Cellular Respiration Part IV: Oxidative Phosphorylation
... Protein complex of electron carriers ...
... Protein complex of electron carriers ...
Energy metabolism - Donald Edward Winslow
... Entropy increases in closed systems. Entropy is disorder. ...
... Entropy increases in closed systems. Entropy is disorder. ...
Document
... 3. Cyanide binds to cytochrome oxidase (complex IV) abolishing electron transfer to oxygen. It does not directly affect the other respiratory complexes, including complex I (i.e. the complex that accepts electrons from NADH and pumps 4 H+ across the membrane). And yet, cyanide fairly rapidly shuts d ...
... 3. Cyanide binds to cytochrome oxidase (complex IV) abolishing electron transfer to oxygen. It does not directly affect the other respiratory complexes, including complex I (i.e. the complex that accepts electrons from NADH and pumps 4 H+ across the membrane). And yet, cyanide fairly rapidly shuts d ...
Unit Two “Energy Acquisition”
... What makes life possible on Earth is the presence of a medium sized star, the Sun Also, just as important is the fact the Earth is at a near perfect distance from the sun: “not too hot, and not too cold” However, animals like us humans still could not survive for any length of time without plant ...
... What makes life possible on Earth is the presence of a medium sized star, the Sun Also, just as important is the fact the Earth is at a near perfect distance from the sun: “not too hot, and not too cold” However, animals like us humans still could not survive for any length of time without plant ...
Photosynthesis and Respiration 1. What are the three parts of an
... What is the green pigment in plants? Chlorophyll ...
... What is the green pigment in plants? Chlorophyll ...
Honors Biology Notes:
... – atmospheric CO2 has increased ___________ in last 200 years; not enough to cause great increase in photosynthesis – greenhouse effect- greater impact on ________________________________________ than rate of photosynthesis • H2O- if plant goes dry ____________________________, no CO2 taken in. • Te ...
... – atmospheric CO2 has increased ___________ in last 200 years; not enough to cause great increase in photosynthesis – greenhouse effect- greater impact on ________________________________________ than rate of photosynthesis • H2O- if plant goes dry ____________________________, no CO2 taken in. • Te ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... A simple, 6 carbon sugar that serves as the primary energy source ATP (Adenosine triphosphate): The major energy currency of the cell. NADH and FADH2: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain. ...
... A simple, 6 carbon sugar that serves as the primary energy source ATP (Adenosine triphosphate): The major energy currency of the cell. NADH and FADH2: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain. ...
How organisms get energy - Fall River Public Schools
... Stacks of sac-like membranes where light-dependent ...
... Stacks of sac-like membranes where light-dependent ...
September 23 Worksheet - Iowa State University
... of this organelle, including what thylakoids, granum, and stroma are. 4. What is the source of energy for photosynthesis? How do plants make high energy free electrons? 5. What are the two types of reactions that occur in photosynthesis? 6. Describe the basic process of the light reactions. 7. What ...
... of this organelle, including what thylakoids, granum, and stroma are. 4. What is the source of energy for photosynthesis? How do plants make high energy free electrons? 5. What are the two types of reactions that occur in photosynthesis? 6. Describe the basic process of the light reactions. 7. What ...
Cellular Respiration 3 Parts Glycolysis Kreb`s Cycle
... Fermentation vs. Aerobic Respiration Each molecule of glucose can generate 3638 molecules of ATP in aerobic respiration but only 2 ATP molecules in respiration without oxygen (through glycolysis and ...
... Fermentation vs. Aerobic Respiration Each molecule of glucose can generate 3638 molecules of ATP in aerobic respiration but only 2 ATP molecules in respiration without oxygen (through glycolysis and ...
X. NONCYCLIC FLOW OF ELECTRONS (or LINEAR FLOW) A. Both
... 4. Photosystem II supplies electrons to P700 to fill these “holes”. 5. Two photons of light are absorbed by pigment molecules of photosystem II. This energy is transferred to P680 reaction center. 6. Excited electrons are trapped by the primary electron acceptor. 7. Electrons are transferred to the ...
... 4. Photosystem II supplies electrons to P700 to fill these “holes”. 5. Two photons of light are absorbed by pigment molecules of photosystem II. This energy is transferred to P680 reaction center. 6. Excited electrons are trapped by the primary electron acceptor. 7. Electrons are transferred to the ...
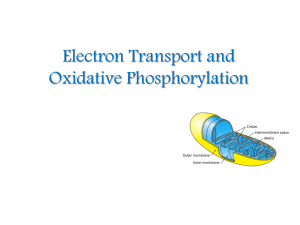
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
... force is carried out by three electron-driven proton pumps: 1- NADH-Q oxidoreductase 2- Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase 3- cytochrome c oxidase. These large transmembrane complexes contain multiple oxidation-reduction centers, including quinones, flavins, ironsulfur clusters, hemes, and copper ions. ...
... force is carried out by three electron-driven proton pumps: 1- NADH-Q oxidoreductase 2- Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase 3- cytochrome c oxidase. These large transmembrane complexes contain multiple oxidation-reduction centers, including quinones, flavins, ironsulfur clusters, hemes, and copper ions. ...
Bio 20-Cellular Respiration Assignment Part A
... 7. Glycolysis takes place in the ____________ of the cells a. Mitochondrial matrix b. Mitochondrial cristae c. Nucleus d. Cytoplasm 8. The carbon containing compounds formed at the end of glycolysis are two molecules of: a. Citric acid b. Carbon dioxide c. Pyruvate d. Lactic acid 9. Muscle fatigue ...
... 7. Glycolysis takes place in the ____________ of the cells a. Mitochondrial matrix b. Mitochondrial cristae c. Nucleus d. Cytoplasm 8. The carbon containing compounds formed at the end of glycolysis are two molecules of: a. Citric acid b. Carbon dioxide c. Pyruvate d. Lactic acid 9. Muscle fatigue ...
Photosynthesis Skeleton Notes
... Each photosystem is light _________________________ Photosystem II is occurs _________________________ Occurs on the membrane of the _________________________ sacs in the chloroplasts 1. _________________________ is split and _________________________ are passed to a protein 2. Once light is a ...
... Each photosystem is light _________________________ Photosystem II is occurs _________________________ Occurs on the membrane of the _________________________ sacs in the chloroplasts 1. _________________________ is split and _________________________ are passed to a protein 2. Once light is a ...
photosynthesis outline 621
... 1. Understand how chemical energy is stored in living things. 2. Describe the difference between ADP and ATP. 3. Know the role of ATP in the cell. 4. Know the overall equation for photosynthesis and understand where each step of the equation is taking place in the plant cell. 5. Understand how the s ...
... 1. Understand how chemical energy is stored in living things. 2. Describe the difference between ADP and ATP. 3. Know the role of ATP in the cell. 4. Know the overall equation for photosynthesis and understand where each step of the equation is taking place in the plant cell. 5. Understand how the s ...
Photosynthesis - Lemon Bay High School
... Chloroplast Structure & Function • Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts • Specifically the thylakoids and stroma • A stack of thylakoids are called a granum ...
... Chloroplast Structure & Function • Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts • Specifically the thylakoids and stroma • A stack of thylakoids are called a granum ...
Micro 071023
... 3 or 4 protons flowing through turns c proteins enough to change conformation of b protein 1 ATP ...
... 3 or 4 protons flowing through turns c proteins enough to change conformation of b protein 1 ATP ...