Mitochondrial Metabolism in Aging Heart
... acetylated proteins in each population, differences between SSM and IFM were observed. The differences included outcomes from both endogenous acetylation/deacetylation and responses to chemical/nonenzymatic acetylation.40 Of note, SIRT3 content was decreased in SSM but remained unaltered in IFM.40 I ...
... acetylated proteins in each population, differences between SSM and IFM were observed. The differences included outcomes from both endogenous acetylation/deacetylation and responses to chemical/nonenzymatic acetylation.40 Of note, SIRT3 content was decreased in SSM but remained unaltered in IFM.40 I ...
03-1 Metabolism of carbohydrate
... levels F-2,6-BP. Phosphofructokinase 2 (PFK-2) catalyzes the formation of F-2,6-BP from F-6P. F-2,6-BP is converted back to F-6P by fructose bisphosphatase 2 (FBPase-2). ...
... levels F-2,6-BP. Phosphofructokinase 2 (PFK-2) catalyzes the formation of F-2,6-BP from F-6P. F-2,6-BP is converted back to F-6P by fructose bisphosphatase 2 (FBPase-2). ...
Review: can diet influence the selective advantage of mitochondrial
... that efficiency of cellular respiration, as a product of mitochondrial function, underlies the associations between ornamentation and performance for a broad range of traits. Reducing the rates of oxygen consumption and ATP production may also induce a decrease in growth rate and body size [21], whi ...
... that efficiency of cellular respiration, as a product of mitochondrial function, underlies the associations between ornamentation and performance for a broad range of traits. Reducing the rates of oxygen consumption and ATP production may also induce a decrease in growth rate and body size [21], whi ...
cyanobacteria: a potential natural source for drug discovery and
... (NO2-) or nitrates (NO3-) in anaerobic conditions through specialized cells called heterocysts with the help of nitrogenase enzyme. Cyanobacteria accumulate metal ions such as Cr, Co, Cu and Zn very effectively and can utilize ammonia, nitrogenous compounds, and phosphates for their metabolism. They ...
... (NO2-) or nitrates (NO3-) in anaerobic conditions through specialized cells called heterocysts with the help of nitrogenase enzyme. Cyanobacteria accumulate metal ions such as Cr, Co, Cu and Zn very effectively and can utilize ammonia, nitrogenous compounds, and phosphates for their metabolism. They ...
This paper is published in a part-themed issue of Photochemical
... In contrast with the adenylation reaction, essentially clarified in the 1960s, except for the effect of oxygen concentration,13 little was known with respect to the second step, the oxidation of LH2 –AMP. In 1962, Seliger and McElroy observed a 1 : 1 stoichiometry between LH2 and O2 and proposed that ...
... In contrast with the adenylation reaction, essentially clarified in the 1960s, except for the effect of oxygen concentration,13 little was known with respect to the second step, the oxidation of LH2 –AMP. In 1962, Seliger and McElroy observed a 1 : 1 stoichiometry between LH2 and O2 and proposed that ...
Slide 1
... Insulin, which rises subsequent to eating, stimulates the expression of phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase. Glucagon, which rises during starvation, inhibits the expression of these enzymes and stimulates the production of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and fructose 1,6bisphosphatase. Transc ...
... Insulin, which rises subsequent to eating, stimulates the expression of phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase. Glucagon, which rises during starvation, inhibits the expression of these enzymes and stimulates the production of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and fructose 1,6bisphosphatase. Transc ...
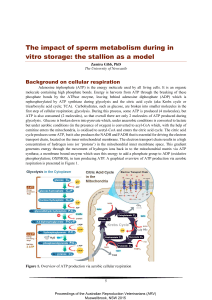
The impact of sperm metabolism during in vitro storage: the stallion
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by all living cells. It is an organic molecule containing high phosphate bonds. Energy is harvests from ATP through the breaking of these phosphate bonds by the ATPase enzyme, leaving behind adenosine diphosphate (ADP) which is rephosphorylate ...
... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the energy molecule used by all living cells. It is an organic molecule containing high phosphate bonds. Energy is harvests from ATP through the breaking of these phosphate bonds by the ATPase enzyme, leaving behind adenosine diphosphate (ADP) which is rephosphorylate ...
Biochemistry of exercise-induced metabolic acidosis
... acidosis. Similarly, there is a wealth of research evidence to show that acidosis is caused by reactions other than lactate production. Every time ATP is broken down to ADP and Pi, a proton is released. When the ATP demand of muscle contraction is met by mitochondrial respiration, there is no proton ...
... acidosis. Similarly, there is a wealth of research evidence to show that acidosis is caused by reactions other than lactate production. Every time ATP is broken down to ADP and Pi, a proton is released. When the ATP demand of muscle contraction is met by mitochondrial respiration, there is no proton ...
Instructor`s Guide to General Chemistry: Guided
... (a) The balanced reaction equation is needed to relate the number of molecules/ions of the reactants to the number of molecules/ions that are produced as products. The number of molecules/ions is measured in units of moles. (b) Steps 2 and 3 make clear what information is given and what needs to be ...
