spontaneous change: entropy and free energy
... that, for the same total energy, in the expanded volume there are more available translational energy levels among which the gas molecules can be distributed. The tendency is for the energy of the system to spread out over a larger number of energy levels. A similar situation—the mixing of ideal gas ...
... that, for the same total energy, in the expanded volume there are more available translational energy levels among which the gas molecules can be distributed. The tendency is for the energy of the system to spread out over a larger number of energy levels. A similar situation—the mixing of ideal gas ...
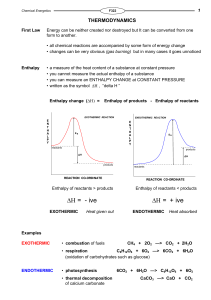
Enthalpy change
... • a substance will then be in its standard state ... Pressure:- 100 kPa (1 atm) ...
... • a substance will then be in its standard state ... Pressure:- 100 kPa (1 atm) ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the "kinetic model" of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS - Clayton State University
... Department of natural sciences Clayton state university ...
... Department of natural sciences Clayton state university ...
chem textbook 2015 - Manitowoc Public School District
... At times it may be beneficial to work with other members of your class or prior chemistry students as they may present material in a different manner than I that could resonate with you and enhance your learning. However I do caution that this relationship can quickly degrade to a scenario in which ...
... At times it may be beneficial to work with other members of your class or prior chemistry students as they may present material in a different manner than I that could resonate with you and enhance your learning. However I do caution that this relationship can quickly degrade to a scenario in which ...
answer ch6 - Mr Khaled Nasr
... (15)A reaction which is used for the determination of the concentration of acids and bases. (16)A reaction which is used for the determination of the concentration of redox substance. (17)A reaction which is used for the determination of the substances that form sparingly soluble products. (18)The p ...
... (15)A reaction which is used for the determination of the concentration of acids and bases. (16)A reaction which is used for the determination of the concentration of redox substance. (17)A reaction which is used for the determination of the substances that form sparingly soluble products. (18)The p ...
Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions 1
... Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions ...
... Chapter 3 Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the 'kinetic model' of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
... All substances are made up of particles called atoms, ions or molecules, and these particles are constantly moving. The degree of movement depends upon the state of the substance. This is known as the 'kinetic model' of matter. In any sample of solution, liquid or gas there is a range of kinetic ene ...
U6B _13-14
... Complete Ionic Equation: shows all the particles in a solution as they really exist, as IONS or MOLECULES. Anything aqueous needs to be split apart into the cation and anion Anything solid stays intact Coefficients need to be multiplied by subscripts to determine the exact amount of each catio ...
... Complete Ionic Equation: shows all the particles in a solution as they really exist, as IONS or MOLECULES. Anything aqueous needs to be split apart into the cation and anion Anything solid stays intact Coefficients need to be multiplied by subscripts to determine the exact amount of each catio ...
B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry
... The course on B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry was introduced in the University of Delhi in 1984 and since then this course has undergone many changes and has become more comprehensive and relevant. The importance of industrial chemistry hardly needs any emphasis. It basically deals with the development, ...
... The course on B.Sc. Industrial Chemistry was introduced in the University of Delhi in 1984 and since then this course has undergone many changes and has become more comprehensive and relevant. The importance of industrial chemistry hardly needs any emphasis. It basically deals with the development, ...
A Low-Fluorine Solution with the F/Ba Mole Ratio of 2 for the
... Cu and Y salts [8, 9]; (3) Cu and Ba salts [10]. Relative to the conventional TFA-MOD solution (100% fluorine content), the fluorine contents in these precursor solutions could be estimated to be about 53.8%, 30.8% (or 23.1% if the poorBa stoichiometry is used [11]) and 23.1%, respectively. Using a ...
... Cu and Y salts [8, 9]; (3) Cu and Ba salts [10]. Relative to the conventional TFA-MOD solution (100% fluorine content), the fluorine contents in these precursor solutions could be estimated to be about 53.8%, 30.8% (or 23.1% if the poorBa stoichiometry is used [11]) and 23.1%, respectively. Using a ...
LABORATORY MANUAL FOR GENERAL CHEMISTRY I
... 3. Do not eat or drink in the laboratory. 4. Do not taste any chemical. 5. Do not smell any chemicals directly. Use your fingers to waft the odor to your nose. 6. Do not pipet solutions by mouth. Rubber pipet bulbs are provided at each lab station. 7. Do not put flammable liquids near an open flame. ...
... 3. Do not eat or drink in the laboratory. 4. Do not taste any chemical. 5. Do not smell any chemicals directly. Use your fingers to waft the odor to your nose. 6. Do not pipet solutions by mouth. Rubber pipet bulbs are provided at each lab station. 7. Do not put flammable liquids near an open flame. ...
