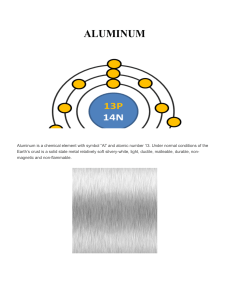
Topic 7b Redox notes
... Potassium dichromate is an oxidising agent and can oxidise ethanol to a substance called ethanal. During this process the dichromate Cr2O72- (which is orange) is itself reduced to green Cr3+. ...
... Potassium dichromate is an oxidising agent and can oxidise ethanol to a substance called ethanal. During this process the dichromate Cr2O72- (which is orange) is itself reduced to green Cr3+. ...
Slide 1
... Analyze: We are given four equations and asked to predict the sign of ΔS for each chemical reaction. Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The ...
... Analyze: We are given four equations and asked to predict the sign of ΔS for each chemical reaction. Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The ...
No Slide Title
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsyst = - qsurr. Since the combustion process occurs under conditions of constant volume, q = E, the change in internal energy. Example: 1.412 g of carbon (M = 12.01 g/mol) are burned in ...
... The negative sign in the above equation occurs because we are measuring the value of q for the surroundings, and qsyst = - qsurr. Since the combustion process occurs under conditions of constant volume, q = E, the change in internal energy. Example: 1.412 g of carbon (M = 12.01 g/mol) are burned in ...
19 BROWN Chemical Thermodynamics PPTSExercise
... Analyze: We are given four equations and asked to predict the sign of ΔS for each chemical reaction. Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The ...
... Analyze: We are given four equations and asked to predict the sign of ΔS for each chemical reaction. Plan: The sign of ΔS will be positive if there is an increase in temperature, an increase in the volume in which the molecules move, or an increase in the number of gas particles in the reaction. The ...
Test bank questions
... The system is at equilibrium, thus no concentration changes will occur. The concentrations of HI and I2 will increase as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentration of HI will increase as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentrations of H2 and HI will fall as the system moves toward ...
... The system is at equilibrium, thus no concentration changes will occur. The concentrations of HI and I2 will increase as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentration of HI will increase as the system approaches equilibrium. The concentrations of H2 and HI will fall as the system moves toward ...
laman web smk raja perempuan, ipoh
... Cl2CHCOOH and CI3CCOOH ; between CH2CH2CH2COOH and CH3CH2CHCICOOH 21. use the concept of delocalisation of electrons to explain the differences in acidity between ethanol and phenol, as well as the differences in basicity between CH3NH2 and C6H5NH2 Candidates should be able to : 1. explain alkanes a ...
... Cl2CHCOOH and CI3CCOOH ; between CH2CH2CH2COOH and CH3CH2CHCICOOH 21. use the concept of delocalisation of electrons to explain the differences in acidity between ethanol and phenol, as well as the differences in basicity between CH3NH2 and C6H5NH2 Candidates should be able to : 1. explain alkanes a ...
Oxidation
... H2SO4(aq) + 2 KOH(aq) K2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l) 2 H3PO4(aq) + 3 Ba(OH)2(aq) Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6 H2O(l) HNO3(aq) + NH3(aq) NH4NO3(aq) 2 HBr(aq) + K2CO3(aq) 2 KBr(aq) + H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) HI(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) NaI(aq) + H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) ...
... H2SO4(aq) + 2 KOH(aq) K2SO4(aq) + 2 H2O(l) 2 H3PO4(aq) + 3 Ba(OH)2(aq) Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6 H2O(l) HNO3(aq) + NH3(aq) NH4NO3(aq) 2 HBr(aq) + K2CO3(aq) 2 KBr(aq) + H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) HI(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) NaI(aq) + H2CO3(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) ...
Document
... in the analysis of a wide variety of enantiomeric and diastereomeric guests. Recent work in our laboratory has shown that the intercalation of chiral cationic host molecules into R-zirconium phosphate, a lamellar cation exchanger, provides a useful medium for batchwise resolution of racemic mixtures ...
... in the analysis of a wide variety of enantiomeric and diastereomeric guests. Recent work in our laboratory has shown that the intercalation of chiral cationic host molecules into R-zirconium phosphate, a lamellar cation exchanger, provides a useful medium for batchwise resolution of racemic mixtures ...
ExamView - 2002 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... (1) Test Questions are Copyright © 1984-2002 by College Entrance Examination Board, Princeton, NJ. All rights reserved. For face-to-face teaching purposes, classroom teachers are permitted to reproduce the questions. Web or Mass distribution prohibited. (2) AP® is a registered trademark of the Colle ...
... (1) Test Questions are Copyright © 1984-2002 by College Entrance Examination Board, Princeton, NJ. All rights reserved. For face-to-face teaching purposes, classroom teachers are permitted to reproduce the questions. Web or Mass distribution prohibited. (2) AP® is a registered trademark of the Colle ...
H2-rich fluids from serpentinization: Geochemical and biotic
... compounds in this situation (25). More transient reducing atmospheres from the oxidation of metallic Fe occurred after large asteroid impacts (26). In both cases, the presence of H2 increases the yield of complex organic compounds (27). Similarly, complex organic compounds formed within the highly r ...
... compounds in this situation (25). More transient reducing atmospheres from the oxidation of metallic Fe occurred after large asteroid impacts (26). In both cases, the presence of H2 increases the yield of complex organic compounds (27). Similarly, complex organic compounds formed within the highly r ...