... (a) The balanced reaction equation is needed to relate the number of molecules/ions of the reactants to the number of molecules/ions that are produced as products. The number of molecules/ions is measured in units of moles. (b) Steps 2 and 3 make clear what information is given and what needs to be ...
This article is dedicated to Professor AL
... Destructive, degradative and adaptive rearrangements take place in mitochondria membranes in plant organs after transfer from aerobic to anaerobic environments (Figs 1B and C and 2A±D). Mitochondria of aerobic cells (Fig. 1A) are round or oval, contain several cristae and have a dense matrix. After ...
... Destructive, degradative and adaptive rearrangements take place in mitochondria membranes in plant organs after transfer from aerobic to anaerobic environments (Figs 1B and C and 2A±D). Mitochondria of aerobic cells (Fig. 1A) are round or oval, contain several cristae and have a dense matrix. After ...
Acetyl CoA - WordPress.com
... The oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA commits the carbon atoms of glucose to two principle fates -oxidation to CO2 by the citric acid cycle (and energy ...
... The oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA commits the carbon atoms of glucose to two principle fates -oxidation to CO2 by the citric acid cycle (and energy ...
Nature template
... stoichiometries of a metabolic network, all possible distinct routes by which substrates can flow through the network are described and all feasible metabolic conversions can be described by linear combinations of the flux vectors of the resulting elementary modes. Elementary-modes analysis of oil s ...
... stoichiometries of a metabolic network, all possible distinct routes by which substrates can flow through the network are described and all feasible metabolic conversions can be described by linear combinations of the flux vectors of the resulting elementary modes. Elementary-modes analysis of oil s ...
Drosophila Sirt2/mammalian SIRT3 deacetylates ATP synthase and
... We performed metabolomic profiling on sphingolipid mutants that accumulate ceramide to gain insight into metabolic pathways that could be altered in these mutants. Our earlier study combined metabolomic profiling with genetic and biochemical approaches and demonstrated that dcerk1 mutants show an in ...
... We performed metabolomic profiling on sphingolipid mutants that accumulate ceramide to gain insight into metabolic pathways that could be altered in these mutants. Our earlier study combined metabolomic profiling with genetic and biochemical approaches and demonstrated that dcerk1 mutants show an in ...
The role of the C8 proton of ATP in the catalysis of shikimate kinase
... acid [6]. SK (EC 2.7.1.71), the fifth enzyme in the shikimate biosynthetic pathway, catalyzes phosphate transfer from ATP to the 3-hydroxy group of shikimate, forming shikimate-3-phosphate. Adenylate kinases (AKs) contribute to the homeostasis of adenine nucleotides by maintaining intracellular nucl ...
... acid [6]. SK (EC 2.7.1.71), the fifth enzyme in the shikimate biosynthetic pathway, catalyzes phosphate transfer from ATP to the 3-hydroxy group of shikimate, forming shikimate-3-phosphate. Adenylate kinases (AKs) contribute to the homeostasis of adenine nucleotides by maintaining intracellular nucl ...
PDF
... citryl-CoA lyase; CCS, citryl-CoA synthetase; (Re)/(Si)-CS, (Re)/(Si)-citrate synthase; ED, Entner–Doudoroff; EMP, Emden–Meyerhof–Parnas; FAPs, filamentous anoxygenic phototrophs; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; Fd, ferredoxin; GAP, d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; Glc, glucose; GSBs, green sulfur bacte ...
... citryl-CoA lyase; CCS, citryl-CoA synthetase; (Re)/(Si)-CS, (Re)/(Si)-citrate synthase; ED, Entner–Doudoroff; EMP, Emden–Meyerhof–Parnas; FAPs, filamentous anoxygenic phototrophs; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; Fd, ferredoxin; GAP, d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; Glc, glucose; GSBs, green sulfur bacte ...
PDF
... citryl-CoA lyase; CCS, citryl-CoA synthetase; (Re)/(Si)-CS, (Re)/(Si)-citrate synthase; ED, Entner–Doudoroff; EMP, Emden–Meyerhof–Parnas; FAPs, filamentous anoxygenic phototrophs; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; Fd, ferredoxin; GAP, d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; Glc, glucose; GSBs, green sulfur bacte ...
... citryl-CoA lyase; CCS, citryl-CoA synthetase; (Re)/(Si)-CS, (Re)/(Si)-citrate synthase; ED, Entner–Doudoroff; EMP, Emden–Meyerhof–Parnas; FAPs, filamentous anoxygenic phototrophs; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; Fd, ferredoxin; GAP, d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; Glc, glucose; GSBs, green sulfur bacte ...
THE ATP SYNTHASE—A SPLENDID MOLECULAR MACHINE
... and chemical derivatization studies. Crystallization was in the presence of Mg2+ , 5 µM ADP, and 250 µM AMP-PNP. One catalytic site is filled with ADP, another with AMP-PNP, and a third site is empty. All three noncatalytic sites have bound AMP-PNP. Below a central dimple of about 15 Å, the core is ...
