Document
... First, it only applies to ions. Molecules that are not charged have an activity coefficient of 1.0 according to this theory (in reality, that is not true, but their activity coefficients will be much closer to 1 than will that of an ion). Second, the charges that appear in the equation are only thos ...
... First, it only applies to ions. Molecules that are not charged have an activity coefficient of 1.0 according to this theory (in reality, that is not true, but their activity coefficients will be much closer to 1 than will that of an ion). Second, the charges that appear in the equation are only thos ...
HONG KONG DIPLOMA OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
... Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. Mars has a very different atmosphere from that of the Earth. The atmosphere is relatively thin with an average pressure of 0.6 kilopascals (kPa) (compared to Earth’s 101.3 kPa). It is actually less than 1% the atmospheric density of Earth. Therefore, there is ...
... Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. Mars has a very different atmosphere from that of the Earth. The atmosphere is relatively thin with an average pressure of 0.6 kilopascals (kPa) (compared to Earth’s 101.3 kPa). It is actually less than 1% the atmospheric density of Earth. Therefore, there is ...
CHEM MINI-COURSE SERIES M1.2___
... chemical equation must show the fact that no atom can be destroyed or created; i.e., the same number of each type of atoms must appear on both sides of an equation. The atoms merely rearrange or regroup into different elements or compounds; they will not change into other atoms or be lost through a ...
... chemical equation must show the fact that no atom can be destroyed or created; i.e., the same number of each type of atoms must appear on both sides of an equation. The atoms merely rearrange or regroup into different elements or compounds; they will not change into other atoms or be lost through a ...
3 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS
... 10. ZEROTH LAW: “Two bodies in thermal equilibrium with a third are in thermal equilibrium with each other” (Basis of the concept of temperature) 11. FIRST LAW: “The alegraic sum of all energy changes in an isolated system is zero” (Conservation of energy). Energy can be converted from one form to a ...
... 10. ZEROTH LAW: “Two bodies in thermal equilibrium with a third are in thermal equilibrium with each other” (Basis of the concept of temperature) 11. FIRST LAW: “The alegraic sum of all energy changes in an isolated system is zero” (Conservation of energy). Energy can be converted from one form to a ...
Chapter 25 Electric Potential. Solutions of Home Work
... A particle having charge q = +2.00 C and mass m = 0.010 0 kg is connected to a string that is L = 1.50 m long and is tied to the pivot point P in Figure (25.14). The particle, string and pivot point all lie on a frictionless horizontal table. The particle is released from rest when the string makes ...
... A particle having charge q = +2.00 C and mass m = 0.010 0 kg is connected to a string that is L = 1.50 m long and is tied to the pivot point P in Figure (25.14). The particle, string and pivot point all lie on a frictionless horizontal table. The particle is released from rest when the string makes ...
Structure of atoms and solids
... The high electrical and thermal conductivities of metals follows from the ability of these free electrons to freely move throughout their crystal structure. This is not the case in covalent or ionic bonding where electrons are tightly bound to single or groups of atoms. Unlike other crystals, metals ...
... The high electrical and thermal conductivities of metals follows from the ability of these free electrons to freely move throughout their crystal structure. This is not the case in covalent or ionic bonding where electrons are tightly bound to single or groups of atoms. Unlike other crystals, metals ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... In some parts of the country the water supplied to homes is hard water. (a) What is hard water? (2 marks) (b) Give the names and formulae of the two ions that can make water hard. (4 marks) (c) There are some advantages of drinking hard water. Give one of them. (1 mark) (d) What happens if you use t ...
... In some parts of the country the water supplied to homes is hard water. (a) What is hard water? (2 marks) (b) Give the names and formulae of the two ions that can make water hard. (4 marks) (c) There are some advantages of drinking hard water. Give one of them. (1 mark) (d) What happens if you use t ...
chapter 7 - chemical formulas and chemical compounds
... 2) H SO : O and S are each more electronegative than H, so H has an oxidation number of +1. O is ...
... 2) H SO : O and S are each more electronegative than H, so H has an oxidation number of +1. O is ...
sample paper chemistry clas xi set 3
... 5. What is the entropy change when a liquid vaporizes? 6. What is the conjugate acid of NH3? 7. Which out of the two- lithium or sodium forms nitrides? 8. What effect does branching of an alkane has on its boiling point? 9. How many grams of NaOH should be dissolved to make 100 ml of 0.15 M NaOH sol ...
... 5. What is the entropy change when a liquid vaporizes? 6. What is the conjugate acid of NH3? 7. Which out of the two- lithium or sodium forms nitrides? 8. What effect does branching of an alkane has on its boiling point? 9. How many grams of NaOH should be dissolved to make 100 ml of 0.15 M NaOH sol ...
Name - Madison County Schools
... G. If a reaction is going to take place, which Halogen would you expect to react the fastest? Fluorine H. If K reacts very violently in water, what you expect Fr to do? React even more violently I. Define Ionization Energy. Which metal has the highest ionization energy? Why? The amount of energy nee ...