Moles
... You would need 2 moles of Hydrogen to make 2 moles of water 1 mole of oxygen would make 2 moles of water If you made 6 moles of water, how much hydrogen would you need? ...
... You would need 2 moles of Hydrogen to make 2 moles of water 1 mole of oxygen would make 2 moles of water If you made 6 moles of water, how much hydrogen would you need? ...
The Acidic Environment #2
... motor cars. The annual average concentration of SO2 and NO2 in most large cities around the world is 0.01 ppm for each gas. This is about 10 times the value for clean air, though a concentration of 0.01 ppm for either gas is not harmful. Globally, because SO2 and NO2 are washed out of the atmosph ...
... motor cars. The annual average concentration of SO2 and NO2 in most large cities around the world is 0.01 ppm for each gas. This is about 10 times the value for clean air, though a concentration of 0.01 ppm for either gas is not harmful. Globally, because SO2 and NO2 are washed out of the atmosph ...
WRITING CHEMICAL FORMULAE
... HCl particles which are involved. The water is just a carrier for the acid, so when we measure out a volume of the solution, we want to know how much acid it contains. To do this, we need to define the CONCENTRATION of the solution. This tells us how much solute there is in a fixed volume of the sol ...
... HCl particles which are involved. The water is just a carrier for the acid, so when we measure out a volume of the solution, we want to know how much acid it contains. To do this, we need to define the CONCENTRATION of the solution. This tells us how much solute there is in a fixed volume of the sol ...
48th CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD CHEMISTRY
... most important buffer system is a carbonate buffer, which is prepared by a salt (HCO3−) and acid (H2CO3) in molar ratio 20:1 (precisely). The exhaled CO2 is released out from a metacarbonic acid, which participates in equilibrium in a blood. a) For the I and II dissociation stages of metacarbonic ac ...
... most important buffer system is a carbonate buffer, which is prepared by a salt (HCO3−) and acid (H2CO3) in molar ratio 20:1 (precisely). The exhaled CO2 is released out from a metacarbonic acid, which participates in equilibrium in a blood. a) For the I and II dissociation stages of metacarbonic ac ...
CHEM 1212 Module Ten-Chapter 16 Name
... products instead of the equilibrium concentration so as to determine the direction of the equilibrium shift. ___________________5. ____________ ________________ states that if a change is imposed on a system in equilibrium , the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to red ...
... products instead of the equilibrium concentration so as to determine the direction of the equilibrium shift. ___________________5. ____________ ________________ states that if a change is imposed on a system in equilibrium , the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to red ...
June 2000 Practice Diploma
... thermometer contains 3.21 g of mercury. When the thermometer reading changes from 17.3°C to 101.2°C, the mercury has absorbed __________ J of energy. (Record your three-digit answer in the numerical-response section on the answer sheet.) ...
... thermometer contains 3.21 g of mercury. When the thermometer reading changes from 17.3°C to 101.2°C, the mercury has absorbed __________ J of energy. (Record your three-digit answer in the numerical-response section on the answer sheet.) ...
Exam 1
... molecules block the transmission of pain through the central nervous system. The amino acid sequence in one such compound, methionine enkephalin, is Tyr – Gly – Gly – Phe – Met The number of amine, carboxylic acid and amide (peptide) functional groups in this polypeptide is –COOH –CONH –NH2 A. 0 ...
... molecules block the transmission of pain through the central nervous system. The amino acid sequence in one such compound, methionine enkephalin, is Tyr – Gly – Gly – Phe – Met The number of amine, carboxylic acid and amide (peptide) functional groups in this polypeptide is –COOH –CONH –NH2 A. 0 ...
Cl 2
... % Yield = Actual Yield ÷ Theoretical Yield X 100% • The percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a reaction carried out in the laboratory. ...
... % Yield = Actual Yield ÷ Theoretical Yield X 100% • The percent yield is a measure of the efficiency of a reaction carried out in the laboratory. ...
Ans:- (i) Gluconic acid - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2, Kribhco, Surat
... Q-1. What is the non- stoichiometry defect in the crystals? Ans. These defects occur when the ratio of the cations and anions in the resulting compound is different from that as indicated by the laws of the chemical combinations. Q-2. How many atoms are there in a simple or primitive unit cell body ...
... Q-1. What is the non- stoichiometry defect in the crystals? Ans. These defects occur when the ratio of the cations and anions in the resulting compound is different from that as indicated by the laws of the chemical combinations. Q-2. How many atoms are there in a simple or primitive unit cell body ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.