Chemistry Test Review - Greenslime Home Page
... balanced because of all 3 elements not being the same on both sides of the equation] List the following information about the element Potassium: atomic number, symbol, atomic mass, number of protons, electrons, neutrons, and # of valence electrons. a. atomic number = 19 b. symbol = K c. atomic mass ...
... balanced because of all 3 elements not being the same on both sides of the equation] List the following information about the element Potassium: atomic number, symbol, atomic mass, number of protons, electrons, neutrons, and # of valence electrons. a. atomic number = 19 b. symbol = K c. atomic mass ...
CHEM 1411 NAME: PRACTICE EXAM #3 (Chapters 6
... C) B, Si, As, Te D) F, Cl, Br, I E) Na, Mg, Al, Si ...
... C) B, Si, As, Te D) F, Cl, Br, I E) Na, Mg, Al, Si ...
Solutions - Seattle Central
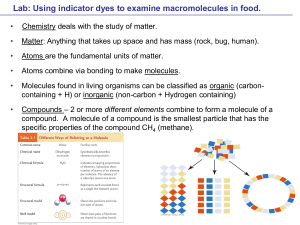
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
Dipole Moment & Polarity
... 2. CO2 has polar bonds, but is a linear molecule; D.M. of C-O is 2.3 D, the bond dipoles cancel each other and it has no net dipole moment ( = 0 D). Bonds are polar but molecule, is non-polar b) D.M. >0 unsymmetrical shape e.g. H2 O • Two O-H bonds, as there is some D.M. so the mol is angular The H ...
... 2. CO2 has polar bonds, but is a linear molecule; D.M. of C-O is 2.3 D, the bond dipoles cancel each other and it has no net dipole moment ( = 0 D). Bonds are polar but molecule, is non-polar b) D.M. >0 unsymmetrical shape e.g. H2 O • Two O-H bonds, as there is some D.M. so the mol is angular The H ...
Unit 1: Chapter 3
... Part One: Ionic Bonding 1. Predict the formation of cations & anions from a representative atom, based on the location on the Periodic Table; more specifically, based on the atom’s Group and the atom’s desire to obtain an OCTET of electrons (or a noble-gas electron configuration). Be able to draw a ...
... Part One: Ionic Bonding 1. Predict the formation of cations & anions from a representative atom, based on the location on the Periodic Table; more specifically, based on the atom’s Group and the atom’s desire to obtain an OCTET of electrons (or a noble-gas electron configuration). Be able to draw a ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... Chemical Formula: In which the symbols for the elements are used to indicate the types of atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds ar ...
... Chemical Formula: In which the symbols for the elements are used to indicate the types of atoms present and subscripts are used to indicate the relative numbers of atoms. CO2 indicates each molecule contains 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. Structural Formula: In which the individual bonds ar ...
Review Material
... Ensure that each atom ends up with the “correct” number of valence electrons. Most elements end up with eight valence electrons (the “octet rule”). Hydrogen ends up with two valence electrons. Boron and beryllium usually end up with fewer than eight valence electrons. Some elements from periods 3, a ...
... Ensure that each atom ends up with the “correct” number of valence electrons. Most elements end up with eight valence electrons (the “octet rule”). Hydrogen ends up with two valence electrons. Boron and beryllium usually end up with fewer than eight valence electrons. Some elements from periods 3, a ...
Ions and Ionic Compounds
... The electron cannot be lost entirely, so it is transferred to a chlorine atom, Cl, which then becomes an anion: Cl-. The Na+ and Cl- ions are attracted to form an ionic NaCl lattice which crystallizes. ...
... The electron cannot be lost entirely, so it is transferred to a chlorine atom, Cl, which then becomes an anion: Cl-. The Na+ and Cl- ions are attracted to form an ionic NaCl lattice which crystallizes. ...
Hybrid Orbitals – sp 3 Quiz
... 1. Based only on the number of unpaired electrons, how many bonds would a carbon atom be expected to form? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 ...
... 1. Based only on the number of unpaired electrons, how many bonds would a carbon atom be expected to form? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 ...
Chapter 2 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry This chapter deals with
... 1. all matter is composed of small, invisible particles called atoms 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses and other properties 4. chemical reactions involv ...
... 1. all matter is composed of small, invisible particles called atoms 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses and other properties 4. chemical reactions involv ...
