Lecture #2 - Dr.Nazar Abbas Home Page
... configurable (programmable) logic blocks of logic alongwith configurable interconnects between thes blocks ...
... configurable (programmable) logic blocks of logic alongwith configurable interconnects between thes blocks ...
JohnAnalog
... of 400 microns. The whole structure is surrounded by an additional n+ diffusion which acts as the collector of an npn structure. The collector scoops up current discharged into the substrate more effectively than the p+ cathode strips alone. Each such diode has a total capacitance, area plus fringe, ...
... of 400 microns. The whole structure is surrounded by an additional n+ diffusion which acts as the collector of an npn structure. The collector scoops up current discharged into the substrate more effectively than the p+ cathode strips alone. Each such diode has a total capacitance, area plus fringe, ...
Principles of Computer Architecture Dr. Mike Frank
... fluctuation in dopant concentrations. • Source-to-drain tunneling. ...
... fluctuation in dopant concentrations. • Source-to-drain tunneling. ...
Lab I Critique
... Comment: If the utility infrastructure had been developed to act as a current source, customer equipment, as well as compensation devices, would have to be connected in series. Think about the practical problems associated with such a scheme. ...
... Comment: If the utility infrastructure had been developed to act as a current source, customer equipment, as well as compensation devices, would have to be connected in series. Think about the practical problems associated with such a scheme. ...
KIRCHOFF`S VOLTAGE LAW: EXAMPLE 1
... Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law is a useful tool for circuit analysis. The voltage drops across both resistors were equal even though the currents were different. The voltage drop is ALWAYS the same across two resistors in parallel. Notice that IR1 + IR2 = I. This means that current is conserved. We will ...
... Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law is a useful tool for circuit analysis. The voltage drops across both resistors were equal even though the currents were different. The voltage drop is ALWAYS the same across two resistors in parallel. Notice that IR1 + IR2 = I. This means that current is conserved. We will ...
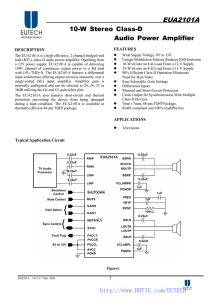
EUA2101A 10-W Stereo Class-D Audio Power Amplifier
... The EUA2101A is a high efficiency, 2 channel bridged-tied load (BTL), class-D audio power amplifier. Operating from a 12V power supply, EUA2101A is capable of delivering 10W/ channel of continuous output power to a 8Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EUA2101A features a differential input architecture offer ...
... The EUA2101A is a high efficiency, 2 channel bridged-tied load (BTL), class-D audio power amplifier. Operating from a 12V power supply, EUA2101A is capable of delivering 10W/ channel of continuous output power to a 8Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EUA2101A features a differential input architecture offer ...
DM7420 Dual 4-Input NAND Gate
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
Lecture 10 - UniMAP Portal
... • Transistor gate, source, drain all have capacitance – I = C (DV/Dt) -> Dt = (C/I) DV – Capacitance and current determine speed ...
... • Transistor gate, source, drain all have capacitance – I = C (DV/Dt) -> Dt = (C/I) DV – Capacitance and current determine speed ...
CMOS Design With Delay Constraints: Design for Performance
... output to the input gate – called Bootstrapping or Miller Effect – as input rises and output falls, Cgd couples back a portion of output transient to the input, thus slowing the input rising waveform – SPICE simulation at left shows impact on input node ‘a’ due to a 0.05pF bootstrap capacitor versus ...
... output to the input gate – called Bootstrapping or Miller Effect – as input rises and output falls, Cgd couples back a portion of output transient to the input, thus slowing the input rising waveform – SPICE simulation at left shows impact on input node ‘a’ due to a 0.05pF bootstrap capacitor versus ...
An Improved Current Mode Logic Latch
... load resistors are replaced by P-type MOSFETs (M1 and M2) with their gates connected to ground. This configuration is some similar to one proposed by Ref.[14]. However, in this paper, the lower supply feature is discussed in details. In addition, a cross coupled pair (M5 and M6) is added to compensat ...
... load resistors are replaced by P-type MOSFETs (M1 and M2) with their gates connected to ground. This configuration is some similar to one proposed by Ref.[14]. However, in this paper, the lower supply feature is discussed in details. In addition, a cross coupled pair (M5 and M6) is added to compensat ...
Find the Thévenin equivalent circuit at the terminals U, V.
... Begin by applying a 1V source and arranging the current according to passive sign convention. So it should enter the terminal associated with the positive voltage. This means that Va is 1V, so our left dependent source is 2 V. We want the current that flows through this mesh, specifically current Ib ...
... Begin by applying a 1V source and arranging the current according to passive sign convention. So it should enter the terminal associated with the positive voltage. This means that Va is 1V, so our left dependent source is 2 V. We want the current that flows through this mesh, specifically current Ib ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.