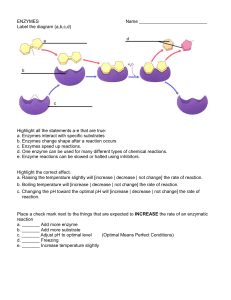
ENZYMES
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
... a. _______ Add more enzyme b. _______ Add more substrate c. _______ Adjust pH to optimal level (Optimal Means Perfect Conditions) d. _______ Freezing e. _______ Increase temperature slightly ...
Chemistry - El Camino College
... B. ______ - two or more different atoms chemically bonded together. C. Two major types of ______ join atoms: ionic and covalent bonds 1. ______ Bond - very strong attraction between negatively and positively charged ions a. In ionic reactions, atoms give or take _________ to get a full outer electro ...
... B. ______ - two or more different atoms chemically bonded together. C. Two major types of ______ join atoms: ionic and covalent bonds 1. ______ Bond - very strong attraction between negatively and positively charged ions a. In ionic reactions, atoms give or take _________ to get a full outer electro ...
Honors Chemistry
... Balancing Chemical Equations: truly a trial and error process if there ever was one Helpful hints: 1. 1 atom at a time 2. Balance atoms that appear only 1X per side first 3. Balance polyatomic ions as whole units 4. Balance diatomic elements last 5. Save H + O for last if this doesn’t succeed, try d ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations: truly a trial and error process if there ever was one Helpful hints: 1. 1 atom at a time 2. Balance atoms that appear only 1X per side first 3. Balance polyatomic ions as whole units 4. Balance diatomic elements last 5. Save H + O for last if this doesn’t succeed, try d ...
Chemical Reactions
... In a synthesis reaction two or more substances combine to form a more complex substance. A decomposition reaction is the opposite of synthesis and breaks down a compound into two or more substances. In a single replacement reaction, one substance in a compound is replaced by another, more active, su ...
... In a synthesis reaction two or more substances combine to form a more complex substance. A decomposition reaction is the opposite of synthesis and breaks down a compound into two or more substances. In a single replacement reaction, one substance in a compound is replaced by another, more active, su ...
8th Grade Ch. 7 Chemical Reactions Study guide
... ____ 25. Chemical reactions usually speed up at ____ temperatures. A. Celsius B. lower C. higher D. absolute ____ 26. Catalysts ____ the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction. A. inhibit B. increase C. reduce D. balance ____ 27. To check that an equation is balanced, count the number ...
... ____ 25. Chemical reactions usually speed up at ____ temperatures. A. Celsius B. lower C. higher D. absolute ____ 26. Catalysts ____ the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction. A. inhibit B. increase C. reduce D. balance ____ 27. To check that an equation is balanced, count the number ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized equation is A + X AX A decomposition reaction is one where one product breaks down into tw ...
... (elements that lose electrons). The letters X and Y will represent negative ions (elements that gain electrons). In a synthesis reaction, two or more reactants are combined to form one product. The generalized equation is A + X AX A decomposition reaction is one where one product breaks down into tw ...
File
... “Exothermic” means that heat is released during the reaction. This often results in the reaction container feeling warm to the touch (heat is given off). Reactants Products + HEAT (heat on product side because released) “Endothermic” means that heat is absorbed during the reaction. This often resu ...
... “Exothermic” means that heat is released during the reaction. This often results in the reaction container feeling warm to the touch (heat is given off). Reactants Products + HEAT (heat on product side because released) “Endothermic” means that heat is absorbed during the reaction. This often resu ...
Chemical Synthesis (sat6)
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
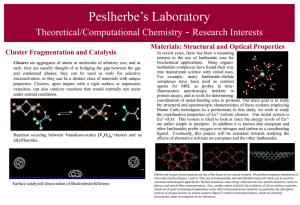
Cluster Fragmentation and Catalysis
... fundamental interest to study solvent effects on the thermodynamic and dynamic properties of species. Hence, theoretical investigations of clusters are extremely useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvation in chemical reactions. For example, the study of simple ion-cluster pro ...
... fundamental interest to study solvent effects on the thermodynamic and dynamic properties of species. Hence, theoretical investigations of clusters are extremely useful to study basic processes such as the role of microsolvation in chemical reactions. For example, the study of simple ion-cluster pro ...
Name - rwebbchem
... 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
... 1. Would a precipitate form from a reaction of aluminum chloride and sodium hydroxide? If yes, write and balance the equation that illustrates the reaction. ...
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.