Chapter 8
... We can interpret this equation in two ways: 1) Two molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen combine to form two molecules of water. 2) Two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen combine to form two moles of water. Note that the second interpretation makes sense even if we have ...
... We can interpret this equation in two ways: 1) Two molecules of hydrogen and one molecule of oxygen combine to form two molecules of water. 2) Two moles of hydrogen and one mole of oxygen combine to form two moles of water. Note that the second interpretation makes sense even if we have ...
Oxidation numbers
... The oxidation number of carbon in the products is 0 and in the reactants it is +4 The oxidation number has increased (become more positive). The oxidation number of oxygen in the products is 0 and in the reactants it is −2 The oxidation number has decreased (become more negative). 2. In the compound ...
... The oxidation number of carbon in the products is 0 and in the reactants it is +4 The oxidation number has increased (become more positive). The oxidation number of oxygen in the products is 0 and in the reactants it is −2 The oxidation number has decreased (become more negative). 2. In the compound ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry STOICHIOMETRY: The chemical arithmetic
... With a 50 % Yield, How many moles of NH3 are produced from (a) 3 grams of H2 and ½ mole of N2? ½ mole = (½ mole)x(17 g/mole) grams of NH3 (b) 3 grams of H2 and 28 grams of N2? ...
... With a 50 % Yield, How many moles of NH3 are produced from (a) 3 grams of H2 and ½ mole of N2? ½ mole = (½ mole)x(17 g/mole) grams of NH3 (b) 3 grams of H2 and 28 grams of N2? ...
F:\Users\Steven\Documents\Chemistry\CHEM120\Problem Set
... When I went to write this problem I looked at the periodic table and saw that Rubidium had a mass of 85.467. Since the mass of all isotopes are even (or nearly so) and this average was uneven I knew immediately that rubidium had to have two major isotopes. When I looked up the isotopes sure enough t ...
... When I went to write this problem I looked at the periodic table and saw that Rubidium had a mass of 85.467. Since the mass of all isotopes are even (or nearly so) and this average was uneven I knew immediately that rubidium had to have two major isotopes. When I looked up the isotopes sure enough t ...
Chapter 9 - HCC Learning Web
... 62. In the Lewis structure of the iodate ion, IO3-, that satisfies the octet rule, the formal charge on the central iodine atom is A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 62. In the Lewis structure of the iodate ion, IO3-, that satisfies the octet rule, the formal charge on the central iodine atom is A. B. C. D. E. ...
CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
... there are an ____________________ number of equilibrium positions. 11. The specific equilibrium position adopted by a system depends on the initial concentrations, but the equilibrium constant does not. EQUILIBRIUM EXPRESSIONS INVOLVING PRESSURES ...
... there are an ____________________ number of equilibrium positions. 11. The specific equilibrium position adopted by a system depends on the initial concentrations, but the equilibrium constant does not. EQUILIBRIUM EXPRESSIONS INVOLVING PRESSURES ...
TOPIC 11 Further equilibrium 11.1 Chemical equilibrium
... The value of Kc does not change (1). Only a change in temperature can change the value of an equilibrium constant (1). The value of Kc increases (1). The forward reaction is endothermic so the position of equilibrium shifts to the right, increasing [HI(g)] whilst decreasing [H 2(g)] and [I2(g)] (1). ...
... The value of Kc does not change (1). Only a change in temperature can change the value of an equilibrium constant (1). The value of Kc increases (1). The forward reaction is endothermic so the position of equilibrium shifts to the right, increasing [HI(g)] whilst decreasing [H 2(g)] and [I2(g)] (1). ...
BS Chemistry - Government College University Faisalabad
... Basic concepts in chemical bonding Localized and delocalized bonding. Concept of hybridization leading to bond angles, bond energies and geometry of simple organic molecules; dipole moment; inductive effect; resonance, resonance energy, rules of resonance, resonance effect, steric inhibition of reso ...
... Basic concepts in chemical bonding Localized and delocalized bonding. Concept of hybridization leading to bond angles, bond energies and geometry of simple organic molecules; dipole moment; inductive effect; resonance, resonance energy, rules of resonance, resonance effect, steric inhibition of reso ...
