
Cellular Respiration Review
... Proton pump pumps hydrogen ions creates H+ gradient or proton gradient This gradient is equivalent to a pH gradient or an electrical gradient with lots of potential energy These hydrogen ions eventually want to come back across the inner membrane but can do so only by passing via a special pr ...
... Proton pump pumps hydrogen ions creates H+ gradient or proton gradient This gradient is equivalent to a pH gradient or an electrical gradient with lots of potential energy These hydrogen ions eventually want to come back across the inner membrane but can do so only by passing via a special pr ...
Plants and Photosynthesis
... What Reaction uses water to make/build something more complex? – ____________________________________ ...
... What Reaction uses water to make/build something more complex? – ____________________________________ ...
How do Plants Obtain the Food they Need to Live and Grow Review.
... Photosynthesis is summarised by the equation: carbon dioxide + water (+ light energy) ...
... Photosynthesis is summarised by the equation: carbon dioxide + water (+ light energy) ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
... chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
... chain so that their energy can be used to convert ADP into ATP These reactions require oxygen, which accepts the H+ ions to form water Occurs in the mitochondria The entire process of aerobic respiration produces 36 ATP molecules ...
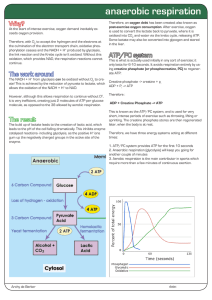
anaerobic respiration
... Therefore, with O2 to accept the hydrogen and the electrons at the culmination of the electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation ceases and the NADH + H+ produced by glycolysis, the link reaction and the Krebs cycle isn’t oxidized. Without this oxidation, which provides NAD, the respiration ...
... Therefore, with O2 to accept the hydrogen and the electrons at the culmination of the electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation ceases and the NADH + H+ produced by glycolysis, the link reaction and the Krebs cycle isn’t oxidized. Without this oxidation, which provides NAD, the respiration ...
SBI-4U1 Exam Review
... At low light intensities, light intensity limits the photosynthetic rate. The amount of NADPH and ATP produced depends on availability of light. As light intensity increases, the light-saturation point is reached: this is the point where light is no longer the limiting factor – it will be either CO2 ...
... At low light intensities, light intensity limits the photosynthetic rate. The amount of NADPH and ATP produced depends on availability of light. As light intensity increases, the light-saturation point is reached: this is the point where light is no longer the limiting factor – it will be either CO2 ...
V. Chemical reactions
... XI. Naming organic compounds A. Prefixes1. Based on number of carbons 2. Know the first five prefixes. (meth, eth, prop, but, pent) B. Suffixes ...
... XI. Naming organic compounds A. Prefixes1. Based on number of carbons 2. Know the first five prefixes. (meth, eth, prop, but, pent) B. Suffixes ...
Chlorophyll (60 Softgels)
... Chlorophyll, the green matter in plants, is found abundantly in nature. Through the process of photosynthesis, chlorophyll harnesses the sun’s energy in order to perform various metabolic functions. When humans and other animals eat plant chlorophyll they benefit from the sun’s energy, too. The mulb ...
... Chlorophyll, the green matter in plants, is found abundantly in nature. Through the process of photosynthesis, chlorophyll harnesses the sun’s energy in order to perform various metabolic functions. When humans and other animals eat plant chlorophyll they benefit from the sun’s energy, too. The mulb ...
Mitochondrion Pyruvate Oxidation & Kreb`s Cycle
... Energy factories of the cell; produce the majority of the cell's ATP These ATP producing reactions cannot take place without oxygen, therefore the steps of cellular respiration that occur in the mitochondria are said to be aerobic. Pyruvate Oxidation (Link reaction), Krebs Cycle and the Electron ...
... Energy factories of the cell; produce the majority of the cell's ATP These ATP producing reactions cannot take place without oxygen, therefore the steps of cellular respiration that occur in the mitochondria are said to be aerobic. Pyruvate Oxidation (Link reaction), Krebs Cycle and the Electron ...
Bio 110 S.I. chapters 6 & 7
... in the cell to become active. The result may change the cell permanently or temporarily ...
... in the cell to become active. The result may change the cell permanently or temporarily ...
Biology Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration Notes Glycolysis: “Glucose splits”
... Explain how the human body uses its daily supply of ATP. Minimum functions (maintenance) = 75% of calories taken in each day Voluntary Activity = varies according to activity ...
