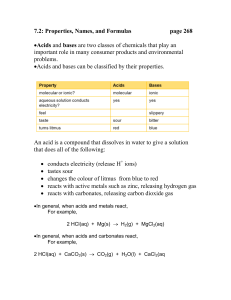
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
Saturday Study Session 1 1st Class Reactions
... . A 0.345 g sample of anhydrous BeC2O4, which contains an inert impurity, was dissolved in sufficient Water to produce 100.0 mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of this solution was titrated with KMnO4(aq). The balanced equation for the reaction that occurs is: 16H+(aq) + 2 MnO4-(aq) + 5 C2O42-(aq) ...
... . A 0.345 g sample of anhydrous BeC2O4, which contains an inert impurity, was dissolved in sufficient Water to produce 100.0 mL of solution. A 20.0 mL portion of this solution was titrated with KMnO4(aq). The balanced equation for the reaction that occurs is: 16H+(aq) + 2 MnO4-(aq) + 5 C2O42-(aq) ...
Review for Final Exam - Short Answer and Problems
... A student in lab titrates an unknown cobalt (II) oxalate dihydrate sample with 23.4 mL of 0.0203 M KMnO4 (aq). The balanced net ionic equation for the titration is: 2 MnO4– (aq) + 5 C2O42– (aq) + 16 H+ (aq) 2 Mn2+ (aq) + 10 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (l) Calculate the mass, in g, of oxalate ion present in th ...
... A student in lab titrates an unknown cobalt (II) oxalate dihydrate sample with 23.4 mL of 0.0203 M KMnO4 (aq). The balanced net ionic equation for the titration is: 2 MnO4– (aq) + 5 C2O42– (aq) + 16 H+ (aq) 2 Mn2+ (aq) + 10 CO2 (g) + 8 H2O (l) Calculate the mass, in g, of oxalate ion present in th ...
answer
... • Alfred Werner, one of the founders of the field of coordination chemistry, prepared a series of platinum complexes that contained ammonia and chloride ions. One of these had the empirical formula PtCl4.4NH3 and when reacted with silver nitrate released two chloride ions per formula unit. Write the ...
... • Alfred Werner, one of the founders of the field of coordination chemistry, prepared a series of platinum complexes that contained ammonia and chloride ions. One of these had the empirical formula PtCl4.4NH3 and when reacted with silver nitrate released two chloride ions per formula unit. Write the ...
File
... as a unit. Energy is stored in chemical bonds. To break bonds, energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction. For example, the burning of wood is a chemical reaction (see F ...
... as a unit. Energy is stored in chemical bonds. To break bonds, energy must be added. When bonds form, energy is released. All chemical reactions involve changes in energy. Energy is either produced or absorbed during a chemical reaction. For example, the burning of wood is a chemical reaction (see F ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... 48- A sample of a gas occupies (30 mL) at standard temperature and pressure (STP). What will be the temperature when the volume increases to (60 mL) and the pressure to (2280 mmHg)? a- 1638ºC b- 1968ºC c- 1638K d- 45.5ºC ...
... 48- A sample of a gas occupies (30 mL) at standard temperature and pressure (STP). What will be the temperature when the volume increases to (60 mL) and the pressure to (2280 mmHg)? a- 1638ºC b- 1968ºC c- 1638K d- 45.5ºC ...
Lecture 6
... from its metastable state to its stable state. (2 minus 1) Equilibrium exists when the phase is at its lowest energy level for the current P-T conditions. (3) (Two minerals that are reactive with one another, may be found to be in equilibrium at particular P-T conditions which on phase diagrams ar ...
... from its metastable state to its stable state. (2 minus 1) Equilibrium exists when the phase is at its lowest energy level for the current P-T conditions. (3) (Two minerals that are reactive with one another, may be found to be in equilibrium at particular P-T conditions which on phase diagrams ar ...
AP_chemistry_Summer_Assignment_2014
... temperature is 68˚F. How many moles are present in the flask when the pressure is 1.10 atm and the temperature is 33˚C? 74.On a warm day, an amusement park balloon is filled with 47.8 g He. The temperature is 33˚C and the pressure in the balloon is 2.25 atm. Calculate the volume of the balloon. 75.A ...
... temperature is 68˚F. How many moles are present in the flask when the pressure is 1.10 atm and the temperature is 33˚C? 74.On a warm day, an amusement park balloon is filled with 47.8 g He. The temperature is 33˚C and the pressure in the balloon is 2.25 atm. Calculate the volume of the balloon. 75.A ...
Science 1206 Unit 3 Part 1
... Recall from last year that you can draw the electron levels in a Bohr diagram. There are two ways to do this, either with circles (messy) or with lines The number of energy levels in a Bohr diagram is equal to the row number in which the element is found. ...