Chapter 9 Lota_2 Dæmi A4 Varmafræði
... The specific heat of gold is 0.13 J g–1 K–1, and that of copper is 0.39 J g–1 K–1. Suppose that we heat both a 25-g sample of gold and a 25-g sample of copper to 80°C and then drop each into identical beakers containing 100 mL of cold water at 10°C. When each beaker reaches thermal equilibrium, whic ...
... The specific heat of gold is 0.13 J g–1 K–1, and that of copper is 0.39 J g–1 K–1. Suppose that we heat both a 25-g sample of gold and a 25-g sample of copper to 80°C and then drop each into identical beakers containing 100 mL of cold water at 10°C. When each beaker reaches thermal equilibrium, whic ...
HSC Chemistry Syllabus Notes 2007
... 3. Manufactured products, including food, drugs and household chemicals, are analysed to determine or ensure their chemical composition66 4. Human activity has caused changes in the composition and the structure of the atmosphere. Chemists monitor these changes so that further damage can be limited ...
... 3. Manufactured products, including food, drugs and household chemicals, are analysed to determine or ensure their chemical composition66 4. Human activity has caused changes in the composition and the structure of the atmosphere. Chemists monitor these changes so that further damage can be limited ...
doc - Dartmouth College
... tall. Suppose a column of Hg is set up where the bath is open to the atmosphere, and the column height of Hg is 760.0 mm with the top of the enclosed column being a vacuum. Next, suppose some diethyl ether (a volatile liquid) is injected into the top of the vacuum above the Hg column such that the s ...
... tall. Suppose a column of Hg is set up where the bath is open to the atmosphere, and the column height of Hg is 760.0 mm with the top of the enclosed column being a vacuum. Next, suppose some diethyl ether (a volatile liquid) is injected into the top of the vacuum above the Hg column such that the s ...
14.1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq , and the Mass Action Expression
... When making assumptions, if a reaction has a relatively small keq and a relatively large initial reactant concentration, then the concentration change (x) can often be neglected without introducing significant error. This does not mean x = 0, because then this would mean there is no reaction. It mea ...
... When making assumptions, if a reaction has a relatively small keq and a relatively large initial reactant concentration, then the concentration change (x) can often be neglected without introducing significant error. This does not mean x = 0, because then this would mean there is no reaction. It mea ...
Unit 7 Homework and Lab Packet
... o What would happen if too much air bag chemical were put into an airbag? o What would happen if not enough air bag chemical were put into an airbag? Iowa Core Essential Concepts and Skills -Design and conduct scientific investigations -Use technology and mathematics to improve investigations and co ...
... o What would happen if too much air bag chemical were put into an airbag? o What would happen if not enough air bag chemical were put into an airbag? Iowa Core Essential Concepts and Skills -Design and conduct scientific investigations -Use technology and mathematics to improve investigations and co ...
contact - DTU Kemi
... ephedrine – all “household names” – are members of the alkaloid family, a group of naturally occurring compounds containing nitrogen atoms. Besides these well-known examples, a large variety of other alkaloids exist. Many of these occur in nature, while others are synthetic, typically produced as dr ...
... ephedrine – all “household names” – are members of the alkaloid family, a group of naturally occurring compounds containing nitrogen atoms. Besides these well-known examples, a large variety of other alkaloids exist. Many of these occur in nature, while others are synthetic, typically produced as dr ...
Quaternary Neptunium Compounds: Syntheses and
... 99.99%), and S (Mallinckrodt, 99.6%). Brittle 237Np chunks (ORNL, 99.99%) were crushed and used as provided. The reactive fluxes40 used in these syntheses, K2S, Rb2S3, and Cs2S3, were prepared by stoichiometric reactions of the elements in liquid NH3. Caution! 237Np is an R- and γ-emitting radioisot ...
... 99.99%), and S (Mallinckrodt, 99.6%). Brittle 237Np chunks (ORNL, 99.99%) were crushed and used as provided. The reactive fluxes40 used in these syntheses, K2S, Rb2S3, and Cs2S3, were prepared by stoichiometric reactions of the elements in liquid NH3. Caution! 237Np is an R- and γ-emitting radioisot ...
Amidine: Structure, Reactivity and Complexation Behaviour
... corresponds to isomer(fig5b) with cis oriented chloro ligands and trans oriented imino donar sites of the heterotropic iminohydroxamato ligands. To evaluate the catalytic performance of these above complexes a standard polymerization procedure was applied. In term of activity, all [N,O] and [N,N] zi ...
