PHOSPHORUS AND SULFUR COSMOCHEMISTRY
... phosphorus compounds, energetic organic compounds, or unusual physical conditions. Meteoritic schreibersite provided an abundant source of reactive phosphorus for the early Earth. Water corrodes schreibersite to form a mixed valence series of phosphorus compounds. Schreibersite corrosion was studied ...
... phosphorus compounds, energetic organic compounds, or unusual physical conditions. Meteoritic schreibersite provided an abundant source of reactive phosphorus for the early Earth. Water corrodes schreibersite to form a mixed valence series of phosphorus compounds. Schreibersite corrosion was studied ...
Version A
... 5. If the temperature increases from 10°C to 60°C at a constant pressure of 0.4 atmosphere, which of the processes occurs? ...
... 5. If the temperature increases from 10°C to 60°C at a constant pressure of 0.4 atmosphere, which of the processes occurs? ...
Chapter 9: Chemical Bonding I: Basic Concepts
... 29. Pi bonds are covalent bonds in which the electron density is concentrated above and below a plane containing the nuclei of the bonding atoms. Ans: True Category: Easy Section: 10.5 30. A bonding molecular orbital is of lower energy (more stable) than the atomic orbitals from which it was formed. ...
... 29. Pi bonds are covalent bonds in which the electron density is concentrated above and below a plane containing the nuclei of the bonding atoms. Ans: True Category: Easy Section: 10.5 30. A bonding molecular orbital is of lower energy (more stable) than the atomic orbitals from which it was formed. ...
Physical Chemistry 3: — Chemical Kinetics
... based on an interferometric method to measure a delay of 21 ± 5 as in the photo-induced emission of electrons from the 2 orbitals of neon atoms with respect to emission from the 2 orbital by a 100 eV light pulse (Schultze et al, Science 328, 1658 (2010)). ...
... based on an interferometric method to measure a delay of 21 ± 5 as in the photo-induced emission of electrons from the 2 orbitals of neon atoms with respect to emission from the 2 orbital by a 100 eV light pulse (Schultze et al, Science 328, 1658 (2010)). ...
101
... polyatomic cyanide ion, CN− . The electronegativity of nitrogen (3.04) is greater than the electronegativity of carbon (2.55). Thus, the three shared pairs of electrons are all considered to belong to the nitrogen atom. As a result, the carbon atom is considered to have two valence electrons, which ...
... polyatomic cyanide ion, CN− . The electronegativity of nitrogen (3.04) is greater than the electronegativity of carbon (2.55). Thus, the three shared pairs of electrons are all considered to belong to the nitrogen atom. As a result, the carbon atom is considered to have two valence electrons, which ...
manual - University of Bath
... is printed and assumed. If SCAL has been specified, then only the value of SF associated with the first valence coordinate is significant: this is the factor by which the entire force-constant matrix is to be multiplied. (Note that this is equivalent to multiplying all the vibrational frequencies by ...
... is printed and assumed. If SCAL has been specified, then only the value of SF associated with the first valence coordinate is significant: this is the factor by which the entire force-constant matrix is to be multiplied. (Note that this is equivalent to multiplying all the vibrational frequencies by ...
Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... atoms transfer their valence electrons to form ionic bonds, while other atoms share valence electrons to form covalent bonds; Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds; Compare the properties of substances with different types of bonds Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predic ...
... atoms transfer their valence electrons to form ionic bonds, while other atoms share valence electrons to form covalent bonds; Differentiate between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds; Compare the properties of substances with different types of bonds Name simple ionic and covalent compounds; Predic ...
Construction of Porous Solids from Hydrogen
... to a maximum of θ ) 25.08°, giving 2628 unique reflections. Lattice parameters were obtained from least-squares analyses of 25 computercentered reflections with 15 e 2θ e 30. The raw intensity data was converted to structure factor amplitudes and their estimated standard deviations by correction for ...
... to a maximum of θ ) 25.08°, giving 2628 unique reflections. Lattice parameters were obtained from least-squares analyses of 25 computercentered reflections with 15 e 2θ e 30. The raw intensity data was converted to structure factor amplitudes and their estimated standard deviations by correction for ...
Mole-Volume Conversion Assignment
... If we use 2 litres of nitrogen oxide, how many litres of hydrogen would be needed? How many litres of Water vapour? How many litres of nitrogen? ...
... If we use 2 litres of nitrogen oxide, how many litres of hydrogen would be needed? How many litres of Water vapour? How many litres of nitrogen? ...