Net Ionic Equation Powerpoint Tutorial
... Again, try to figure this one out on your own right now. The possible cross-products are Na with I and H with CO3. Na-I is not insoluble (by rule #1); it’s not a weak acid; and it’s not a decomposer. Na and I have decided to take the rest of the day off! H-CO3 is not insoluble (by rule #3); it is a ...
... Again, try to figure this one out on your own right now. The possible cross-products are Na with I and H with CO3. Na-I is not insoluble (by rule #1); it’s not a weak acid; and it’s not a decomposer. Na and I have decided to take the rest of the day off! H-CO3 is not insoluble (by rule #3); it is a ...
LECTURE PPT: Chapter 8
... • MTBE (methyl tertiary butyl ether, CH3OC(CH3)3) was the additive of choice by the oil companies. • MTBE is a compound that does not biodegrade readily. • MTBE made its way into drinking water through gasoline spills at gas stations, from boat motors, and from leaking underground storage tanks. • E ...
... • MTBE (methyl tertiary butyl ether, CH3OC(CH3)3) was the additive of choice by the oil companies. • MTBE is a compound that does not biodegrade readily. • MTBE made its way into drinking water through gasoline spills at gas stations, from boat motors, and from leaking underground storage tanks. • E ...
5. Stoichiometry - Sakshi Education
... • In O2F2 and OF2 oxygen oxidation states are +1 and +2 respectively. • Transition elements exhibit more than one oxidation state. • Osmium and Ruthenium show the highest oxidation state i.e. +8. • The oxidation state of any atom in its elementary state is zero. • Nitrogen exhibits large number of o ...
... • In O2F2 and OF2 oxygen oxidation states are +1 and +2 respectively. • Transition elements exhibit more than one oxidation state. • Osmium and Ruthenium show the highest oxidation state i.e. +8. • The oxidation state of any atom in its elementary state is zero. • Nitrogen exhibits large number of o ...
The reaction pathways of hydrogen peroxide in
... enthalpy, entropy and free energy of the transition states of the formation and breakdown of the intermediate have been calculated. The metal-catalyzed pathway of hydrogen peroxide is dealing with the effect of hydroxyl radicals created by the Fenton reaction and their potential to oxidize the disul ...
... enthalpy, entropy and free energy of the transition states of the formation and breakdown of the intermediate have been calculated. The metal-catalyzed pathway of hydrogen peroxide is dealing with the effect of hydroxyl radicals created by the Fenton reaction and their potential to oxidize the disul ...
Sugar Amino Acids - The Krasavin research group
... Ag2 O, followed by esterification with diazomethane, and final catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C catalysis to give the final furanoid α-amino acid 5, as the α- or β-anomer, depending on the stereochemistry of starting thiazolyl ketol acetate. This approach was also reported for a galacto-derived pyr ...
... Ag2 O, followed by esterification with diazomethane, and final catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C catalysis to give the final furanoid α-amino acid 5, as the α- or β-anomer, depending on the stereochemistry of starting thiazolyl ketol acetate. This approach was also reported for a galacto-derived pyr ...
Redox
... loses all of its valence electrons. When this occurs it goes from a neutral atom (0 charge) to a cation with a positive charge of: ...
... loses all of its valence electrons. When this occurs it goes from a neutral atom (0 charge) to a cation with a positive charge of: ...
Task 4 6 points - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... The lab assistand carrying out the experiments labeled the samples “A“ and “B“, conducted the measurements, wrote down the results and then left for lunch. On his return, however, he unfortunately had forgotten which substance actually was “A“ and which was “B“. ...
... The lab assistand carrying out the experiments labeled the samples “A“ and “B“, conducted the measurements, wrote down the results and then left for lunch. On his return, however, he unfortunately had forgotten which substance actually was “A“ and which was “B“. ...
Theoretical problems
... The acids which are stronger than pure sulfuric acid are called superacids. Superacids are very strong proton donors being capable of protonating even weak Lewis acids such as Xe, H2, Cl2, Br2, and CO2. Cations, which never exist in other media, have been observed in superacid solutions. George Olah ...
... The acids which are stronger than pure sulfuric acid are called superacids. Superacids are very strong proton donors being capable of protonating even weak Lewis acids such as Xe, H2, Cl2, Br2, and CO2. Cations, which never exist in other media, have been observed in superacid solutions. George Olah ...
Examination - SCSA - School Curriculum and Standards Authority
... CH3CH3 CH3CH2OH CH3CHO CH3COOH CH3CH3 CH3CHO CH3CH2OH CH3COOH CH3CH2OH CH3CH3 CH3COOH CH3CHO CH3COOH CH3CHO CH3CH2OH CH3CH3 ...
... CH3CH3 CH3CH2OH CH3CHO CH3COOH CH3CH3 CH3CHO CH3CH2OH CH3COOH CH3CH2OH CH3CH3 CH3COOH CH3CHO CH3COOH CH3CHO CH3CH2OH CH3CH3 ...
Learning Outcomes
... (e) deduce from the given melting point and boiling point the identities of substances and their purity ......................................................................................................................................... 13 (f) explain that the measurement of purity in substance ...
... (e) deduce from the given melting point and boiling point the identities of substances and their purity ......................................................................................................................................... 13 (f) explain that the measurement of purity in substance ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.