... Explain how the human body uses its daily supply of ATP. Minimum functions (maintenance) = 75% of calories taken in each day Voluntary Activity = varies according to activity ...
4. Photosynthesis Booklet [A2]
... photosystems I and II. The stroma is the fluid-filled matrix of the chloroplast in which the reactions of the light independent phase of photosynthesis takes place. The light independent phase is the process of carbon fixation via the Calvin cycle. The thylakoid membranes provide a large surface are ...
... photosystems I and II. The stroma is the fluid-filled matrix of the chloroplast in which the reactions of the light independent phase of photosynthesis takes place. The light independent phase is the process of carbon fixation via the Calvin cycle. The thylakoid membranes provide a large surface are ...
lec33_F2015
... to water. Note that the oxygen only serves as a final acceptor of electrons in this process. In many organisms other compounds besides oxygen can serve as electron sinks, allowing organisms to perform 'oxidative' phosphorylation in the absence of O2. The actual synthesis of ATP is from a proton grad ...
... to water. Note that the oxygen only serves as a final acceptor of electrons in this process. In many organisms other compounds besides oxygen can serve as electron sinks, allowing organisms to perform 'oxidative' phosphorylation in the absence of O2. The actual synthesis of ATP is from a proton grad ...
power point plants
... the leaves – this is how the oxygen is also removed. The water required is absorbed by the roots. The word equation for this reaction is... ...
... the leaves – this is how the oxygen is also removed. The water required is absorbed by the roots. The word equation for this reaction is... ...
ch4 reading guide
... __________________________________________________________________ 2. One end of a tRNA molecule contains ________________________________ and the other end contains_____________________________________________ 3. An anticodon is __________________________________________________ 4. The nucleotides ...
... __________________________________________________________________ 2. One end of a tRNA molecule contains ________________________________ and the other end contains_____________________________________________ 3. An anticodon is __________________________________________________ 4. The nucleotides ...
The Chemistry of Life
... • The atom that lost an electron becomes positively charged anion, while the atom that has gained an electron becomes a negatively charged cation. • Cations and anions are mutually attracted to one another by their charges. • This mutual attraction results in the formation of a crystal, which is a h ...
... • The atom that lost an electron becomes positively charged anion, while the atom that has gained an electron becomes a negatively charged cation. • Cations and anions are mutually attracted to one another by their charges. • This mutual attraction results in the formation of a crystal, which is a h ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular R
... The ETC converts the chemical energy to a form used to drive oxidative phosphorylation. Cycle generates 1 ATP per turn by substrate phosphorylation…but most of the chemical energy is transferred during the redox reactions to NAD+ and FAD. The reduced coenzymes, NADH and FADH2, shuttle their cargo of ...
... The ETC converts the chemical energy to a form used to drive oxidative phosphorylation. Cycle generates 1 ATP per turn by substrate phosphorylation…but most of the chemical energy is transferred during the redox reactions to NAD+ and FAD. The reduced coenzymes, NADH and FADH2, shuttle their cargo of ...
Review for Unit 3 Exam
... Organisms acquire energy from their surroundings. Cells cannot exchange materials with their environment. The metabolism of an organism is isolated from its surroundings. Heat produced by the organism is conserved in the organism and not lost to the environment. Because energy must be conserved, org ...
... Organisms acquire energy from their surroundings. Cells cannot exchange materials with their environment. The metabolism of an organism is isolated from its surroundings. Heat produced by the organism is conserved in the organism and not lost to the environment. Because energy must be conserved, org ...
Ionic Bonding
... noble gas core, they are not found in ionic compounds with a noble gas core (thus they may have color). Some examples which can form a noble gas core (and be colorless): Ag: [Kr]5s14d10 Ag+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: AgCl Cd: [Kr]5s24d10 Cd2+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: CdS The valence electrons do not adhere to the ...
... noble gas core, they are not found in ionic compounds with a noble gas core (thus they may have color). Some examples which can form a noble gas core (and be colorless): Ag: [Kr]5s14d10 Ag+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: AgCl Cd: [Kr]5s24d10 Cd2+ [Kr]4d10 Compound: CdS The valence electrons do not adhere to the ...















![4. Photosynthesis Booklet [A2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003124571_1-bb10566ec715b4c9138d0adabd909b9d-300x300.png)






