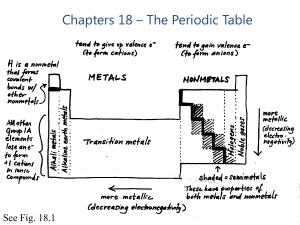
Figure 2: Alternative Periodic Table
... K4+ -> K5+ + eb) Explain the large jumps in ionization energy between the 9th and the 10th and the 17th and the 18th. The jump between the 9th and 10th represents a change from ionizing n=3 electron to ionizing n=2 electrons. The jump between the 17th and 18th represents a change from ionizing n=2 e ...
... K4+ -> K5+ + eb) Explain the large jumps in ionization energy between the 9th and the 10th and the 17th and the 18th. The jump between the 9th and 10th represents a change from ionizing n=3 electron to ionizing n=2 electrons. The jump between the 17th and 18th represents a change from ionizing n=2 e ...
Chemistry 116: General Chemistry
... The reaction is faster at higher temperatures. The reaction has only one type of reactant. The rate remains constant when the reactant concentration is doubled. The reaction slows down as time goes on. The half life remains constant as time goes on. ...
... The reaction is faster at higher temperatures. The reaction has only one type of reactant. The rate remains constant when the reactant concentration is doubled. The reaction slows down as time goes on. The half life remains constant as time goes on. ...
Review 3
... 2. Calculate the equilibrium constant for a given 3. Know the factors that affect reaction rate, and be able to apply them to a specific reaction. ...
... 2. Calculate the equilibrium constant for a given 3. Know the factors that affect reaction rate, and be able to apply them to a specific reaction. ...
9.2 Oxidation Numbers
... Are these reactions oxidation‑reduction reactions? Are electrons transferred? Simply reading a chemical equation does not always tell us whether oxidation and reduction have occurred, so chemists have developed a numerical system to help identify a reaction as redox. For redox reactions, this system ...
... Are these reactions oxidation‑reduction reactions? Are electrons transferred? Simply reading a chemical equation does not always tell us whether oxidation and reduction have occurred, so chemists have developed a numerical system to help identify a reaction as redox. For redox reactions, this system ...
Study of graphite electrode surface with In and Pt deposits E.M.
... reduction (IV). This leads to the process of platinum ions electroreduction overlapping and the simultaneous oxygen release from water, as it occurs at the potentials which are greater than 1 V. In addition, electro-oxidation of platinum occurs before its oxide [3]. Our research showed [4,5] that de ...
... reduction (IV). This leads to the process of platinum ions electroreduction overlapping and the simultaneous oxygen release from water, as it occurs at the potentials which are greater than 1 V. In addition, electro-oxidation of platinum occurs before its oxide [3]. Our research showed [4,5] that de ...
Oxidation of Silicon
... typically in the range of 900-1200 degrees C. The atmosphere in the furnace where oxidation takes place can either contain pure oxygen or water vapor. Both of these molecules diffuse easily through the growing SiO2 layer at these high temperatures. Oxygen arriving at the silicon surface can then com ...
... typically in the range of 900-1200 degrees C. The atmosphere in the furnace where oxidation takes place can either contain pure oxygen or water vapor. Both of these molecules diffuse easily through the growing SiO2 layer at these high temperatures. Oxygen arriving at the silicon surface can then com ...
Electric Potential Energy
... An application that you may not think about is the potential or the electric field present inside a conducting cavity. If we assume that there is no charge present inside the cavity, the electric field inside the cavity must be zero, regardless of the charge distribution on the outside surface of t ...
... An application that you may not think about is the potential or the electric field present inside a conducting cavity. If we assume that there is no charge present inside the cavity, the electric field inside the cavity must be zero, regardless of the charge distribution on the outside surface of t ...
File
... The dz2 and dx2y2 orbitals lie on the same axes as negative charges. Therefore, there is a large, unfavorable interaction between ligand (-) orbitals. These orbitals form the degenerate high energy pair of energy levels. The dxy , dyx and dxz orbitals bisect the negative charges. Therefore, there is ...
... The dz2 and dx2y2 orbitals lie on the same axes as negative charges. Therefore, there is a large, unfavorable interaction between ligand (-) orbitals. These orbitals form the degenerate high energy pair of energy levels. The dxy , dyx and dxz orbitals bisect the negative charges. Therefore, there is ...
nomenclature review
... ________ Magnesium chloride is dissolved in water. ________ Hydrochloric acid neutralizes sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride and water. 13. Why are phase changes considered only physical changes? 14. Sketch an example of the following at the molecular level: a. a gaseous compound b. a mixture ...
... ________ Magnesium chloride is dissolved in water. ________ Hydrochloric acid neutralizes sodium hydroxide to form sodium chloride and water. 13. Why are phase changes considered only physical changes? 14. Sketch an example of the following at the molecular level: a. a gaseous compound b. a mixture ...
Midterm Review Packet - Mrs. McKenzie`s Chemistry and ICP Classes
... 10. In an ionic bond, __________ atoms of ________________ charge are held together by _________________________ attraction. 11. The part of an atom that has a neutral charge is a _______________________. 12. Most of the mass of an atom is found in the _____________________. 13. A pure substance mad ...
... 10. In an ionic bond, __________ atoms of ________________ charge are held together by _________________________ attraction. 11. The part of an atom that has a neutral charge is a _______________________. 12. Most of the mass of an atom is found in the _____________________. 13. A pure substance mad ...
General Equilibrium
... If K is very large, that the equilibrium lies far to the right (or towards products). If K is small, the reaction lies towards reactants. For example, the KHP we are using in lab is a monoprotic acid that undergoes the following equilibrium: ...
... If K is very large, that the equilibrium lies far to the right (or towards products). If K is small, the reaction lies towards reactants. For example, the KHP we are using in lab is a monoprotic acid that undergoes the following equilibrium: ...
POTENTIAL GRADIENT & CATHODE RAY TUBE
... proceeding. The accelerating and focusing anodes serve this purpose. The accelerating anode is located in the third grid; it emits a large positive electromagnetic field which draws and accelerates the electrons through the grids and towards the screen. The focusing anode also emits a large posi ...
... proceeding. The accelerating and focusing anodes serve this purpose. The accelerating anode is located in the third grid; it emits a large positive electromagnetic field which draws and accelerates the electrons through the grids and towards the screen. The focusing anode also emits a large posi ...
Paper - Edexcel
... reaction 1 ................... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ........................................ .............................................................................................. ...
... reaction 1 ................... . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ........................................ .............................................................................................. ...
MIDTERM REVIEW UNIT 1: Mass/Measurement
... a) write the formulas for the reactants and the products and balance the equation b) If 0.67 moles of copper (II) bromide react with 0.52 grams of lead (II) nitrate, how many grams of lead(II) bromid ...
... a) write the formulas for the reactants and the products and balance the equation b) If 0.67 moles of copper (II) bromide react with 0.52 grams of lead (II) nitrate, how many grams of lead(II) bromid ...
Michael Faraday - giftedcrandall
... fact that a conductor at rest and a steady magnetic field do not interact and that to get an induced current either the conductor or the field has to move. On Aug. 29, 1831, he discovered electromagnetic induction. During the next 10 years Faraday explored and expanded the field of electricity. In 1 ...
... fact that a conductor at rest and a steady magnetic field do not interact and that to get an induced current either the conductor or the field has to move. On Aug. 29, 1831, he discovered electromagnetic induction. During the next 10 years Faraday explored and expanded the field of electricity. In 1 ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.