Lecture 6 - TCD Chemistry
... How Molecular Oribital Theory enhances our understanding of the chemistry of transition metal complexes ...
... How Molecular Oribital Theory enhances our understanding of the chemistry of transition metal complexes ...
Dangerous Goods - `OnGuard®` Safety Training
... Corrosives may be acids or alkalies (bases). They may be liquid or in solid form such as powder, granules or flakes. Even though they all are Dangerous Goods of Class 8, many are NOT compatible with each other and in fact may react dangerously with each other. ...
... Corrosives may be acids or alkalies (bases). They may be liquid or in solid form such as powder, granules or flakes. Even though they all are Dangerous Goods of Class 8, many are NOT compatible with each other and in fact may react dangerously with each other. ...
Experiment 1 - Melting Points - NAU jan.ucc.nau.edu web server
... a physical property that can be used for its identification. It is a measure of the amount of kinetic energy (heat) that must be supplied to the particles of the substance in order to overcome the intermolecular forces (such as Van der Waals, dipole-dipole, and Hbonding) that confine them to the sol ...
... a physical property that can be used for its identification. It is a measure of the amount of kinetic energy (heat) that must be supplied to the particles of the substance in order to overcome the intermolecular forces (such as Van der Waals, dipole-dipole, and Hbonding) that confine them to the sol ...
CP - Fundamentals
... We can take the elemental composition problem one step further by adding knowledge about a compound’s actual molecular weight. There are a variety of analytical techniques for determining the molecular weight of a compound, mass spectrometry being the most famous of the bunch.) Thus if we know: 1. T ...
... We can take the elemental composition problem one step further by adding knowledge about a compound’s actual molecular weight. There are a variety of analytical techniques for determining the molecular weight of a compound, mass spectrometry being the most famous of the bunch.) Thus if we know: 1. T ...
Chem 1B Fa2015 FinalExam Review
... [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] is a tetrahedral complex, which is a weak-field complex, and with 3d8 electron configuration for Ni2+, the complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] would be paramagnetic. In addition, a tetrahedral complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] will not exhibit isomerism. (Show d8 configuration in tetrahedral crystal field diagr ...
... [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] is a tetrahedral complex, which is a weak-field complex, and with 3d8 electron configuration for Ni2+, the complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] would be paramagnetic. In addition, a tetrahedral complex [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] will not exhibit isomerism. (Show d8 configuration in tetrahedral crystal field diagr ...
Regents Review Questions
... The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure on the surface of the liquid. The heat of vaporization of ethanol is 838 joules per gram. A sample of ethanol has a mass of 65.0 grams and is boiling at 1.00 atmosphere. ...
... The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the pressure on the surface of the liquid. The heat of vaporization of ethanol is 838 joules per gram. A sample of ethanol has a mass of 65.0 grams and is boiling at 1.00 atmosphere. ...
Preparation of Supported Catalysts
... 2. At least one additional layer near to the surface with properties different from the bulk solvent. → melting and boiling point and dielectric constant different from bulk water; → unmixing / separation in water containing organic solvents → formation of a thin aqueous layer at the solid surface ( ...
... 2. At least one additional layer near to the surface with properties different from the bulk solvent. → melting and boiling point and dielectric constant different from bulk water; → unmixing / separation in water containing organic solvents → formation of a thin aqueous layer at the solid surface ( ...
1 Acids and Bases
... the formula will begin with an H: H2 SO4 , HCl, HNO3 , and HClO4 are all acids. When a formula involves hydrogen plus an anion that you are familiar with, it is highly likely that the compound is an acid. One common type of weak acid is generally written in the form R-COOH or R-CO2 H, where R is usu ...
... the formula will begin with an H: H2 SO4 , HCl, HNO3 , and HClO4 are all acids. When a formula involves hydrogen plus an anion that you are familiar with, it is highly likely that the compound is an acid. One common type of weak acid is generally written in the form R-COOH or R-CO2 H, where R is usu ...
Worksheet Significant Figures
... You and your classmates will be participating in many hands-on laboratory activities this year. Some of these activities may require the use of materials or pieces of equipment that are potentially harmful if not handled in a safe manner. Carefully review the following rules for student conduct. Aft ...
... You and your classmates will be participating in many hands-on laboratory activities this year. Some of these activities may require the use of materials or pieces of equipment that are potentially harmful if not handled in a safe manner. Carefully review the following rules for student conduct. Aft ...
Untitled
... c. How many grams of CO2 are produced from 18.5 g of oxygen gas and excess propane? d. How many grams of H2O can be produced from the reaction of 8.50 * 1022 molecules of propane gas? Acetylene gas, C2H2, burns in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. If 62.0 g of CO2 is produced when 22.5 g o ...
... c. How many grams of CO2 are produced from 18.5 g of oxygen gas and excess propane? d. How many grams of H2O can be produced from the reaction of 8.50 * 1022 molecules of propane gas? Acetylene gas, C2H2, burns in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water. If 62.0 g of CO2 is produced when 22.5 g o ...