Lecture 04 2/1/09 Atoms, Molecules, and Matter
... surface. These Kanji characters represent the word “atom”. ...
... surface. These Kanji characters represent the word “atom”. ...
Unit 1 - Morgan Science
... ◦ Colorless gases that are extremely nonreactive ◦ Full valence shell, non-reactive ◦ All are found in small amounts in our atmosphere ...
... ◦ Colorless gases that are extremely nonreactive ◦ Full valence shell, non-reactive ◦ All are found in small amounts in our atmosphere ...
Chem vocab quiz definitons
... Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell and control the elements reactivity. Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound that has all the properties of the compound. Compound is a pure substance that is made of two or more elements chemically bound together. Pure substances are bo ...
... Valence electrons are the electrons in the outer shell and control the elements reactivity. Molecule is the smallest particle of a compound that has all the properties of the compound. Compound is a pure substance that is made of two or more elements chemically bound together. Pure substances are bo ...
Chemistry Unit Study Guide Key
... or more elements that are bonded together; An element is a pure, single substance made of one type of atom. 2) examples of compounds – CO2, C6H12O6, NaCl, N2, O2, Fe2O3, H2O 3) where metals and nonmetals are found on the periodic table – Metals are to the left of the zig-zag line; Non-metals are to ...
... or more elements that are bonded together; An element is a pure, single substance made of one type of atom. 2) examples of compounds – CO2, C6H12O6, NaCl, N2, O2, Fe2O3, H2O 3) where metals and nonmetals are found on the periodic table – Metals are to the left of the zig-zag line; Non-metals are to ...
2015-2016 AP CHEMISTRY MIDTERM EXAM Review
... 30. Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 31. Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no more than two electrons 32. Predicts that it is impossible to determine simultaneously the exact position and the exact velocity of an electron Questions 33-35 refer to the phase diagram ...
... 30. Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 31. Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no more than two electrons 32. Predicts that it is impossible to determine simultaneously the exact position and the exact velocity of an electron Questions 33-35 refer to the phase diagram ...
Matter
... “want” to have full outer electron shells. An atom gets a full outer shell by getting involved in one of the two types of bonds. ...
... “want” to have full outer electron shells. An atom gets a full outer shell by getting involved in one of the two types of bonds. ...
Molecular Structure and Covalent Bonding Theories
... • A polar bond is created if the atoms sharing the electron pair have different electronegativities – HCl and the associated dipole moment. This molecule is polar. For diatomics, determination of polarity is easy. What if the molecule has two or more atoms? All the dipole have to be summed. If the s ...
... • A polar bond is created if the atoms sharing the electron pair have different electronegativities – HCl and the associated dipole moment. This molecule is polar. For diatomics, determination of polarity is easy. What if the molecule has two or more atoms? All the dipole have to be summed. If the s ...
Labs - newtunings.com
... 5.2h Metals tend to react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. Nonmetals tend to react with other nonmetals to form molecular (covalent) compounds. Ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions have both ionic and covalent bonding. 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is forme ...
... 5.2h Metals tend to react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. Nonmetals tend to react with other nonmetals to form molecular (covalent) compounds. Ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions have both ionic and covalent bonding. 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is forme ...
Chapter 2
... number of covalent bonds that it can form, this number is called an atom’s valence. – The valence of H=1, O=2, N=3, and C=4 Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... number of covalent bonds that it can form, this number is called an atom’s valence. – The valence of H=1, O=2, N=3, and C=4 Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
The Helium Atom
... This is useful, since the only thing left to do is to guess a good wave function . The best guess will have the lowest energy! the one-electron 1s wave functions in atomic units for distance are ...
... This is useful, since the only thing left to do is to guess a good wave function . The best guess will have the lowest energy! the one-electron 1s wave functions in atomic units for distance are ...
Common Chemical Formula List
... with chemical symbols, as then you will be able to see how many atoms of each type are in each chemical. Example 1 Unbalanced Equation:- C3H8 + O2 ---> H2O + CO2 There are three carbons on the left, but only one on the right. There are eight hydrogens on the left but only two on the right. There are ...
... with chemical symbols, as then you will be able to see how many atoms of each type are in each chemical. Example 1 Unbalanced Equation:- C3H8 + O2 ---> H2O + CO2 There are three carbons on the left, but only one on the right. There are eight hydrogens on the left but only two on the right. There are ...