Equilibrium - AP Chemistry
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
Chapter 16: Energy and Chemical Change
... money in each account has changed, the total amount of your money in the bank remains the same. When applied to energy, this analogy embodies the law of conservation of energy. The law of conservation of energy states that in any chemical reaction or physical process, energy can be converted from on ...
... money in each account has changed, the total amount of your money in the bank remains the same. When applied to energy, this analogy embodies the law of conservation of energy. The law of conservation of energy states that in any chemical reaction or physical process, energy can be converted from on ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
Equilibrium - Tenafly High School
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
... • Chemical equilibrium is the point at which the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. At that point, the concentrations of all species are constant. • Using the collision model: – as the amount of NO2 builds up, there is a chance that two NO2 molecules will coll ...
2 - Gordon State College
... Catalysts CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR Carefully examine the following reaction sequence for the catalytic formation of ozone, O3, from molecular oxygen, O2. Which chemical compound is behaving as the catalyst? O2 + 2 NO 2 NO2 2 NO2 2 NO + 2 O 2 O + 2 O 2 2 O3 A. Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 ...
... Catalysts CHECK YOUR NEIGHBOR Carefully examine the following reaction sequence for the catalytic formation of ozone, O3, from molecular oxygen, O2. Which chemical compound is behaving as the catalyst? O2 + 2 NO 2 NO2 2 NO2 2 NO + 2 O 2 O + 2 O 2 2 O3 A. Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 ...
thermodynamics
... gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry cell. Thus, various forms of energy are interrelated and under certain conditions, these may be transformed from one fo ...
... gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry cell. Thus, various forms of energy are interrelated and under certain conditions, these may be transformed from one fo ...
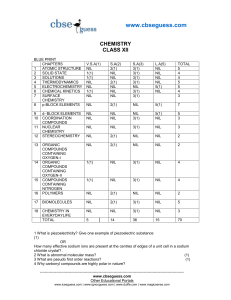
guess paper class xii
... 21 How will you prepare the following compounds from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom. (i) Methyl benzoate (ii) m-nitrobenzoic acid (iii) Phenylacetic acid ...
... 21 How will you prepare the following compounds from benzene? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom. (i) Methyl benzoate (ii) m-nitrobenzoic acid (iii) Phenylacetic acid ...
Organic Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... molecules have no electrical charge, many of them such as haloalkanes (R-X), alcohols (ROH), and amines (R-NH2) have polar bonds. [graphic 3.7] Electron Distribution in Polar Bonds. Chemical bonds are polar when the electron distribution in their bonding molecular orbital is not symmetrically distri ...
... molecules have no electrical charge, many of them such as haloalkanes (R-X), alcohols (ROH), and amines (R-NH2) have polar bonds. [graphic 3.7] Electron Distribution in Polar Bonds. Chemical bonds are polar when the electron distribution in their bonding molecular orbital is not symmetrically distri ...
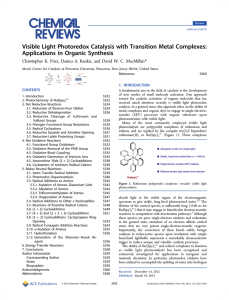
Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis with Transition
... not amenable to redox neutral transformations. Furthermore, single-electron-transfer events often provide access to radical ion intermediates having reactivity patterns fundamentally different from those of their ground electronic or excited states.14 Access to these intermediates using other means o ...
... not amenable to redox neutral transformations. Furthermore, single-electron-transfer events often provide access to radical ion intermediates having reactivity patterns fundamentally different from those of their ground electronic or excited states.14 Access to these intermediates using other means o ...
18-19 SpontEnt
... SPONTANEITY AND WORK Is this process spontaneous? Can this process do work? What is the reverse of this process? Is the reverse process spontaneous? ...
... SPONTANEITY AND WORK Is this process spontaneous? Can this process do work? What is the reverse of this process? Is the reverse process spontaneous? ...
Lab announcements – 2 lab quiz week before spring break
... Lab announcements – 2nd lab quiz week before spring break photocopy before turning in or study before turning in -same as 101/other 102 sections be extra careful with dilutions this week (Expt. 21) Most chemical reactions do not go to completion. chemical equilibrium – two opposing reactions occur s ...
