Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... about one two-thousandth the mass of the simplest type of hydrogen atom, which is the smallest atom known. More-accurate experiments conducted since then indicate that the electron has a mass of 9.109 × 10−31kg, or 1/1837 the mass of the simplest type of hydrogen atom. Millikan’s experiments also co ...
... about one two-thousandth the mass of the simplest type of hydrogen atom, which is the smallest atom known. More-accurate experiments conducted since then indicate that the electron has a mass of 9.109 × 10−31kg, or 1/1837 the mass of the simplest type of hydrogen atom. Millikan’s experiments also co ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... to the relatively weak London dispersion and dipole forces, which are broken during the melting of SO2. d. Liquid Cl2 is held together by London dispersion forces, which although weak increase in strength as the number of electrons increases. Liquid HCl is held together by dipole forces in addition ...
... to the relatively weak London dispersion and dipole forces, which are broken during the melting of SO2. d. Liquid Cl2 is held together by London dispersion forces, which although weak increase in strength as the number of electrons increases. Liquid HCl is held together by dipole forces in addition ...
1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the
... Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? ...
... Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? ...
Atomic Structure
... different masses as well. How did Dalton miss this? It turns out that elements found in nature exist as uniform mixtures with a constant ratio of their naturally occurring isotopes. In other words, a piece of lithium always contains both types of naturally occurring lithium (the type with 3 neutrons ...
... different masses as well. How did Dalton miss this? It turns out that elements found in nature exist as uniform mixtures with a constant ratio of their naturally occurring isotopes. In other words, a piece of lithium always contains both types of naturally occurring lithium (the type with 3 neutrons ...
Chemistry
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been i ...
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O-Level, students have been i ...
幻灯片 1
... century. A more rigorous foundation came, first with the use of spectroscopy to determine atomic number and, second with the development of the quantum theory of atomic structure. ...
... century. A more rigorous foundation came, first with the use of spectroscopy to determine atomic number and, second with the development of the quantum theory of atomic structure. ...
1 - KFUPM Faculty List
... 15. Which of the following is a strong electrolyte solution? A) KMnO4(aq) KMnO4 is a normal salt, and thus this is a strong electrolyte solution B) C2H5OH(aq) This is a dissolved polar molecule (an alcohol) and thus it is a non-electrolyte solution C) NH3(aq) This is a weak base solution and thus a ...
... 15. Which of the following is a strong electrolyte solution? A) KMnO4(aq) KMnO4 is a normal salt, and thus this is a strong electrolyte solution B) C2H5OH(aq) This is a dissolved polar molecule (an alcohol) and thus it is a non-electrolyte solution C) NH3(aq) This is a weak base solution and thus a ...
Chapter 8: Ionic Compounds
... Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one valence electron, forming an ion with a 1+ charge. Group 2A elements, [noble gas]ns2, lose their two valence elect ...
... Reactivity of metals is based on the ease with which they lose valence electrons to achieve a stable octet, or noble gas configuration. Group 1A elements, [noble gas]ns1, lose their one valence electron, forming an ion with a 1+ charge. Group 2A elements, [noble gas]ns2, lose their two valence elect ...
Chemistry Senior External Syllabus 1998
... Candidates should come to understand that no real distinction can be made between ‘chemicals’ and matter. Chemistry possesses a theoretical framework that allows new knowledge to be organised and related to other aspects of the discipline. The modern chemical approach seeks an understanding of natur ...
... Candidates should come to understand that no real distinction can be made between ‘chemicals’ and matter. Chemistry possesses a theoretical framework that allows new knowledge to be organised and related to other aspects of the discipline. The modern chemical approach seeks an understanding of natur ...
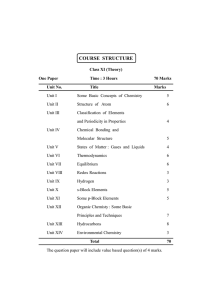
COURSE STRUCTURE
... In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ratio by mass. Law of multiple proportion : Two elements combined together ...
... In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of reactants is equal to that of products. Law of constant composition : A chemical compound is always found to be made of same elements combined together in the same fixed ratio by mass. Law of multiple proportion : Two elements combined together ...
STUDY MATERIAL 2015-16 CHEMISTRY CLASS XI
... all round development of the students. Time to time various strategies have been adopted to adorn the students with academic excellence. This support material is one such effort by Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, an empirical endeavour to help students learn more effectively and efficiently. It is des ...
... all round development of the students. Time to time various strategies have been adopted to adorn the students with academic excellence. This support material is one such effort by Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, an empirical endeavour to help students learn more effectively and efficiently. It is des ...
Class XI Physical Chemistry Short note
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. 5. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ...
... Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. 5. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ...
The Greek Concept of Atomos: The Indivisible Atom - Mr
... Giles of Rome (ca. 1247-1316) taght that there are natural minima below which physical substances cannot exist. This implies an atomic theory of matter. He also investigated the nature of the vacuum using a clepsydra (a water clock) and a siphon, showing that the void exerted a force of suction. The ...
... Giles of Rome (ca. 1247-1316) taght that there are natural minima below which physical substances cannot exist. This implies an atomic theory of matter. He also investigated the nature of the vacuum using a clepsydra (a water clock) and a siphon, showing that the void exerted a force of suction. The ...
Chem101, 2nd Major Exam, term061
... 1. A candle which is made of 151.2 g of an organic acid (Molar Mass = 284 g/mol) was burned and used to warm 500.0 g of water, which was initially at 22.6C. When the burning was stopped the temperature of the water was 33.5C. Assuming all heat produced by the organic acid was absorbed by the water ...
... 1. A candle which is made of 151.2 g of an organic acid (Molar Mass = 284 g/mol) was burned and used to warm 500.0 g of water, which was initially at 22.6C. When the burning was stopped the temperature of the water was 33.5C. Assuming all heat produced by the organic acid was absorbed by the water ...
Chapter 2 slides
... The first draft of the periodic table was developed between 1879 and 1871, and published by Dmitri Mendeleev. Note that this was before the subatomic particles were discovered, so it was not based on atomic number. The 63 known elements were arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass, and ...
... The first draft of the periodic table was developed between 1879 and 1871, and published by Dmitri Mendeleev. Note that this was before the subatomic particles were discovered, so it was not based on atomic number. The 63 known elements were arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass, and ...