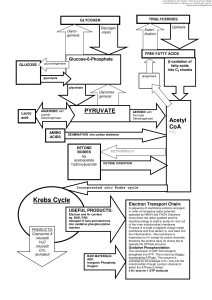
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Aerobic Cellular Respiration
... Respiration: the life process by which organisms convert the chemical energy stored in food to a form of energy more easily utilized by the cell Process of Cell Respiration: a biochemical process used by cells to release energy from organic molecules (food) such as glucose ~this energy is stored in ...
... Respiration: the life process by which organisms convert the chemical energy stored in food to a form of energy more easily utilized by the cell Process of Cell Respiration: a biochemical process used by cells to release energy from organic molecules (food) such as glucose ~this energy is stored in ...
AP Respiration Test Review
... 3. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? 4. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that use store energy to build macromoleulces? 5. What is the primary role of the ADP-ATP cycle? 6. What is the difference between reduction an ...
... 3. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? 4. What is the term for the metabolic pathways that use store energy to build macromoleulces? 5. What is the primary role of the ADP-ATP cycle? 6. What is the difference between reduction an ...
CH 9 Study Guide
... A. What powers this reaction? Sunlight B. What is happening in the light reaction? (What was made?) Energized Electrons C. Where does it occur? Thylakoid D. What is the byproduct? Oxygen E. Where do we cash in these electrons? Electron Transport Chain And who carries the energy for them to the next ...
... A. What powers this reaction? Sunlight B. What is happening in the light reaction? (What was made?) Energized Electrons C. Where does it occur? Thylakoid D. What is the byproduct? Oxygen E. Where do we cash in these electrons? Electron Transport Chain And who carries the energy for them to the next ...
Photosynthesis
... b. __________________energy-capturing portion of photosynthesis that takes place in thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and cannot proceed without solar energy, it produces ATP and NADPH c. __________________green pigment that absorbs solar energy and is important in photosynthesis d. ______________ ...
... b. __________________energy-capturing portion of photosynthesis that takes place in thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and cannot proceed without solar energy, it produces ATP and NADPH c. __________________green pigment that absorbs solar energy and is important in photosynthesis d. ______________ ...
Photosynthesis - kestrelteambiology
... Internal membranes define space (lumen) that is separate from the rest of the stroma ...
... Internal membranes define space (lumen) that is separate from the rest of the stroma ...
Chapter 9 / Energy-Releasing Pathways and Biosynthesis I
... a. takes place on inner mitochondrial membrane b. electrons from Hs carried by NADH and FADH2 c. electron transport chain consists of molecules that are electron acceptors and proteins called cytochromes d. energy from electrons passing through chain is used to make ATP e. final electron acceptor is ...
... a. takes place on inner mitochondrial membrane b. electrons from Hs carried by NADH and FADH2 c. electron transport chain consists of molecules that are electron acceptors and proteins called cytochromes d. energy from electrons passing through chain is used to make ATP e. final electron acceptor is ...
Photosynthesis SG Answers
... 6. What is the big difference between an “autotroph” and a “heterotroph”? Autotrophs make their own food using sunlight and chlorophyll and heterotrophs have to obtain their food from the environment. 7. What role do pigments play in the process of photosynthesis? Absorb the sunlight to excite elect ...
... 6. What is the big difference between an “autotroph” and a “heterotroph”? Autotrophs make their own food using sunlight and chlorophyll and heterotrophs have to obtain their food from the environment. 7. What role do pigments play in the process of photosynthesis? Absorb the sunlight to excite elect ...
Krebs Cycle - Deranged Physiology
... operated by NADH and FADH. Electrons move down the redox gradient and the resulting energy is used to pump H+ ions out of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Purpose is to build a negative charge inside membrane and thus attract H+ ions back into the mitochondrion. (the membrane is impervious to H+ ex ...
... operated by NADH and FADH. Electrons move down the redox gradient and the resulting energy is used to pump H+ ions out of the inner mitochondrial membrane. Purpose is to build a negative charge inside membrane and thus attract H+ ions back into the mitochondrion. (the membrane is impervious to H+ ex ...
Biology 112/111
... 9. a) Where do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur? b) Where do the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis occur? c) Where does glycolysis occur? d) Where does the Krebs cycle occur? e) Where does electron transport in cellular respiration occur? 10. What is needed for the ...
... 9. a) Where do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur? b) Where do the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis occur? c) Where does glycolysis occur? d) Where does the Krebs cycle occur? e) Where does electron transport in cellular respiration occur? 10. What is needed for the ...
CHAPTER-V BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION
... Complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase; labeled IV), which uses the electrons and hydrogen ions to reduce molecular oxygen to water. Four membrane-bound complexes have been identified in mitochondria. Each is an extremely complex transmembrane structure that is embedded in the inner membrane. Three of the ...
... Complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase; labeled IV), which uses the electrons and hydrogen ions to reduce molecular oxygen to water. Four membrane-bound complexes have been identified in mitochondria. Each is an extremely complex transmembrane structure that is embedded in the inner membrane. Three of the ...
Metal Ions Involved in Photosynthesis
... LH2 is a transmembrane 16-mer protein complex It absorbs light at short wavelength. The energy is then funneled to LH1, and then further to the reaction centre LH2 binds 24 bacteriochlorophyll a (BChl a) and 8 lycopene (carotenoid) molecules 16 BChl a molecules form a 16-bladed “turbine”, in which i ...
... LH2 is a transmembrane 16-mer protein complex It absorbs light at short wavelength. The energy is then funneled to LH1, and then further to the reaction centre LH2 binds 24 bacteriochlorophyll a (BChl a) and 8 lycopene (carotenoid) molecules 16 BChl a molecules form a 16-bladed “turbine”, in which i ...
