Inorganometallic Chemistry
... resulting ion, the ratio of the ionic charge to its radius, and σ–donor, σ-acceptor, πdonor and π-acceptor properties of ligands and their structure. The main group elements have four valence orbitals ns and np, while the transition metals have nine valences orbitals (n-1)d, ns, and np. Therefore, t ...
... resulting ion, the ratio of the ionic charge to its radius, and σ–donor, σ-acceptor, πdonor and π-acceptor properties of ligands and their structure. The main group elements have four valence orbitals ns and np, while the transition metals have nine valences orbitals (n-1)d, ns, and np. Therefore, t ...
Class-X Science - Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan Regional Office
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Damoh
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No.1, Satna
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
X -Science Support Material
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
... Hydronium Ions: They are formed by reaction of H+ (from acid) and H2O. It is because H+ is unstable. Universal Indicator: A universal indicator is a mixture of indicators which shows a gradual but well-marked series of colour changes over a very wide range of change in concentration of H+ ion. Stron ...
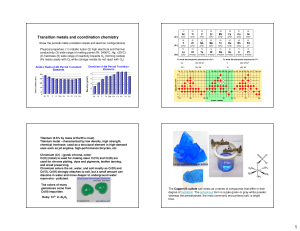
Transition metals and coordination chemistry
... Classify the following ligands as monodentate, bidentate, or tridentate. ...
... Classify the following ligands as monodentate, bidentate, or tridentate. ...
Equilibrium - District 196
... • Sometimes at equilibrium, there is a higher concentration of reactants or products • To determine this by: • 1. Looking at the equilibrium constant • 2. Looking at the reversible arrows shown in the equation ...
... • Sometimes at equilibrium, there is a higher concentration of reactants or products • To determine this by: • 1. Looking at the equilibrium constant • 2. Looking at the reversible arrows shown in the equation ...
Non-native transition metal monoxide nanostructures
... properties.11–14 Importantly, thermodynamically unstable phases can be stabilized by coupling the excess surface energy of nanomaterials with careful control of kinetic parameters in synthetic reactions. For instance, the cubic phase of MnSe is generally stable in bulk powders and thin films, but the ...
... properties.11–14 Importantly, thermodynamically unstable phases can be stabilized by coupling the excess surface energy of nanomaterials with careful control of kinetic parameters in synthetic reactions. For instance, the cubic phase of MnSe is generally stable in bulk powders and thin films, but the ...
Glossary - Chemistry (Intro)
... Notation of E.: Elements of the periodic table are assigned with a mass- and atomic number to quantify its number of protons (Z) and number of protons and neutrons (A); see chemistry atom. Representative E.: Elements in groups 1A through 7A, all of which have incompletely filled s or p subshell of h ...
... Notation of E.: Elements of the periodic table are assigned with a mass- and atomic number to quantify its number of protons (Z) and number of protons and neutrons (A); see chemistry atom. Representative E.: Elements in groups 1A through 7A, all of which have incompletely filled s or p subshell of h ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
Chapter 8 and 9 homework
... 16. 17.5 mL of a 0.1050 M Na2CO3 solution is added to 46.0 mL of 0.1250 M NaCl. What is the concentration of sodium ion in the final solution? 17.25.0 mL of a 0.2450 M NH4Cl solution is added to 55.5 mL of 0.1655 M FeCl3. What is the concentration of chloride ion in the final solution? 18.When 38.0 ...
... 16. 17.5 mL of a 0.1050 M Na2CO3 solution is added to 46.0 mL of 0.1250 M NaCl. What is the concentration of sodium ion in the final solution? 17.25.0 mL of a 0.2450 M NH4Cl solution is added to 55.5 mL of 0.1655 M FeCl3. What is the concentration of chloride ion in the final solution? 18.When 38.0 ...
Chemistry - Tumkur University
... Recapitulation of s- and p-Block Elements Periodicity in s- and p-block elements with respect to electronic configuration, atomic and ionic size, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity (Pauling, Mulliken, and Alfred-Rochow scales).Allotropy in C, S, and P. Inert pair effect, diagonal relationship an ...
... Recapitulation of s- and p-Block Elements Periodicity in s- and p-block elements with respect to electronic configuration, atomic and ionic size, ionization enthalpy, electronegativity (Pauling, Mulliken, and Alfred-Rochow scales).Allotropy in C, S, and P. Inert pair effect, diagonal relationship an ...
DRAFT AP® CHEMISTRY 2005 SCORING GUIDELINES
... Should accept oxygen gas causes splint to RE_IGNITE. The popping sound presumed the accessibility of oxygen, which is not explicit in the directions. What to do if a student claims that the splint will be extinguished? I would give the credit. Also, would accept ‘re-ignite’ for oxygen. I have a prob ...
... Should accept oxygen gas causes splint to RE_IGNITE. The popping sound presumed the accessibility of oxygen, which is not explicit in the directions. What to do if a student claims that the splint will be extinguished? I would give the credit. Also, would accept ‘re-ignite’ for oxygen. I have a prob ...
Step 2
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
... number to each element wherever it appears in the equation. If the reaction is a redox reaction, identify the element that undergoes an increase in oxidation number and the elements the undergoes a decrease. Find the numerical values of the increase and decrease. Determine the smallest whole-number ...
Combinatorial chemistry: A novel method in drug discovery and its
... light in the preceding step. The solution of amino acid is removed and the substrate is again illuminated through a second mask, activating a different region for reaction with a second protected building lock. The pattern of masks and sequence of reactance define the products and their location. Si ...
