CENTRIPENTAL ACCELERATION AND FORCE PROBLEMS
... occurs in the current? 12. If the resistance of a circuit remains constant while the voltage across the circuit decreases to half its former value, what change occurs in the current? 13. Why is it that a bird can perch without harm on a high voltage wire? ...
... occurs in the current? 12. If the resistance of a circuit remains constant while the voltage across the circuit decreases to half its former value, what change occurs in the current? 13. Why is it that a bird can perch without harm on a high voltage wire? ...
CMOS VLSI Design 4th Ed.
... 3-input NAND Gate Y pulls low if ALL inputs are 1 Y pulls high if ANY input is 0 ...
... 3-input NAND Gate Y pulls low if ALL inputs are 1 Y pulls high if ANY input is 0 ...
Crossbar
... so they do not experience the, size, power, leakage or heat problems that transistors do. ...
... so they do not experience the, size, power, leakage or heat problems that transistors do. ...
Circuit Sums with ac
... would expect in a purely inductive circuit (A) and in a circuit containing both inductance and resistance (B). What is the PHASE SHIFT or PHASE DIFFERENCE between the voltage and current in each case ? (1 full cycle = 360 degree). If the circuit contains capacitance, the opposite effect happens; the ...
... would expect in a purely inductive circuit (A) and in a circuit containing both inductance and resistance (B). What is the PHASE SHIFT or PHASE DIFFERENCE between the voltage and current in each case ? (1 full cycle = 360 degree). If the circuit contains capacitance, the opposite effect happens; the ...
Water level indicator with alarm
... regulation, eliminating the distribution problems associated with single point regulation. Each type employs internal current limiting, thermal shut-down and safe area protection, making it essentially indestructible. If adequate heat sinking is provided, they can deliver over 1 A output current. Al ...
... regulation, eliminating the distribution problems associated with single point regulation. Each type employs internal current limiting, thermal shut-down and safe area protection, making it essentially indestructible. If adequate heat sinking is provided, they can deliver over 1 A output current. Al ...
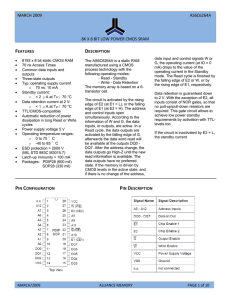
AS6C6264A - Alliance Memory
... All voltages are referenced to VSS = 0 V (ground). All characteristics are valid in the power supply voltage range and in the operating temperature range specified. Dynamic measurements are based on a rise and fall time of ≤ 5 ns, measured between 10 % and 90 % of VI, as well as input levels of VIL ...
... All voltages are referenced to VSS = 0 V (ground). All characteristics are valid in the power supply voltage range and in the operating temperature range specified. Dynamic measurements are based on a rise and fall time of ≤ 5 ns, measured between 10 % and 90 % of VI, as well as input levels of VIL ...
High-voltage circuits for power management on 65 nm CMOS
... of standard device interfaces and batteries. Thus one common method to design high-voltage circuits is to use highvoltage transistors, which are technology dependent (Bandyopadhyay et al., 2011). In contrast, high-voltage circuits based on stacked low-voltage CMOS transistors are more efficient beca ...
... of standard device interfaces and batteries. Thus one common method to design high-voltage circuits is to use highvoltage transistors, which are technology dependent (Bandyopadhyay et al., 2011). In contrast, high-voltage circuits based on stacked low-voltage CMOS transistors are more efficient beca ...
A simple experiment was devised to check out ground-loop effects....
... Therefore, by thoroughly adjusting both feedback resistors, a linear relation between input and output voltages can be attained. Additionally, the 1.5 kΩ load resistor is used to limit the maximum current that could flow through the LED (~15 mA) and thus avoid LED damage. After the incorporation of ...
... Therefore, by thoroughly adjusting both feedback resistors, a linear relation between input and output voltages can be attained. Additionally, the 1.5 kΩ load resistor is used to limit the maximum current that could flow through the LED (~15 mA) and thus avoid LED damage. After the incorporation of ...
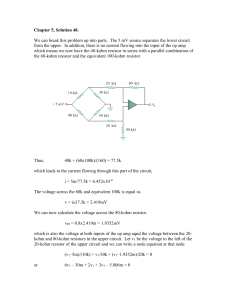
S04_EXAM_Final_Sol - Engineering Class s
... Bonus Problem: (30%) The small signal model pertinent to determining the effective resistance seen by capacitance C is given below. From this model, and using the fact that M1 and M2 are identical transistors conducting identical quiescent currents, ...
... Bonus Problem: (30%) The small signal model pertinent to determining the effective resistance seen by capacitance C is given below. From this model, and using the fact that M1 and M2 are identical transistors conducting identical quiescent currents, ...
SIMULATED DESIGN OF 5 STAGE CMOS RING OSCILLATOR FOR
... scaling technology, increase of resistance R and obviously high-speed data-rate. The serial-link structure performed at high speed offers significant flexibility both in case of fibre-channel and giga-bit Ethernet standard. The interfered signals in a channel form the shape of an eye. The shared bus ...
... scaling technology, increase of resistance R and obviously high-speed data-rate. The serial-link structure performed at high speed offers significant flexibility both in case of fibre-channel and giga-bit Ethernet standard. The interfered signals in a channel form the shape of an eye. The shared bus ...
Circuits and Circuit Diagrams
... • Voltage drop across each device depends directly on its resistance (V = I x R) • Total voltage divides among the individual electric devices in the circuit (Rtotal = RA + RB) ...
... • Voltage drop across each device depends directly on its resistance (V = I x R) • Total voltage divides among the individual electric devices in the circuit (Rtotal = RA + RB) ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.