... G. If a reaction is going to take place, which Halogen would you expect to react the fastest? Fluorine H. If K reacts very violently in water, what you expect Fr to do? React even more violently I. Define Ionization Energy. Which metal has the highest ionization energy? Why? The amount of energy nee ...
Iodine Clock Reaction and Photochemical Reduction
... the initial time. Shake the reaction mixture throughout the addition of Na2 S2 O 3 solution. For rapid mixing, an electric motor with glass stirrer may also be arranged in the flask. In order to determine the order with respect to HI, the experiment may be repeated by changing only the KI concentrat ...
... the initial time. Shake the reaction mixture throughout the addition of Na2 S2 O 3 solution. For rapid mixing, an electric motor with glass stirrer may also be arranged in the flask. In order to determine the order with respect to HI, the experiment may be repeated by changing only the KI concentrat ...
1st Semester Practice Test
... a. a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances. b. a substance, made of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded, that can be broken down into simpler, stable substances. c. the smallest unit of matter that maintains its chemical identity. d. any substance ...
... a. a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances. b. a substance, made of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded, that can be broken down into simpler, stable substances. c. the smallest unit of matter that maintains its chemical identity. d. any substance ...
C. Adding acid shifts the equilibrium to the right
... 30. Which best explains why cations are smaller than the atoms from which they are formed? A. The metallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. B. The metallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an entire energy level. C. The nonmetallic atom gains electrons, causin ...
... 30. Which best explains why cations are smaller than the atoms from which they are formed? A. The metallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. B. The metallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an entire energy level. C. The nonmetallic atom gains electrons, causin ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O Notice that there are 4 hydrogen atoms in the reactants and only 2 in the products. Notice that there are only 2 oxygen atoms in the reactants and 3 in the products ...
... CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O Notice that there are 4 hydrogen atoms in the reactants and only 2 in the products. Notice that there are only 2 oxygen atoms in the reactants and 3 in the products ...
Introduction to reaction dynamics
... (i.e. a few femtoseconds), after which it has reached a new point x2 on the surface. We can then calculate the forces at this new point on the surface, set up and solve Newton’s equations to move to a third point x3 , and so on. i.e. we can run a complete trajectory from the beginning to the end of ...
... (i.e. a few femtoseconds), after which it has reached a new point x2 on the surface. We can then calculate the forces at this new point on the surface, set up and solve Newton’s equations to move to a third point x3 , and so on. i.e. we can run a complete trajectory from the beginning to the end of ...
Unit 7 Packet
... Hydrazine (N2H4) and hydrogen peroxide are used together as rocket fuel. The products are nitrogen gas and water. ...
... Hydrazine (N2H4) and hydrogen peroxide are used together as rocket fuel. The products are nitrogen gas and water. ...
Chapter_4_Reactions_in_Aqueous_Solution
... about 0.25 g of chloride, which is a little less than half of the mass of the original sample. Therefore, the calculated percent chloride of 47.51 percent is reasonable. ...
... about 0.25 g of chloride, which is a little less than half of the mass of the original sample. Therefore, the calculated percent chloride of 47.51 percent is reasonable. ...
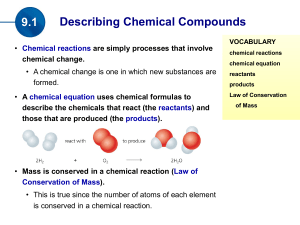
(the products). Mass is conserved in a chemical reaction
... • Some chemical reactions are slow, some are fast. • For example a car rusting is slow; a matchstick burning is fast. • The reaction rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of reactant consumed per unit time or the amount of product formed per unit time. • It is the “speed” of the reaction. ...
... • Some chemical reactions are slow, some are fast. • For example a car rusting is slow; a matchstick burning is fast. • The reaction rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of reactant consumed per unit time or the amount of product formed per unit time. • It is the “speed” of the reaction. ...
High School Curriculum Standards: Chemistry
... Chemistry is the study of matter—its properties and its changes. The idea that matter is made up of particles is over 2000 years old, but the idea of using properties of these particles to explain observable characteristics of matter has more recent origins. In ancient Greece, it was proposed that m ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter—its properties and its changes. The idea that matter is made up of particles is over 2000 years old, but the idea of using properties of these particles to explain observable characteristics of matter has more recent origins. In ancient Greece, it was proposed that m ...
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry that studies chemical reactions which take place at the interface of an electrode, usually a solid metal or a semiconductor, and an ionic conductor, the electrolyte. These reactions involve electric charges moving between the electrodes and the electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). Thus electrochemistry deals with the interaction between electrical energy and chemical change.When a chemical reaction is caused by an externally supplied current, as in electrolysis, or if an electric current is produced by a spontaneous chemical reaction as in a battery, it is called an electrochemical reaction. Chemical reactions where electrons are transferred directly between molecules and/or atoms are called oxidation-reduction or (redox) reactions. In general, electrochemistry describes the overall reactions when individual redox reactions are separate but connected by an external electric circuit and an intervening electrolyte.