... Lab announcements – 2nd lab quiz week before spring break photocopy before turning in or study before turning in -same as 101/other 102 sections be extra careful with dilutions this week (Expt. 21) Most chemical reactions do not go to completion. chemical equilibrium – two opposing reactions occur s ...
Table of Contents - slccscience`s Home Page
... and its compounds. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon and its compounds. Since there are 117 known elements, it often seems odd that an entire branch of chemistry is devoted to a single element and its compounds while the other 116 elements and their compounds are all lumped together in a sepa ...
... and its compounds. Organic chemistry is the study of carbon and its compounds. Since there are 117 known elements, it often seems odd that an entire branch of chemistry is devoted to a single element and its compounds while the other 116 elements and their compounds are all lumped together in a sepa ...
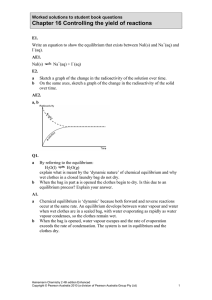
Chapter 16 Controlling the yield of reactions
... a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium 0.44 mol of H2 and 0.44 mol of I2 were present. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature. c A third mixture consisted of ...
... a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium 0.44 mol of H2 and 0.44 mol of I2 were present. Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature. c A third mixture consisted of ...
Rubidium
... This element is considered to be the 16th most abundant element in the earth's crust. It occurs naturally in the minerals leucite, pollucite, and zinnwaldite, which contains traces of up to 1% of its oxide. Lepidolite contains 1.5% rubidium and this is the commercial source of the element. Some pota ...
... This element is considered to be the 16th most abundant element in the earth's crust. It occurs naturally in the minerals leucite, pollucite, and zinnwaldite, which contains traces of up to 1% of its oxide. Lepidolite contains 1.5% rubidium and this is the commercial source of the element. Some pota ...
Acid-Base
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
Chapter 19: Acids and Bases
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
... You now know that HCl and HF are acids because they can donate a hydrogen ion in an acid-base reaction. From their chemical formulas, you can see that each acid can donate only one hydrogen ion per molecule. An acid that can donate only one hydrogen ion is called a monoprotic acid. Other monoprotic ...
Catalysts Containing Depleted Uranium Compounds
... are easy for recycling, whereas reaction products can be readily purified. It has been revealed that complexes of U4+ è U6+ are bright coloured, readily forming acilated ions, not forming complexes with ketones and aromatic esters. A possible mechanism for acylation reaction involving uranium salts ...
... are easy for recycling, whereas reaction products can be readily purified. It has been revealed that complexes of U4+ è U6+ are bright coloured, readily forming acilated ions, not forming complexes with ketones and aromatic esters. A possible mechanism for acylation reaction involving uranium salts ...
inorganic chemistry
... Halogens are highly reactive, and as such can be harmful or lethal to biological organisms in sufficient quantities. This high reactivity is due to the atoms being highly electronegative due to their high effective nuclear charge. They can gain an electron by reacting with atoms of other elements. F ...
... Halogens are highly reactive, and as such can be harmful or lethal to biological organisms in sufficient quantities. This high reactivity is due to the atoms being highly electronegative due to their high effective nuclear charge. They can gain an electron by reacting with atoms of other elements. F ...
Chapter 16: Energy and Chemical Change
... about the caloric content of various foods. When your body breaks down sugars and fats to form carbon dioxide and water, these exothermic reactions generate heat that can be measured in Calories. Note that the nutritional Calorie is capitalized. That’s because one nutritional Calorie, also known as ...
... about the caloric content of various foods. When your body breaks down sugars and fats to form carbon dioxide and water, these exothermic reactions generate heat that can be measured in Calories. Note that the nutritional Calorie is capitalized. That’s because one nutritional Calorie, also known as ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... So far in this text, when we present a chemical reaction, we have implicitly assumed that the reaction goes to completion. Indeed, our stoichiometric calculations were based on this; when we asked how much of a product is produced when so much of a reactant reacts, we are assuming that all of a reac ...
... So far in this text, when we present a chemical reaction, we have implicitly assumed that the reaction goes to completion. Indeed, our stoichiometric calculations were based on this; when we asked how much of a product is produced when so much of a reactant reacts, we are assuming that all of a reac ...