Other Pathways of Photosynthesis
... membrane are used by enzymes in stroma during light-independent reactions. ...
... membrane are used by enzymes in stroma during light-independent reactions. ...
cellular respiration
... cycle, is broken down into CO2 – Used by ATP synthase • Products of Krebs cycle are ATP and electron carriers • ATP and electron carriers are used up • Electron carriers power electron absorbing CO2 making transport chain which creates 3-carbon sugar in the proton gradient ...
... cycle, is broken down into CO2 – Used by ATP synthase • Products of Krebs cycle are ATP and electron carriers • ATP and electron carriers are used up • Electron carriers power electron absorbing CO2 making transport chain which creates 3-carbon sugar in the proton gradient ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... 1st electron valence shell holds _2_ electrons 2nd electron valence shell holds _8_ electrons 3rd electron valence shell holds _8_ electrons ...
... 1st electron valence shell holds _2_ electrons 2nd electron valence shell holds _8_ electrons 3rd electron valence shell holds _8_ electrons ...
Biology-1 Exam Two Sample Questions Substrates bind to an
... 2. Which of the following statements regarding enzyme function is false? a. An enzyme's function depends on its three-dimensional shape. b. Enzymes are very specific for certain substrates. c. Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. d. Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they catalyze. e. ...
... 2. Which of the following statements regarding enzyme function is false? a. An enzyme's function depends on its three-dimensional shape. b. Enzymes are very specific for certain substrates. c. Enzymes are used up in chemical reactions. d. Enzymes emerge unchanged from the reactions they catalyze. e. ...
Aerobic Respiration
... • The electron is transferred to the first electron carrier, whilst H+ remains in solution. • As the electron is transferred to oxygen, H+ is drawn from solution to reduce oxygen to water. ...
... • The electron is transferred to the first electron carrier, whilst H+ remains in solution. • As the electron is transferred to oxygen, H+ is drawn from solution to reduce oxygen to water. ...
10 - GEOCITIES.ws
... iii. Flow of protons is used to make ATP iv. Eventually excited electrons are captured by NADP b. Cyclic i. Photosystem I feeds electrons back into the cytochrome complex ii. Makes more ATP but no NADP c. Realtionship i. Noncyclic doesn't make the right ratio of ATP/NADP for use in Calcin cycle ii. ...
... iii. Flow of protons is used to make ATP iv. Eventually excited electrons are captured by NADP b. Cyclic i. Photosystem I feeds electrons back into the cytochrome complex ii. Makes more ATP but no NADP c. Realtionship i. Noncyclic doesn't make the right ratio of ATP/NADP for use in Calcin cycle ii. ...
Study Guide
... Krebs (aka Citric Acid) Cycle, net yields of energy molecules – location of pathway Role of Coenzyme A (CoA) Substrate level phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP Mitochondrial structure Electron transport chain (ETC), role of NADH, FADH2 in donating electrons to ETC, where located, function of ETC ...
... Krebs (aka Citric Acid) Cycle, net yields of energy molecules – location of pathway Role of Coenzyme A (CoA) Substrate level phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP Mitochondrial structure Electron transport chain (ETC), role of NADH, FADH2 in donating electrons to ETC, where located, function of ETC ...
Name KEY Block Date Ch 8 – Photosynthesis + Ch 9 – Cellular
... 10. What are the two stages of photosynthesis? Briefly summarize each: a. Light-Dependent Reactions – (light absorption) uses sunlight to produce two energy carriers, NADPH and ATP b. Light-independent reactions – uses carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce glucose, using energy from NADPH and ATP (from st ...
... 10. What are the two stages of photosynthesis? Briefly summarize each: a. Light-Dependent Reactions – (light absorption) uses sunlight to produce two energy carriers, NADPH and ATP b. Light-independent reactions – uses carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce glucose, using energy from NADPH and ATP (from st ...
Presentation
... 3. Which spectrum(s) of light is used by plants and the pigments associated with light spectrum. 4. The two stages of photosynthesis and their products ...
... 3. Which spectrum(s) of light is used by plants and the pigments associated with light spectrum. 4. The two stages of photosynthesis and their products ...
Chapter 1 The Framework of Biology
... 6.2 Photosynthesis harnesses the energy in sunlight. Many types of organisms are capable of performing photosynthesis including some bacteria, certain single-celled eukaryotes, algae and plants. The biochemical pathways of photosynthesis take place largely inside chloroplasts. Chloroplast structure ...
... 6.2 Photosynthesis harnesses the energy in sunlight. Many types of organisms are capable of performing photosynthesis including some bacteria, certain single-celled eukaryotes, algae and plants. The biochemical pathways of photosynthesis take place largely inside chloroplasts. Chloroplast structure ...
Hughes respiration homework (2)
... Our bodies digest the food we eat by mixing it with fluids (acids and enzymes) in the stomach. When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose. Glucose has energy stored in its chemical bonds,these bonds are bro ...
... Our bodies digest the food we eat by mixing it with fluids (acids and enzymes) in the stomach. When the stomach digests food, the carbohydrate (sugars and starches) in the food breaks down into another type of sugar, called glucose. Glucose has energy stored in its chemical bonds,these bonds are bro ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation and Electron Transport Chain(ETC)
... the citric acid cycle , they contain three 2Fe-2S centers, bound FAD, and a binding site for the substrate,succinate. The path of electron transfer from the succinate-binding site to FAD, then through the FeS centers to the Q-binding site. • Complex III: Ubiquinone to Cytochrome c The next respirato ...
... the citric acid cycle , they contain three 2Fe-2S centers, bound FAD, and a binding site for the substrate,succinate. The path of electron transfer from the succinate-binding site to FAD, then through the FeS centers to the Q-binding site. • Complex III: Ubiquinone to Cytochrome c The next respirato ...