... corresponds to isomer(fig5b) with cis oriented chloro ligands and trans oriented imino donar sites of the heterotropic iminohydroxamato ligands. To evaluate the catalytic performance of these above complexes a standard polymerization procedure was applied. In term of activity, all [N,O] and [N,N] zi ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... These are not listed in order of priority. Many of these Aims are reflected in the Assessment Objectives which follow; others are not readily assessed. The syllabus aims are to: ...
... These are not listed in order of priority. Many of these Aims are reflected in the Assessment Objectives which follow; others are not readily assessed. The syllabus aims are to: ...
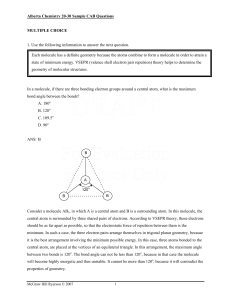
Alberta Chemistry 20-30 Sample CAB Questions - McGraw
... central atom is surrounded by three shared pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, these electrons should be as far apart as possible, so that the electrostatic force of repulsion between them is the minimum. In such a case, the three electron pairs arrange themselves in trigonal planar geome ...
... central atom is surrounded by three shared pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, these electrons should be as far apart as possible, so that the electrostatic force of repulsion between them is the minimum. In such a case, the three electron pairs arrange themselves in trigonal planar geome ...
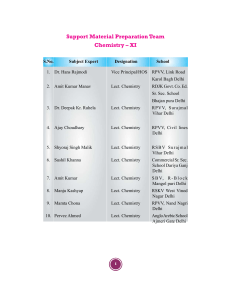
Support Material
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions (John Dalton) : When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, then the different masses of one element, which combine with a ®xed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another. Gay Lussac’s Law : When gases combine or are produced in a chemical reac ...
Reactions of Plutonium Dioxide with Water and Oxygen
... below 10(YC and dcsorbs at higher temperatures, while reacting at a relatively slow rate to form a higher oxide, PU02+X,and H2. Exposure of a 21, mixture of H2+02 to the dioxide at 2S”C results in surkice-catalyzed formatjon of water, a product that subsequently reacts via a catalytic cycle , ~at c6 ...
... below 10(YC and dcsorbs at higher temperatures, while reacting at a relatively slow rate to form a higher oxide, PU02+X,and H2. Exposure of a 21, mixture of H2+02 to the dioxide at 2S”C results in surkice-catalyzed formatjon of water, a product that subsequently reacts via a catalytic cycle , ~at c6 ...
Chapter 8 Quantities in Chemical Reactions
... • MTBE (methyl tertiary butyl ether, CH3OC(CH3)3) was the additive of choice by the oil companies. • MTBE is a compound that does not biodegrade readily. • MTBE made its way into drinking water through gasoline spills at gas stations, from boat motors, and from leaking underground storage tanks. • E ...
... • MTBE (methyl tertiary butyl ether, CH3OC(CH3)3) was the additive of choice by the oil companies. • MTBE is a compound that does not biodegrade readily. • MTBE made its way into drinking water through gasoline spills at gas stations, from boat motors, and from leaking underground storage tanks. • E ...
Problem 1-2 - IPN-Kiel
... iv) Calcium Which acid/base properties do the aqueous solutions of the products show? ...
... iv) Calcium Which acid/base properties do the aqueous solutions of the products show? ...
ppt
... Explain the concept of chemical equilibrium and how it applies to the concentration of reactants and products in a chemical reaction at equilibrium. Create and complete an ICE table for an equilibrium system. Draw graphs of c vs. t to illustrate a chemical system approaching equilibrium. Use appropr ...
... Explain the concept of chemical equilibrium and how it applies to the concentration of reactants and products in a chemical reaction at equilibrium. Create and complete an ICE table for an equilibrium system. Draw graphs of c vs. t to illustrate a chemical system approaching equilibrium. Use appropr ...
Laboratory Manual
... oing to a new school can be very exciting and challenging. There are always a lot of things to learn, such as the location of your classes, the library, cafeteria, and gym. You also have new rules to learn and what some things are called. When you walk into a chemistry laboratory the first time, the ...
... oing to a new school can be very exciting and challenging. There are always a lot of things to learn, such as the location of your classes, the library, cafeteria, and gym. You also have new rules to learn and what some things are called. When you walk into a chemistry laboratory the first time, the ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.