... and chemical derivatization studies. Crystallization was in the presence of Mg2+ , 5 µM ADP, and 250 µM AMP-PNP. One catalytic site is filled with ADP, another with AMP-PNP, and a third site is empty. All three noncatalytic sites have bound AMP-PNP. Below a central dimple of about 15 Å, the core is ...
Review of N and Metal co-Doped TiO for Water Purification under
... In last years, various attempts have been carried out by introduction of non-metals, such as carbon [6], nitrogen [7], sulfur [8], fluorine [9], iodine [10] and boron [11] into the TiO2 bulk to successfully cause the red shift of the absorption onset of TiO2 to the visible region and enhance the pho ...
... In last years, various attempts have been carried out by introduction of non-metals, such as carbon [6], nitrogen [7], sulfur [8], fluorine [9], iodine [10] and boron [11] into the TiO2 bulk to successfully cause the red shift of the absorption onset of TiO2 to the visible region and enhance the pho ...
Mitochondrial Functions in Mood Disorders
... dative stress and/or altered calcium homeostasis [25]. An excess of glutamate in the synapse [26] leads to an excess of cytosolic calcium, which produces overactivity of calcium-depend‐ ent enzymes and an overload of mitochondria by calcium; it leads to cytoskeletal degrada‐ tion, protein malformati ...
... dative stress and/or altered calcium homeostasis [25]. An excess of glutamate in the synapse [26] leads to an excess of cytosolic calcium, which produces overactivity of calcium-depend‐ ent enzymes and an overload of mitochondria by calcium; it leads to cytoskeletal degrada‐ tion, protein malformati ...
Cytochrome P450-enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of mono
... et al. 2011). This finding was not only unexpected because of the low sequence identity with other flavonoid 30 -hydroxylases (35–37 % identity on amino acid level), but also because of the different locations of the biosynthesis of flavonoids and monoterpenoids in planta (Kaltenbach et al. 1999; Ou ...
... et al. 2011). This finding was not only unexpected because of the low sequence identity with other flavonoid 30 -hydroxylases (35–37 % identity on amino acid level), but also because of the different locations of the biosynthesis of flavonoids and monoterpenoids in planta (Kaltenbach et al. 1999; Ou ...
Fermentation metabolism and its evolution in algae
... organisms to maintain viability can only be met if they can stay far from equilibrium. To achieve this situation, they must use energy to satisfy their metabolic demands, which includes continuous synthesis of the cellular energy currency (mostly ATP) along with maintenance of redox and ionic balanc ...
... organisms to maintain viability can only be met if they can stay far from equilibrium. To achieve this situation, they must use energy to satisfy their metabolic demands, which includes continuous synthesis of the cellular energy currency (mostly ATP) along with maintenance of redox and ionic balanc ...
Metabolism, Lectures 25-27 Quadrant – 2 - vtu-nptel
... b) oxygen-forming photosynthesis c) the degradation of organic molecules with the released energy stored in ATP d) anaerobic respiration 4. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy can be a) created b) destroyed c) converted d) all of the above 5. The universal energy currency for all cell ...
... b) oxygen-forming photosynthesis c) the degradation of organic molecules with the released energy stored in ATP d) anaerobic respiration 4. The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy can be a) created b) destroyed c) converted d) all of the above 5. The universal energy currency for all cell ...
Structure-Functional Study of Tyrosine and Methionine Dipeptides
... In the case of the ORAC assay, the additive AOC effect was revealed for all dipeptides with an exception of Trp-Tyr, where a synergic effect was indicated (3.6 vs. 5.1 µmol TE/µmol). The effect of intramolecular electron transfer in Trp-Tyr from Tyr residue to the tryptophan radical was indicated ea ...
... In the case of the ORAC assay, the additive AOC effect was revealed for all dipeptides with an exception of Trp-Tyr, where a synergic effect was indicated (3.6 vs. 5.1 µmol TE/µmol). The effect of intramolecular electron transfer in Trp-Tyr from Tyr residue to the tryptophan radical was indicated ea ...
Full-Text PDF
... photochemical energy conversion, and calculate necessary number of photons per mole glucose fixed just by using the energy of photons [7]. The simple fact that about 1/4 (depending on assumptions and situations) of light energy absorbed by the reaction center cannot be used for performing work accor ...
... photochemical energy conversion, and calculate necessary number of photons per mole glucose fixed just by using the energy of photons [7]. The simple fact that about 1/4 (depending on assumptions and situations) of light energy absorbed by the reaction center cannot be used for performing work accor ...
Escherichia coli ATP Synthase
... Overall, F1 Fo -ATP synthase is structurally and functionally similar among sources with only a few exceptions such as in chloroplasts, where there are two isoforms, and in mitochondria, where there are 7–9 additional subunits. ATP hydrolysis and synthesis occur on three catalytic sites in the F1 se ...
... Overall, F1 Fo -ATP synthase is structurally and functionally similar among sources with only a few exceptions such as in chloroplasts, where there are two isoforms, and in mitochondria, where there are 7–9 additional subunits. ATP hydrolysis and synthesis occur on three catalytic sites in the F1 se ...