crossing — A random coil can't change from one conformation to a closely related shap ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Atomic Theory
... A skeleton equation shows only the formulas of the elements/compounds Shows atoms, but is not balanced K(s) + O2 (g) K2O(s) A balanced chemical equation shows the correct number of each atom Balancing ensures that the number of each atom is the same on both sides of the reaction arrow ...
... A skeleton equation shows only the formulas of the elements/compounds Shows atoms, but is not balanced K(s) + O2 (g) K2O(s) A balanced chemical equation shows the correct number of each atom Balancing ensures that the number of each atom is the same on both sides of the reaction arrow ...
Bonds - Cloudfront.net
... Determining Neutral Compounds When writing a formula it is important to know that the compound is neutral (even thought the individual ions carry a charge) The formula must have the right # of +ions and the right # of –ions so the charges balance Use oxidation numbers or their least common mu ...
... Determining Neutral Compounds When writing a formula it is important to know that the compound is neutral (even thought the individual ions carry a charge) The formula must have the right # of +ions and the right # of –ions so the charges balance Use oxidation numbers or their least common mu ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... 39. Write the electron configuration for the following: a. O b. N3c. Sr d. Mg2+ 40. Define the following trends: a. Atomic radius b. Ion radius c. Electronegativity d. Ionization energy e. 2nd ionization energy 41. What are cations and anions? Which type of elements form each? 42. Write the ions for ...
... 39. Write the electron configuration for the following: a. O b. N3c. Sr d. Mg2+ 40. Define the following trends: a. Atomic radius b. Ion radius c. Electronegativity d. Ionization energy e. 2nd ionization energy 41. What are cations and anions? Which type of elements form each? 42. Write the ions for ...
PowerPoint Template
... the total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction - Antoine Lavoisier (1 743-1 794) The number of substances may change, but the total amount of matter remains constant. ...
... the total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction - Antoine Lavoisier (1 743-1 794) The number of substances may change, but the total amount of matter remains constant. ...
Solon City Schools
... PERIODIC TRENDS • All the atoms in the same period have the same energy level. • Same shielding. • Increasing nuclear charge • So IE generally increases from left to right. • Exceptions at full and 1/2 fill orbitals. ...
... PERIODIC TRENDS • All the atoms in the same period have the same energy level. • Same shielding. • Increasing nuclear charge • So IE generally increases from left to right. • Exceptions at full and 1/2 fill orbitals. ...
Chapter 2
... PERIODIC TRENDS • All the atoms in the same period have the same energy level. • Same shielding. • Increasing nuclear charge • So IE generally increases from left to right. • Exceptions at full and 1/2 fill orbitals. ...
... PERIODIC TRENDS • All the atoms in the same period have the same energy level. • Same shielding. • Increasing nuclear charge • So IE generally increases from left to right. • Exceptions at full and 1/2 fill orbitals. ...