Two-Electron Reduction of a Vanadium(V) Nitride by CO to Release
... and is fostered by N2 extrusion.1 The analogous transformation involving isocyanate and production of CO is less well documented. A previous study by Fickes et al. showed that the 1e reduction of a niobium(IV) isocyanate complex (OCN)Nb(N[t-Bu]Ar)3 (1-Nb(NCO), Ar = 3,5-Me2C6H3) results in formation ...
... and is fostered by N2 extrusion.1 The analogous transformation involving isocyanate and production of CO is less well documented. A previous study by Fickes et al. showed that the 1e reduction of a niobium(IV) isocyanate complex (OCN)Nb(N[t-Bu]Ar)3 (1-Nb(NCO), Ar = 3,5-Me2C6H3) results in formation ...
COMPOUNDS OF CARBON CONTAINING NITROGEN
... (v) Reaction with nitrous acid : Primary aromatic amines react with nitrous acid to give diazonium salts and this reaction is known as diazotisation. Nitrous acid is an unstable compound and can not be stored, so it is prepared during the reaction by mixing sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid. The ...
... (v) Reaction with nitrous acid : Primary aromatic amines react with nitrous acid to give diazonium salts and this reaction is known as diazotisation. Nitrous acid is an unstable compound and can not be stored, so it is prepared during the reaction by mixing sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid. The ...
Student Review Packet
... NOTE: Graph should have “pH” as the vertical axis and “added base” as the horizontal axis. The graph should be in a “double S” shape. The middle of the lower part of the “first S” indicates the point of maximum buffering of the first buffering zone where [H2A] / [HA-] = 1. The middle of the “first S ...
... NOTE: Graph should have “pH” as the vertical axis and “added base” as the horizontal axis. The graph should be in a “double S” shape. The middle of the lower part of the “first S” indicates the point of maximum buffering of the first buffering zone where [H2A] / [HA-] = 1. The middle of the “first S ...
Pirogov National Medical Univercity of Vinnitsa
... 2. Duty student receives the necessary work for the group equipment and reagents, and places them in the workplace. 3. In the chemical laboratory, it is permitted to work only when there is a white robe and cap. Each student is given a permanent job, which he should keep clean, do not clutter up his ...
... 2. Duty student receives the necessary work for the group equipment and reagents, and places them in the workplace. 3. In the chemical laboratory, it is permitted to work only when there is a white robe and cap. Each student is given a permanent job, which he should keep clean, do not clutter up his ...
ANSWERS Problem Set 5a – Chemical Reactions
... changed. Why? Subscripts define which compounds are being used in the reaction. The coefficients are used to define the quantity of each compound, not the chemical make-up. ...
... changed. Why? Subscripts define which compounds are being used in the reaction. The coefficients are used to define the quantity of each compound, not the chemical make-up. ...
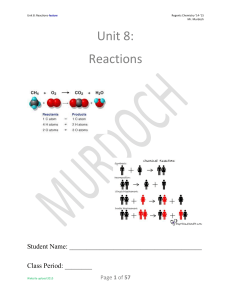
Unit 8: Reactions
... 1. Given that 35.0 g of N2(g) react with an unknown amount of H2(g) to produce 42.5 g of NH3(g), how many grams of H2(g) were used? i. 35.0 g of N2(g) + X g of H2(g) = 42.5 of NH3(g), therefore you first solve for 42.5 g– 35.0 g = 7.5 g, so 7.5 g of H2(g) was used making 42.5 of NH3(g). 2. How many ...
... 1. Given that 35.0 g of N2(g) react with an unknown amount of H2(g) to produce 42.5 g of NH3(g), how many grams of H2(g) were used? i. 35.0 g of N2(g) + X g of H2(g) = 42.5 of NH3(g), therefore you first solve for 42.5 g– 35.0 g = 7.5 g, so 7.5 g of H2(g) was used making 42.5 of NH3(g). 2. How many ...
PDF Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics
... is second order overall, because 1 + 1 does equal 2. Determining Rate Laws Using the Method of Initial Rates Rate laws are not derived from the reaction equation. No matter how many times we say, people keep thinking it’s true. But it’s not. Rate laws are derived from experimental data. There ar ...
... is second order overall, because 1 + 1 does equal 2. Determining Rate Laws Using the Method of Initial Rates Rate laws are not derived from the reaction equation. No matter how many times we say, people keep thinking it’s true. But it’s not. Rate laws are derived from experimental data. There ar ...