(+1) + - Edublogs
... shared but not equally. For electrons that are shared in these compounds, we assign the shared electrons to the most electronegative element. We are just acting as though the electronegativity difference was large enough for the transfer of electrons to occur. ...
... shared but not equally. For electrons that are shared in these compounds, we assign the shared electrons to the most electronegative element. We are just acting as though the electronegativity difference was large enough for the transfer of electrons to occur. ...
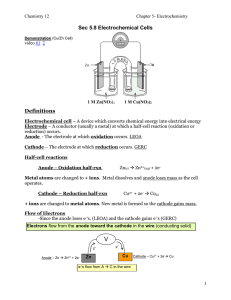
Sec 5.8 - 5.11 notes
... white solid (PbSO4) forms on both plates. Originally, [H+] & [HSO4-] is high. i.e.) H2SO4 is denser than H2O therefore the density (specific gravity) of the electrolyte is high to start with. As the cell discharges, H2SO4 (H+ & HSO4-) is used up and H2O is formed. Therefore, electrolyte gets less de ...
... white solid (PbSO4) forms on both plates. Originally, [H+] & [HSO4-] is high. i.e.) H2SO4 is denser than H2O therefore the density (specific gravity) of the electrolyte is high to start with. As the cell discharges, H2SO4 (H+ & HSO4-) is used up and H2O is formed. Therefore, electrolyte gets less de ...
Hydrolases as Catalysts for Green Chemistry and
... Interestingly, mutations of F407 to alanine or leucine led to a dramatic increase in activity but with reversed selectivity (E=3.3 and E >100 respectively towards the S isomer). On the other hand, PLE-3 isoenzyme selectively hydrolysed the correct isomer, R, with E=10. Immobilized lipase B from Cand ...
... Interestingly, mutations of F407 to alanine or leucine led to a dramatic increase in activity but with reversed selectivity (E=3.3 and E >100 respectively towards the S isomer). On the other hand, PLE-3 isoenzyme selectively hydrolysed the correct isomer, R, with E=10. Immobilized lipase B from Cand ...
Chapter 9
... in the production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine, which is represented by the following equation. ...
... in the production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine, which is represented by the following equation. ...
GCE Getting Started - Edexcel
... Plot a graph of IE across a period and / or down a group and use these to help explain the quantum model for electron configurations. ...
... Plot a graph of IE across a period and / or down a group and use these to help explain the quantum model for electron configurations. ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... Please read the following sheets of information they include notes and practice problems that will be covered the first week of school. The worksheets include work from the first three chapters and should be considered a review of information from PreAP chemistry. If they are not a review, don't ...
... Please read the following sheets of information they include notes and practice problems that will be covered the first week of school. The worksheets include work from the first three chapters and should be considered a review of information from PreAP chemistry. If they are not a review, don't ...
answers to part a of the canadian chemistry
... The people involved in preparing the CCC very much appreciate all the comments and feedback that we get from teachers. We have tried to incorporate some of these comments in with the solutions. We have also tried to indicate how students did in particular questions, although, unfortunately, we have ...
... The people involved in preparing the CCC very much appreciate all the comments and feedback that we get from teachers. We have tried to incorporate some of these comments in with the solutions. We have also tried to indicate how students did in particular questions, although, unfortunately, we have ...
Supplementary Information
... acid 0.1 N (1.0 mL) and CHCl3-MeOH mixture (3.0 mL; 2:1 v/v). Between steps the powder was precipitated by a brief low-speed centrifugation (6000 rpm, 10 min., Haereus Biofuge) and the supernatant phase was decanted. After the treatment, the material did not release any trace of organic substances. ...
... acid 0.1 N (1.0 mL) and CHCl3-MeOH mixture (3.0 mL; 2:1 v/v). Between steps the powder was precipitated by a brief low-speed centrifugation (6000 rpm, 10 min., Haereus Biofuge) and the supernatant phase was decanted. After the treatment, the material did not release any trace of organic substances. ...
DCY1B - Manonmaniam Sundaranar University
... steroids. This catalyst transfers the hydrogen atoms specifically to the 'cis' positions. (ii) It is an ideal catalyst used for catalysing hydrogenations at room temperature and pressure. (iii) Wilkinson's catalyst is more important in pharmaceutical and petrochemical industries for making specific ...
... steroids. This catalyst transfers the hydrogen atoms specifically to the 'cis' positions. (ii) It is an ideal catalyst used for catalysing hydrogenations at room temperature and pressure. (iii) Wilkinson's catalyst is more important in pharmaceutical and petrochemical industries for making specific ...
Topic 5 Energetics File
... Average bond enthalpy: The average enthalpy change of breaking one mole of a bond in a gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indic ...
... Average bond enthalpy: The average enthalpy change of breaking one mole of a bond in a gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indic ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.