Chapter 6: Chemistry in Biology
... __________ are large molecules formed by joining smaller organic molecules together. __________ are molecules made from repeating units of identical or nearly identical compounds linked together by a series of covalent bonds. ...
... __________ are large molecules formed by joining smaller organic molecules together. __________ are molecules made from repeating units of identical or nearly identical compounds linked together by a series of covalent bonds. ...
Unit 5 Study Guide
... Unit 5 Study Guide: Chemical Reactions 1. What are the 7 diatomic molecules? ...
... Unit 5 Study Guide: Chemical Reactions 1. What are the 7 diatomic molecules? ...
Ch. 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) Teacher Relearn
... right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
... right yields products are on the __________ side. The arrow means “________”, or “reacts to produce” when read aloud. ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... 71. In the above reaction, NaCl + F2 NaF + Cl2, F is more or less reactive than Cl? 72. In the activity series of metals are the more reactive metals found on the top or the bottom of the chart? 73. What conditions in the reactants must be present in order for a double-replacement to take place? 7 ...
... 71. In the above reaction, NaCl + F2 NaF + Cl2, F is more or less reactive than Cl? 72. In the activity series of metals are the more reactive metals found on the top or the bottom of the chart? 73. What conditions in the reactants must be present in order for a double-replacement to take place? 7 ...
+ H 2 SO 4(aq) - Rothschild Science
... What do the equations mean? The coefficients indicate the number of moles of the reactants necessary… to form a certain mole of the product. Mole to Mole Ratio ...
... What do the equations mean? The coefficients indicate the number of moles of the reactants necessary… to form a certain mole of the product. Mole to Mole Ratio ...
Chapter 8powerp point for chemical reactions
... The equation must represent known facts The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants & products The law of conservation of mass must be satisfied- which means the same # and type of atoms are present on both sides of the equation. ...
... The equation must represent known facts The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants & products The law of conservation of mass must be satisfied- which means the same # and type of atoms are present on both sides of the equation. ...
10 TEST 2 (of 3)
... Use the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) to calculate the ideal gas law constant R at standard temperature and pressure (273 K, 1.00 atm) assuming a molar volume of 22.4 L. ...
... Use the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) to calculate the ideal gas law constant R at standard temperature and pressure (273 K, 1.00 atm) assuming a molar volume of 22.4 L. ...
AP Chemistry Test Review
... 20) bond order calculation 21) odd # of electrons or 12 or 16 electrons are paramagnetic 22) determining the intermolecular forces in a molecule…L.D. dip-dip, H-bonds 23) interpreting phase diagrams 24) ∆T= K*m*i 25) determining the Rate Law based on lab data 26) graphs of 0, 1st, and 2nd order rate ...
... 20) bond order calculation 21) odd # of electrons or 12 or 16 electrons are paramagnetic 22) determining the intermolecular forces in a molecule…L.D. dip-dip, H-bonds 23) interpreting phase diagrams 24) ∆T= K*m*i 25) determining the Rate Law based on lab data 26) graphs of 0, 1st, and 2nd order rate ...
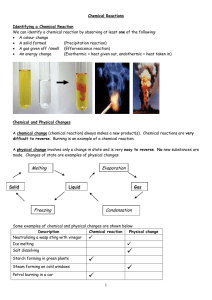
Chemical reaction

A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive elements where both electronic and nuclear changes may occur.The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more products, which usually have properties different from the reactants. Reactions often consist of a sequence of individual sub-steps, the so-called elementary reactions, and the information on the precise course of action is part of the reaction mechanism. Chemical reactions are described with chemical equations, which symbolically present the starting materials, end products, and sometimes intermediate products and reaction conditions.Chemical reactions happen at a characteristic reaction rate at a given temperature and chemical concentration. Typically, reaction rates increase with increasing temperature because there is more thermal energy available to reach the activation energy necessary for breaking bonds between atoms.Reactions may proceed in the forward or reverse direction until they go to completion or reach equilibrium. Reactions that proceed in the forward direction to approach equilibrium are often described as spontaneous, requiring no input of free energy to go forward. Non-spontaneous reactions require input of free energy to go forward (examples include charging a battery by applying an external electrical power source, or photosynthesis driven by absorption of electromagnetic radiation in the form of sunlight).Different chemical reactions are used in combinations during chemical synthesis in order to obtain a desired product. In biochemistry, a consecutive series of chemical reactions (where the product of one reaction is the reactant of the next reaction) form metabolic pathways. These reactions are often catalyzed by protein enzymes. Enzymes increase the rates of biochemical reactions, so that metabolic syntheses and decompositions impossible under ordinary conditions can occur at the temperatures and concentrations present within a cell.The general concept of a chemical reaction has been extended to reactions between entities smaller than atoms, including nuclear reactions, radioactive decays, and reactions between elementary particles as described by quantum field theory.