Campbell Biology, 10e (Reece) Chapter 2 The Chemical Context of
... 5) Knowing the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about which of the following? A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element 6) In what way are ...
... 5) Knowing the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about which of the following? A) the number of electrons in the element B) the number of protons in the element C) the number of protons plus neutrons in the element D) the number of protons plus electrons in the element 6) In what way are ...
Atomic Structure - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole number ratios. e.g., Dalton’s model of atom ...
... 2. Atoms of the same element are exactly alike; in particular, they have the same mass. 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements in fixed, whole number ratios. e.g., Dalton’s model of atom ...
CH.9 - coolchemistrystuff
... trigonal bipyramidal electron-domain geometry. With an expanded octet of 10 electrons, the use of a d orbital on the sulfur is required. The trigonal bipyramidal electron-domain geometry corresponds to SP3 d hybridization. One of the hybrid orbitals that points in an equatorial direction contains a ...
... trigonal bipyramidal electron-domain geometry. With an expanded octet of 10 electrons, the use of a d orbital on the sulfur is required. The trigonal bipyramidal electron-domain geometry corresponds to SP3 d hybridization. One of the hybrid orbitals that points in an equatorial direction contains a ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... Are these correct Bohr models? • What errors are at the ...
... Are these correct Bohr models? • What errors are at the ...
$doc.title
... with one oxygen atom to form one molecule of water. On the atomic scale, we never see an example of one and a half hydrogen atoms combining with an oxygen atom. This was one of the first observations of the early chemists who explored the properties of chemical elements. This observation is known as ...
... with one oxygen atom to form one molecule of water. On the atomic scale, we never see an example of one and a half hydrogen atoms combining with an oxygen atom. This was one of the first observations of the early chemists who explored the properties of chemical elements. This observation is known as ...
Ch. 8.3 – Bonding Theories
... In a pi bond (symbolized by the Greek letter ), the bonding electrons are most likely to be found in sausage-shaped regions above and below the bond axis of the bonded atoms. ...
... In a pi bond (symbolized by the Greek letter ), the bonding electrons are most likely to be found in sausage-shaped regions above and below the bond axis of the bonded atoms. ...
Unit 1 – Physical Science and Chemical Reactions
... elements in order of increasing atomic mass it would now be in order of increasing atomic number The mass of the protons was too small to account for the total atomic mass of the atom so Rutherford predicted that there must be a neutral particle in the nucleus similar in mass to the proton In 19 ...
... elements in order of increasing atomic mass it would now be in order of increasing atomic number The mass of the protons was too small to account for the total atomic mass of the atom so Rutherford predicted that there must be a neutral particle in the nucleus similar in mass to the proton In 19 ...
Chemical Bonding/Chemical Reactions
... The particular combination of standard atomic orbitals added together determines the shapes and energies of the hybrid orbitals. The particular type of hybridization that occurs is the one that yields the lowest overall energy for the molecule. To simplify this process, the electron geometries d ...
... The particular combination of standard atomic orbitals added together determines the shapes and energies of the hybrid orbitals. The particular type of hybridization that occurs is the one that yields the lowest overall energy for the molecule. To simplify this process, the electron geometries d ...
Ch. 3
... The oxidations number indicates if an atom is going to give up electrons or take in electrons in order to become stable. Positive oxidation numbers mean the atom is going to give up electrons. ...
... The oxidations number indicates if an atom is going to give up electrons or take in electrons in order to become stable. Positive oxidation numbers mean the atom is going to give up electrons. ...
Molecule-Shapes-Annotated
... 4. What happens to the bond angle when you add or remove an electron domain? 5. Can you force the atoms into new configurations by pushing atoms around? What does this suggest about the configuration of atoms in real molecules? 6. What is the difference between Electron Geometry and Molecule Geometr ...
... 4. What happens to the bond angle when you add or remove an electron domain? 5. Can you force the atoms into new configurations by pushing atoms around? What does this suggest about the configuration of atoms in real molecules? 6. What is the difference between Electron Geometry and Molecule Geometr ...
Bonding-and-Intermolecular-Forces
... When hydrogen bonds to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, a larger dipole occurs than in other polar bonds. This is because these atoms are highly electronegative due to their high nuclear charge and small size. When these atoms bond to hydrogen, electrons are withdrawn from the H atom, making it slightl ...
... When hydrogen bonds to nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, a larger dipole occurs than in other polar bonds. This is because these atoms are highly electronegative due to their high nuclear charge and small size. When these atoms bond to hydrogen, electrons are withdrawn from the H atom, making it slightl ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... »Gain energy to move to a higher level »Lose energy to move to a lower level ...
... »Gain energy to move to a higher level »Lose energy to move to a lower level ...
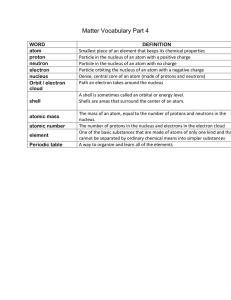
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Final Exam Practice-2017
... 11. Which of the following representations shows the Lewis symbols for the formation of potassium ...
... 11. Which of the following representations shows the Lewis symbols for the formation of potassium ...
C1403_Final Exam p. 1 Friday, January 23, 2004 Printed Last Name
... e. None of the above are correct 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a differe ...
... e. None of the above are correct 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a differe ...
Chapter One
... 0.1172 g of a pure hydrocarbon was burned in a C-H combustion train to produce 0.3509 g of CO2 and 0.1915 g of H2O. Determine the masses of C and H in the sample, the percentage of these elements in this hydrocarbon, and the empirical formula of the compound. ...
... 0.1172 g of a pure hydrocarbon was burned in a C-H combustion train to produce 0.3509 g of CO2 and 0.1915 g of H2O. Determine the masses of C and H in the sample, the percentage of these elements in this hydrocarbon, and the empirical formula of the compound. ...
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. Examples
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
... Density is the mass per unit of volume. It is affected by a change in temperature. Formula: Density = mass D=m Volume V ...
chapter 7-Chemical Bonding
... The Octet Rule • The octet rule states that representative elements usually attain stable noble gas electron configurations in most of their compounds. • Lewis dot formulas are based on the octet rule. • We need to distinguish between bonding (or shared) electrons and nonbonding (or unshared or lone ...
... The Octet Rule • The octet rule states that representative elements usually attain stable noble gas electron configurations in most of their compounds. • Lewis dot formulas are based on the octet rule. • We need to distinguish between bonding (or shared) electrons and nonbonding (or unshared or lone ...
Chemistry 212 Name:
... Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms rendering this point moot. All halogens have high electron affinities and ionizat ...
... Each halogen is obtained by oxidation of the halide ion to the halogen in a molten salt, except fluorine. None of the halogens is particularly abundant in nature, however all are easily accessible in concentrated forms rendering this point moot. All halogens have high electron affinities and ionizat ...
2 - Castle High School
... • A box with a volume of 22.4 L contains 1.0 mol of nitrogen and 2.0 mol of hydrogen at 0C. Which of the following statements is true? • a. The total pressure in the box is 202.6 kPa. • b. The partial pressure of N2 and H2 are equal. • c. The total pressure is 101.3 kPa. • d. The partial pressure of ...
... • A box with a volume of 22.4 L contains 1.0 mol of nitrogen and 2.0 mol of hydrogen at 0C. Which of the following statements is true? • a. The total pressure in the box is 202.6 kPa. • b. The partial pressure of N2 and H2 are equal. • c. The total pressure is 101.3 kPa. • d. The partial pressure of ...