... Recall from last year that you can draw the electron levels in a Bohr diagram. There are two ways to do this, either with circles (messy) or with lines The number of energy levels in a Bohr diagram is equal to the row number in which the element is found. ...
Nothing Lost, Nothing Gained
... amount of stuff. Burn something. Break something. Build something out of sand. All of the little parts, or atoms, that make up everything never grow in number and they never shrink in number. Things might change so that they look very different, but the amount of stuff stays the same. A chemical rea ...
... amount of stuff. Burn something. Break something. Build something out of sand. All of the little parts, or atoms, that make up everything never grow in number and they never shrink in number. Things might change so that they look very different, but the amount of stuff stays the same. A chemical rea ...
File - docstover.org
... Students should be able to summarize the periodic law and explain how relates to physical and chemical properties. Students will be able to use the periodic table as a reference tool. ...
... Students should be able to summarize the periodic law and explain how relates to physical and chemical properties. Students will be able to use the periodic table as a reference tool. ...
oxidationnumbers
... [Note that all of the exceptions given above for oxygen, O, can be determined using Rule 2, after assigning the oxidation numbers of the other elements in the formula. I.e., in MgO2, Mg is in Group 2 and must have a +2 charge, so Rule 2 gives the following: Total charge = 0 = (ox. no. Mg) + 2(ox. no ...
... [Note that all of the exceptions given above for oxygen, O, can be determined using Rule 2, after assigning the oxidation numbers of the other elements in the formula. I.e., in MgO2, Mg is in Group 2 and must have a +2 charge, so Rule 2 gives the following: Total charge = 0 = (ox. no. Mg) + 2(ox. no ...
Halogens - Cronodon
... The chlorine has displaced the bromide because chlorine is a stronger oxidising agent than bromine (equivalently bromide is a stronger reducing agent than chloride). The oxidising power of the halogens decreases in the order: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 (oxidising strength) Q.16. When a halogen oxidises ano ...
... The chlorine has displaced the bromide because chlorine is a stronger oxidising agent than bromine (equivalently bromide is a stronger reducing agent than chloride). The oxidising power of the halogens decreases in the order: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 (oxidising strength) Q.16. When a halogen oxidises ano ...
Word
... At what energy level should you put the activated complex, the top of the peak? Since E a forward = +40 kJ, you know that from the initial reactants (A + B) you need to go up 40 energy units. Pick any value for a starting energy level (let's use a starting point of 10 here), then add 40 to find the ...
... At what energy level should you put the activated complex, the top of the peak? Since E a forward = +40 kJ, you know that from the initial reactants (A + B) you need to go up 40 energy units. Pick any value for a starting energy level (let's use a starting point of 10 here), then add 40 to find the ...
Midterm Review - Closter Public Schools
... Many scientists over a long period of time contributed to the development of the atomic theory. Match each scientist with his contribution. D= Democritus DL= Dalton T= Thomson R= Rutherford B= Bohr S&H= Schrödinger and Heisenberg ...
... Many scientists over a long period of time contributed to the development of the atomic theory. Match each scientist with his contribution. D= Democritus DL= Dalton T= Thomson R= Rutherford B= Bohr S&H= Schrödinger and Heisenberg ...
Document
... d. a molecule that hydrogen bonds well with water. e. a molecule that acts as a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor. 10. The constant Kw, the ion product of water, can be written as: a. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 10-14 b. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 10-7 c. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1014 d. none of these choices e. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1 ...
... d. a molecule that hydrogen bonds well with water. e. a molecule that acts as a proton (hydrogen ion) acceptor. 10. The constant Kw, the ion product of water, can be written as: a. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 10-14 b. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 10-7 c. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1014 d. none of these choices e. Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1 ...
First Year - WordPress.com
... Q. 28. A 50.00 mL sample of a cough mixture prepared by a pharmacist was found to have a mass of 46.0g. what is the density (in g/mL) of this mixture. Stated to the correct number of ...
... Q. 28. A 50.00 mL sample of a cough mixture prepared by a pharmacist was found to have a mass of 46.0g. what is the density (in g/mL) of this mixture. Stated to the correct number of ...
Figure 2: Alternative Periodic Table
... K4+ -> K5+ + eb) Explain the large jumps in ionization energy between the 9th and the 10th and the 17th and the 18th. The jump between the 9th and 10th represents a change from ionizing n=3 electron to ionizing n=2 electrons. The jump between the 17th and 18th represents a change from ionizing n=2 e ...
... K4+ -> K5+ + eb) Explain the large jumps in ionization energy between the 9th and the 10th and the 17th and the 18th. The jump between the 9th and 10th represents a change from ionizing n=3 electron to ionizing n=2 electrons. The jump between the 17th and 18th represents a change from ionizing n=2 e ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.























