4.2 Cellular Respiration - Dr Rob's A
... glycolysis/Krebs will eventually combine with O2 to form water However, they break into H+ and e- first, the protons remaining in solution the electrons passing along a carrier system, hence the electron transport chain Each carrier in the chain is at a slightly lower energy level and the electron i ...
... glycolysis/Krebs will eventually combine with O2 to form water However, they break into H+ and e- first, the protons remaining in solution the electrons passing along a carrier system, hence the electron transport chain Each carrier in the chain is at a slightly lower energy level and the electron i ...
METABOLIC PATHWAYS & ENZYMES
... molecules during oxidation-reduction process • Both processes all take place at the same time • Take place during photosynthesis and cellular respiration ...
... molecules during oxidation-reduction process • Both processes all take place at the same time • Take place during photosynthesis and cellular respiration ...
Cellular Respiration notes HONORS
... – It is split into two three carbon molecules (3Carbon; 3C) called PGAL. Enzymes rearrange the molecules – Energized electrons from the molecules are transferred to molecules of NAD+ to make NADH – A series of reactions converts the PGAL molecules to pyruvate, which will enter the mitochondria for c ...
... – It is split into two three carbon molecules (3Carbon; 3C) called PGAL. Enzymes rearrange the molecules – Energized electrons from the molecules are transferred to molecules of NAD+ to make NADH – A series of reactions converts the PGAL molecules to pyruvate, which will enter the mitochondria for c ...
No Slide Title
... 6) Reaction 4: Isocitrate and NAD+ react to form the energy carrier and oxalosuccinate. 7) Reaction 5: Oxalosuccinate loses a molecule of CO2, forming ketoglutarate. 8) Reaction 6: Ketoglutarate hooks up with Coenzyme A to form succinyl CoA. This process releases 2 electrons and H to form NADH. 9) I ...
... 6) Reaction 4: Isocitrate and NAD+ react to form the energy carrier and oxalosuccinate. 7) Reaction 5: Oxalosuccinate loses a molecule of CO2, forming ketoglutarate. 8) Reaction 6: Ketoglutarate hooks up with Coenzyme A to form succinyl CoA. This process releases 2 electrons and H to form NADH. 9) I ...
Chapter 9.5 and 9.6
... glucose without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid ...
... glucose without an electron transport chain and that produces a characteristic end product, such as ethyl alcohol or lactic acid ...
Lecture 6 POWERPOINT here
... Increase the rate of virtually ALL chemical reactions - fact: A reaction that takes just milliseconds in the presence of an enzyme would take millions of years without (some increase the rate by as much as 1 x 1018 fold!!!) Enzyme pool selectively determines which reactions shall take place insi ...
... Increase the rate of virtually ALL chemical reactions - fact: A reaction that takes just milliseconds in the presence of an enzyme would take millions of years without (some increase the rate by as much as 1 x 1018 fold!!!) Enzyme pool selectively determines which reactions shall take place insi ...
INTERACTIVE GENETICS
... 1. What is the complete chemical equation for photosynthesis? 2. Where does photosynthesis take place - What organelle? - What part of the organelle? - Light Reactions- Dark Reactions- ...
... 1. What is the complete chemical equation for photosynthesis? 2. Where does photosynthesis take place - What organelle? - What part of the organelle? - Light Reactions- Dark Reactions- ...
File
... 6. Answers may vary. Sample answer: ATP is formed when ADP is coupled to an exergonic process, usually involving energy released from the metabolism of food. Then ATP transfers free energy to an endergonic process by phosphorylating other molecules. By doing this it becomes ADP again and is availabl ...
... 6. Answers may vary. Sample answer: ATP is formed when ADP is coupled to an exergonic process, usually involving energy released from the metabolism of food. Then ATP transfers free energy to an endergonic process by phosphorylating other molecules. By doing this it becomes ADP again and is availabl ...
light independent reactions
... 1.) The process by which autotrophs convert sunlight energy into chemical energy for use by their cells is called photosynthesis. 2.) How can it be said that photosynthesis “supports most life on Earth?” With the exception of chemoautotrophs, organisms that make food directly from sunlight (photoaut ...
... 1.) The process by which autotrophs convert sunlight energy into chemical energy for use by their cells is called photosynthesis. 2.) How can it be said that photosynthesis “supports most life on Earth?” With the exception of chemoautotrophs, organisms that make food directly from sunlight (photoaut ...
Document
... external terminal electron acceptor is not O2 eg. NO3- (nitrate), Fe3+, SO4-, CO2, CO32-, fumarate or another organic molecule ...