... light in the preceding step. The solution of amino acid is removed and the substrate is again illuminated through a second mask, activating a different region for reaction with a second protected building lock. The pattern of masks and sequence of reactance define the products and their location. Si ...
EVANS GROUP RESEARCH PROJECT DESCRIPTIONS
... generally carboxylates derived from industrially available carboxylic acids (mixtures of isomers of versatic acid, octanoic acid, or naphthenoic acid), are the starting materials. These ill-defined carboxylates are then treated with an ethylaluminum chloride compound, e.g. EtAlCl2 or Et2AlCl, to for ...
... generally carboxylates derived from industrially available carboxylic acids (mixtures of isomers of versatic acid, octanoic acid, or naphthenoic acid), are the starting materials. These ill-defined carboxylates are then treated with an ethylaluminum chloride compound, e.g. EtAlCl2 or Et2AlCl, to for ...
Chemistry Skills Practice Assignments
... 1. On each of the phase diagrams label the triple point (TP) and the solid, liquid and vapor states. 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allo ...
... 1. On each of the phase diagrams label the triple point (TP) and the solid, liquid and vapor states. 2. For which substance, A or B, does the freezing point decrease as the pressure is increased? 3. One of the substances behaves more like most other substances. Which substance and what property allo ...
Gas Laws
... 15. Write a balance equation and label the states of the reactants and products for each the reactions. After writing the balanced equation, write the net ionic equations below the balanced equation. If there is no driving force for a reaction, write no reaction in place of the net ionic equation. ...
... 15. Write a balance equation and label the states of the reactants and products for each the reactions. After writing the balanced equation, write the net ionic equations below the balanced equation. If there is no driving force for a reaction, write no reaction in place of the net ionic equation. ...
Stoichiometry, Lab Basics, Reactions
... ____ 19. Equal masses of three different ideal gases, X, Y, and Z, are mixed in a sealed rigid container. If the temperature of the system remains constant, which of the following statements about the partial pressure of gas X is correct? A) It is equal to 1/3 of the total pressure. B) It depends on ...
... ____ 19. Equal masses of three different ideal gases, X, Y, and Z, are mixed in a sealed rigid container. If the temperature of the system remains constant, which of the following statements about the partial pressure of gas X is correct? A) It is equal to 1/3 of the total pressure. B) It depends on ...
File
... 29. Write balanced equations for the following reactions. (Be sure to get the FORMULAS right! Part credit awarded for correct formulas) Equations must be balanced using the smallest possible whole number coefficients. ( 12 pts, 3,2,3,2,2) a) Magnesium + silver nitrate magnesium nitrate + silver ...
... 29. Write balanced equations for the following reactions. (Be sure to get the FORMULAS right! Part credit awarded for correct formulas) Equations must be balanced using the smallest possible whole number coefficients. ( 12 pts, 3,2,3,2,2) a) Magnesium + silver nitrate magnesium nitrate + silver ...
Prep UK-intro.p65
... problems. For the solutions of physical chemistry problems the units of the equilibrium constant, depending on the particular circumstances, have to be specified. If the constant appears in thermodynamic equations, the equilibrium constant (Ka) is dimensionless and its value depends on the choice of ...
... problems. For the solutions of physical chemistry problems the units of the equilibrium constant, depending on the particular circumstances, have to be specified. If the constant appears in thermodynamic equations, the equilibrium constant (Ka) is dimensionless and its value depends on the choice of ...
Chapter 1: Aqueous Processing Systems
... For many years the study of the electronic structure and properties of solids has been regarded as the preserve of physicists. Chemists, who spend a good deal of time and effort looking at electronic structures of molecules, have tended to avoid these aspects of solids. The situation is changing, ho ...
... For many years the study of the electronic structure and properties of solids has been regarded as the preserve of physicists. Chemists, who spend a good deal of time and effort looking at electronic structures of molecules, have tended to avoid these aspects of solids. The situation is changing, ho ...
Acids and Bases
... Now let’s see how we knew that water acts as a base in the first reaction in Section 2.1 and as an acid in the second reaction. To determine which of the reactants will be the acid, we need to compare their pKa values: The pKa of hydrogen chloride is -7 and the pKa of water is 15.7. Because hydrogen ...
... Now let’s see how we knew that water acts as a base in the first reaction in Section 2.1 and as an acid in the second reaction. To determine which of the reactants will be the acid, we need to compare their pKa values: The pKa of hydrogen chloride is -7 and the pKa of water is 15.7. Because hydrogen ...
chemistry sp.indd
... 23 Under the Montreal Protocol, the manufacture of chlorofluorocarbons has been phased out, and they are being replaced by fluorocarbons. One chlorofluorocarbon which was widely used as a solvent is CCl2FCClF2. Large stocks of it remain. One process to use up these stocks is to convert it into the f ...
... 23 Under the Montreal Protocol, the manufacture of chlorofluorocarbons has been phased out, and they are being replaced by fluorocarbons. One chlorofluorocarbon which was widely used as a solvent is CCl2FCClF2. Large stocks of it remain. One process to use up these stocks is to convert it into the f ...
REDOX EQUILIBRIA SL - chemistryatdulwich
... When metals react they lose electrons or are oxidized, when non-metals react they gain electrons or are reduced. Therefore the reactivity of a metal or non-metal is about how easily it is oxidized or reduced or how strong a reducing or oxidizing agent it is. The strength of an oxidising or reducing ...
... When metals react they lose electrons or are oxidized, when non-metals react they gain electrons or are reduced. Therefore the reactivity of a metal or non-metal is about how easily it is oxidized or reduced or how strong a reducing or oxidizing agent it is. The strength of an oxidising or reducing ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.