TDB-5: Standards and conventions for TDB publications
... • The designators (cr), (am), (vit), and (s) are used for solid substances. (cr) is used when it is known that the compound is crystalline, (am) when it is known that it is amorphous, and (vit) for glassy substances. Otherwise, (s) is used. • In some cases, more than one crystalline form of the same ...
... • The designators (cr), (am), (vit), and (s) are used for solid substances. (cr) is used when it is known that the compound is crystalline, (am) when it is known that it is amorphous, and (vit) for glassy substances. Otherwise, (s) is used. • In some cases, more than one crystalline form of the same ...
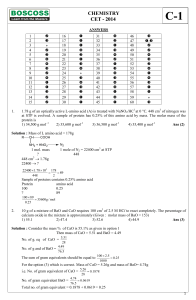
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Acid–Base
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
... A buffer solution contains 0.40 mole of formic acid, HCOOH, and 0.60 mole of sodium formate, HCOONa, in 1.00 litre of solution. The ionization constant, Ka, of formic acid is 1.810–4. (a) Calculate the pH of this solution. (b) If 100. millilitres of this buffer solution is diluted to a volume of 1. ...
2007_UG - St.Joseph`s College
... Isomerism – Types of Isomerism (structural and stereoisomerisms) with appropriate examples – Calculation of empirical and molecular formulae Unit 4: Qualitative Inorganic Analysis Dry test, flame test, borax bead test, Cobalt nitrate test - Wet confirmatory tests for acid radicals - Interfering acid ...
... Isomerism – Types of Isomerism (structural and stereoisomerisms) with appropriate examples – Calculation of empirical and molecular formulae Unit 4: Qualitative Inorganic Analysis Dry test, flame test, borax bead test, Cobalt nitrate test - Wet confirmatory tests for acid radicals - Interfering acid ...
Covert Chemical... 2_Couvertures English chimie 4
... Chemical Reactions 2: Equilibrium and Oxidation-reduction is the third of the three Learning Guides for the Secondary V Chemistry program, which comprises the following three courses: Gases Chemical Reactions 1: Energy and Chemical Dynamics Chemical Reactions 2: Equilibrium and Oxidation-reduction ...
... Chemical Reactions 2: Equilibrium and Oxidation-reduction is the third of the three Learning Guides for the Secondary V Chemistry program, which comprises the following three courses: Gases Chemical Reactions 1: Energy and Chemical Dynamics Chemical Reactions 2: Equilibrium and Oxidation-reduction ...
Lewis acid catalysis
In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common Lewis acid catalysts are based on main group metals such as aluminum, boron, silicon, and tin, as well as many early (titanium, zirconium) and late (iron, copper, zinc) d-block metals. The metal atom forms an adduct with a lone-pair bearing electronegative atom in the substrate, such as oxygen (both sp2 or sp3), nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens. The complexation has partial charge-transfer character and makes the lone-pair donor effectively more electronegative, activating the substrate toward nucleophilic attack, heterolytic bond cleavage, or cycloaddition with 1,3-dienes and 1,3-dipoles.Many classical reactions involving carbon–carbon or carbon–heteroatom bond formation can be catalyzed by Lewis acids. Examples include the Friedel-Crafts reaction, the aldol reaction, and various pericyclic processes that proceed slowly at room temperature, such as the Diels-Alder reaction and the ene reaction. In addition to accelerating the reactions, Lewis acid catalysts are able to impose regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in many cases.Early developments in Lewis acid reagents focused on easily available compounds such as TiCl4, BF3, SnCl4, and AlCl3. The relative strengths of these (and other) Lewis acids may be estimated from NMR spectroscopy by the Childs method or the Gutmann-Beckett method. Over the years, versatile catalysts bearing ligands designed for specific applications have facilitated improvement in both reactivity and selectivity of Lewis acid-catalyzed reactions. More recently, Lewis acid catalysts with chiral ligands have become an important class of tools for asymmetric catalysis.Challenges in the development of Lewis acid catalysis include inefficient catalyst turnover (caused by catalyst affinity for the product) and the frequent requirement of two-point binding for stereoselectivity, which often necessitates the use of auxiliary groups.