... external terminal electron acceptor is not O2 eg. NO3- (nitrate), Fe3+, SO4-, CO2, CO32-, fumarate or another organic molecule ...
Lecture 8
... Cellular respiration, also known as 'oxidative metabolism', is one of the key ways a cell gains useful energy. It is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in organisms' cells To convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release w ...
... Cellular respiration, also known as 'oxidative metabolism', is one of the key ways a cell gains useful energy. It is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in organisms' cells To convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release w ...
Name Date Period 1. What are the end products of aerobic cell
... Name the parts labelled A, B and C and state the function of each. ...
... Name the parts labelled A, B and C and state the function of each. ...
photosynthesis
... - A photosystem is a light harvesting unit made of a protein complex called the reaction center surrounded by light harvesting complexes. - light harvesting complexes consist of various pigments. ...
... - A photosystem is a light harvesting unit made of a protein complex called the reaction center surrounded by light harvesting complexes. - light harvesting complexes consist of various pigments. ...
Intro part 2
... Red light has a wavelength of 750 nm and thus has the longest wavelength (of visible light) with the lowest energy. Violet light has wavelengths of 380 nm and thus has the shortest wavelength (of visible light) with the highest energy. ...
... Red light has a wavelength of 750 nm and thus has the longest wavelength (of visible light) with the lowest energy. Violet light has wavelengths of 380 nm and thus has the shortest wavelength (of visible light) with the highest energy. ...
6.1 Organizing the Periodic Table
... protons does not equal the # of electrons this forms an ion • Ion- charged atom • Formation of an ion requires energy because an electron must be removed Anions are named by using part of the element name and the suffix -ide ...
... protons does not equal the # of electrons this forms an ion • Ion- charged atom • Formation of an ion requires energy because an electron must be removed Anions are named by using part of the element name and the suffix -ide ...
produced in photosynthesis
... photorespiration is less likely to occur, a decided advantage under hot, dry conditions where water may be scarce and the stomata remain closed for long periods, trapping oxygen in the plant. This process is relatively inefficient, but if water is in short supply the inefficient C4 route is still be ...
... photorespiration is less likely to occur, a decided advantage under hot, dry conditions where water may be scarce and the stomata remain closed for long periods, trapping oxygen in the plant. This process is relatively inefficient, but if water is in short supply the inefficient C4 route is still be ...
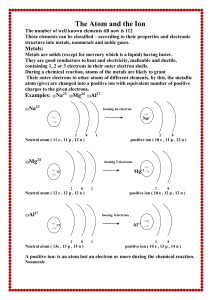
The Atom and the Ion
... atom (give) are changed into a positive ion with equivalent number of positive charges to the given electrons. ...
... atom (give) are changed into a positive ion with equivalent number of positive charges to the given electrons. ...
Mitochondrial Lab - University of Colorado Denver
... Carbon and Hydrogen (C-H) in succinate, it takes the excited electrons and the Hydrogen atoms (actually hydride) from the chemical bonds and gives them to FAD FAD becomes FADH2 FADH2 transfers the electrons to the electron transport chain. Energy from excited electrons used to make ATP ...
... Carbon and Hydrogen (C-H) in succinate, it takes the excited electrons and the Hydrogen atoms (actually hydride) from the chemical bonds and gives them to FAD FAD becomes FADH2 FADH2 transfers the electrons to the electron transport chain. Energy from excited electrons used to make ATP ...
Photosynthesis
... Noncyclic Electron Pathway Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. H2O ...
... Noncyclic Electron Pathway Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. H2O ...
Cellular Respiration - Fulton County Schools
... Occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of Autotrophs and Heterotrophs C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP + Heat ...
... Occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of Autotrophs and Heterotrophs C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP + Heat ...
Chp 4 Cell Energy
... • The electron transport chain uses NADH and FADH2 to make ATP. • The breakdown of one glucose molecule produces up to 38 molecules of ATP. – ATP synthase produces ATP – oxygen picks up electrons and hydrogen ions – water is released as a waste product ...
... • The electron transport chain uses NADH and FADH2 to make ATP. • The breakdown of one glucose molecule produces up to 38 molecules of ATP. – ATP synthase produces ATP – oxygen picks up electrons and hydrogen ions – water is released as a waste product ...
cellular respiration
... and FADH2) are brought to the inner membranes of the mitochondria. The electrons are passed back and forth across the membrane from one cytochrome to another. During this process their energy is gradually decreased and used to transport H+ through the membrane. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor ...
... and FADH2) are brought to the inner membranes of the mitochondria. The electrons are passed back and forth across the membrane from one cytochrome to another. During this process their energy is gradually decreased and used to transport H+ through the membrane. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor ...