Review Outline for Atomic Structure Test
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
ATP Production
... Cellular Respiration (anaerobic) What happens when cells don’t have enough oxygen? Some organisms live in an oxygen-free environment. The Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport How do they get their energy? ...
... Cellular Respiration (anaerobic) What happens when cells don’t have enough oxygen? Some organisms live in an oxygen-free environment. The Kreb’s Cycle and Electron Transport How do they get their energy? ...
Homework 3 BSC 1005 Fall 2011
... a. thylakoids. b. cytoplasm. c. grana. d. stroma. 45.Two products of the light-dependent reactions, which become reactants for the lightindependent reactions, are a. ATP and NADP. b. CO2 and H2O. c. O2 and ATP. d. ATP and NADPH2. 46.O2 is a product of the a. light-dependent reactions. b. light-indep ...
... a. thylakoids. b. cytoplasm. c. grana. d. stroma. 45.Two products of the light-dependent reactions, which become reactants for the lightindependent reactions, are a. ATP and NADP. b. CO2 and H2O. c. O2 and ATP. d. ATP and NADPH2. 46.O2 is a product of the a. light-dependent reactions. b. light-indep ...
Exam Review
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
... A) Subatomic particles a. What are the atomic mass units for protons, neutrons, and electrons? Protons and neutrons = 1 amu; electrons about 0 amu What does the atomic number represent? # of protons b. What does the mass number represent? # of protons + # of neutrons c. What particles are in equal n ...
Answers to study guide
... and releasing more ATP and also NADH and FADH2 ATP synthase—The enzyme embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where H+ ions go through to produce ADP +P into ATP Questions to answer: 1. How much ATP is generated in glycolysis? 2 ATP 2. What is the energy investment/energy payoff relatio ...
... and releasing more ATP and also NADH and FADH2 ATP synthase—The enzyme embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion where H+ ions go through to produce ADP +P into ATP Questions to answer: 1. How much ATP is generated in glycolysis? 2 ATP 2. What is the energy investment/energy payoff relatio ...
Cellular Respiration
... • If oxygen is available: Cellular respiration starts • If oxygen is NOT available, to make more NAD+, your body goes through fermentation. • This way ATP can be made even without Oxygen. ...
... • If oxygen is available: Cellular respiration starts • If oxygen is NOT available, to make more NAD+, your body goes through fermentation. • This way ATP can be made even without Oxygen. ...
Biol 178 Lecture 13
... • Electrostatic repulsion of phosphates Unstable (low AE to break the bonds). • ATP ADP + Pi + Energy (7.3 kcal/mole). ...
... • Electrostatic repulsion of phosphates Unstable (low AE to break the bonds). • ATP ADP + Pi + Energy (7.3 kcal/mole). ...
Solomon chapter 8 practice AP bio test sept 2015
... a hydrolysis reaction. a redox process. a polymerization reaction. an anabolic process. ...
... a hydrolysis reaction. a redox process. a polymerization reaction. an anabolic process. ...
Zoology – The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... 4. Enzymes – mostly large, complex proteins that function as biological catalysts under specific conditions. (A special type of RNA can also function as an enzyme.) a.Enzymes do the following: 1) Break bonds and allow new bonds to form, facilitating chemical reactions 2) Speed up reaction times (sim ...
... 4. Enzymes – mostly large, complex proteins that function as biological catalysts under specific conditions. (A special type of RNA can also function as an enzyme.) a.Enzymes do the following: 1) Break bonds and allow new bonds to form, facilitating chemical reactions 2) Speed up reaction times (sim ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the atoms in order of
... add 0.100 mol of any of the following gases: NH3, H2, CO2, or N2. a) The pressure increases least for the addition of 0.100 mol H2. b) The pressure increases more for the addition of 0.100 mol CO2 than for the addition of the same amount of N2. c) The increase in pressure will be proportional to the ...
... add 0.100 mol of any of the following gases: NH3, H2, CO2, or N2. a) The pressure increases least for the addition of 0.100 mol H2. b) The pressure increases more for the addition of 0.100 mol CO2 than for the addition of the same amount of N2. c) The increase in pressure will be proportional to the ...
Basic Chemistry and Cell Structure
... Transport vesicles bud off the ER and are transported to the forming face of the Golgi. Membrane-bound proteins and secretory proteins then move through the Golgi, where they are modified, usually by ...
... Transport vesicles bud off the ER and are transported to the forming face of the Golgi. Membrane-bound proteins and secretory proteins then move through the Golgi, where they are modified, usually by ...
H 2
... biologically important molecules, e.g. proteins and DNA, and the transport of molecules and ions throughout the organism. Other processes occur only at certain times, such as muscle contraction and other cellular movements. Animals obtain their energy by oxidation of foods, plants do so by trapping ...
... biologically important molecules, e.g. proteins and DNA, and the transport of molecules and ions throughout the organism. Other processes occur only at certain times, such as muscle contraction and other cellular movements. Animals obtain their energy by oxidation of foods, plants do so by trapping ...
File
... Two steps of photosynthesis: 1. Light Dependent Reactions: a. Where: in the thylakoid membranes b. What: sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll (excites electrons) and water is split by light. c. Why?: to provide ATP for step 2 d. Purpose: Take sunlight and turn it into chemical energy (ATP) e. Needs ...
... Two steps of photosynthesis: 1. Light Dependent Reactions: a. Where: in the thylakoid membranes b. What: sunlight is absorbed by chlorophyll (excites electrons) and water is split by light. c. Why?: to provide ATP for step 2 d. Purpose: Take sunlight and turn it into chemical energy (ATP) e. Needs ...
Introduction and Cell Biology
... Transport vesicles bud off the ER and are transported to the forming face of the Golgi. Membrane-bound proteins and secretory proteins then move through the Golgi, where they are modified, usually by ...
... Transport vesicles bud off the ER and are transported to the forming face of the Golgi. Membrane-bound proteins and secretory proteins then move through the Golgi, where they are modified, usually by ...
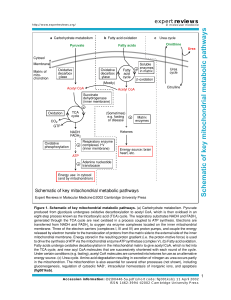
Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways
... Figure 1. Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways. (a) Carbohydrate metabolism. Pyruvate produced from glycolysis undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to acetyl CoA, which is then oxidised in an eight-step process known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The respiratory substrates NADH ...
... Figure 1. Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways. (a) Carbohydrate metabolism. Pyruvate produced from glycolysis undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to acetyl CoA, which is then oxidised in an eight-step process known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The respiratory substrates NADH ...
This is Most of an Old Exam
... Cellular oxidation of food fuels is the immediate source of electrons for oxidative phosphorylation. B. In oxidative phosphorylation, both the electron transport proteins and the ATP synthase molecules are in the same membrane. C. NAD+ and FAD+ are hydrogen carrier molecules. NAD+ can carry one hydr ...
... Cellular oxidation of food fuels is the immediate source of electrons for oxidative phosphorylation. B. In oxidative phosphorylation, both the electron transport proteins and the ATP synthase molecules are in the same membrane. C. NAD+ and FAD+ are hydrogen carrier molecules. NAD+ can carry one hydr ...
... • Also known as cytochrome system or hydrogen transfer system. • Takes place on the cristae of the mitochondria on groups of protein molecules. • The reduced co-enzymes (NADH and FADH2) from the glycolytic and citric acid pathways transfer the hydrogen to a chain of carriers. • High energy electrons ...
Regents Review: Photosynthesis and Respiration
... Describe the process of glycolysis? Does it occur in both types of respiration? How much energy is produced? Splitting of glucose (6-carbons) into two pyruvic acid molecules (3-carbons) which occurs in the cytoplasm. Occurs in both types and produces 4 ATP total for each glucose molecule. ...
... Describe the process of glycolysis? Does it occur in both types of respiration? How much energy is produced? Splitting of glucose (6-carbons) into two pyruvic acid molecules (3-carbons) which occurs in the cytoplasm. Occurs in both types and produces 4 ATP total for each glucose molecule. ...
29 Cellular Respiration Biology “B”
... _____ 2.) There are one-celled bacteria (NOT blue-green) and single-celled yeast that do not have mitochondria. How do they process energy? a.) use sun for energy b.) use glycolysis only c.) use Krebs only _____ 3.) The definition of glycolysis is: a.) the breakage of lipids b.) the breakage of prot ...
... _____ 2.) There are one-celled bacteria (NOT blue-green) and single-celled yeast that do not have mitochondria. How do they process energy? a.) use sun for energy b.) use glycolysis only c.) use Krebs only _____ 3.) The definition of glycolysis is: a.) the breakage of lipids b.) the breakage of prot ...
Match the term to the description Cellular Respiration
... In the Ven diagram able, list similarities between cellular respiration and photosynthesis in the middle and the differences on the sides Photosynthesis only ...
... In the Ven diagram able, list similarities between cellular respiration and photosynthesis in the middle and the differences on the sides Photosynthesis only ...
doc
... a stepwise cascade much like going down a staircase. The path that electrons take on their way down from glucose to oxygen involves many steps. The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. ...
... a stepwise cascade much like going down a staircase. The path that electrons take on their way down from glucose to oxygen involves many steps. The first step is an electron acceptor called NAD+. ...
Cell Respiration Student Notes
... •Enzyme activity increases as __________________________ increases because there are more collisions between substrate molecules and the enzyme. ...
... •Enzyme activity increases as __________________________ increases because there are more collisions between substrate molecules and the enzyme. ...
ATP and Energetics of Metabolism
... • You can’t understand thermodynamics until we clear up some common misconceptions about equilibrium… • Is this reaction at equilibrium or not? • If not, in which direction does the equilibrium lie? ...
... • You can’t understand thermodynamics until we clear up some common misconceptions about equilibrium… • Is this reaction at equilibrium or not? • If not, in which direction does the equilibrium lie? ...
Cellular Respiration
... in the lungs there are millions of little air sacs called alveoli that are surrounded by capillaries here the blood drops off carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen this oxygen will be taken directly to the cells when the oxygen gets to the cell, the mitochondria takes it and begins the process of cellu ...
... in the lungs there are millions of little air sacs called alveoli that are surrounded by capillaries here the blood drops off carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen this oxygen will be taken directly to the cells when the oxygen gets to the cell, the mitochondria takes it and begins the process of cellu ...