0.8V 1GHz Dynamic Comparator in Digital 90nm CMOS Technology
... maximum power dissipation was 222µW, almost half of this was dissipated in the output buffers. As previously stated we have used a similar architecture to that of [7]. They achieved 100µW with 200fF at 50Msamples/s and 1V in a 0.25µm CMOS technology. Since most of the power dissipation in this archi ...
... maximum power dissipation was 222µW, almost half of this was dissipated in the output buffers. As previously stated we have used a similar architecture to that of [7]. They achieved 100µW with 200fF at 50Msamples/s and 1V in a 0.25µm CMOS technology. Since most of the power dissipation in this archi ...
lecture10
... to make the sound. An analog voltage causes the cones to vibrate. The D/A converter helps translate digitally stored music into an analog voltage for the speakers. Digital music (CD, MP3) provides a number indicating the sound amplitude at each sample time. These numbers get translated into analog v ...
... to make the sound. An analog voltage causes the cones to vibrate. The D/A converter helps translate digitally stored music into an analog voltage for the speakers. Digital music (CD, MP3) provides a number indicating the sound amplitude at each sample time. These numbers get translated into analog v ...
Design of a 3-T Half Adder
... performance of microprocessors. Dynamic CMOS circuits are used in microprocessors to improve their timing performance. This method has many challenges like transistor sizing, charge sharing, noise-immunity, leakage current etc. The growing world demands for circuits with ultralow power dissipation. ...
... performance of microprocessors. Dynamic CMOS circuits are used in microprocessors to improve their timing performance. This method has many challenges like transistor sizing, charge sharing, noise-immunity, leakage current etc. The growing world demands for circuits with ultralow power dissipation. ...
1 - UTRGV Faculty Web
... file in the near future. Because it is on the screen, you need to capture the screen an include it with the source code so that the TAs can give you a grade. In an electrical circuit, a current is generated if voltage is applied across one or more resistances. Write a program to calculate Current (a ...
... file in the near future. Because it is on the screen, you need to capture the screen an include it with the source code so that the TAs can give you a grade. In an electrical circuit, a current is generated if voltage is applied across one or more resistances. Write a program to calculate Current (a ...
Test Procedure for the NCP1013LED Evaluation Board Introduction:
... nominal. It is power limited if the power exceeds 5W. A typical transfer function of the output voltage‐ current characteristic is illustrated below. ...
... nominal. It is power limited if the power exceeds 5W. A typical transfer function of the output voltage‐ current characteristic is illustrated below. ...
ec assignment
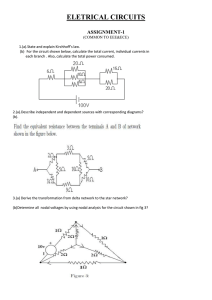
... (b) For the circuit shown below, calculate the total current, individual currents in each branch . Also, calculate the total power consumed. ...
... (b) For the circuit shown below, calculate the total current, individual currents in each branch . Also, calculate the total power consumed. ...
EET421 Exp#3 - UniMAP Portal
... to supply DC voltage to a DC motor through a single-phase semiconverter (as an AC to DC power converter). The motor with a rectifier bridge should have different performance and characteristics. The speed, harmonics, total harmonic distortion (THD) and power factor should be observed as these will h ...
... to supply DC voltage to a DC motor through a single-phase semiconverter (as an AC to DC power converter). The motor with a rectifier bridge should have different performance and characteristics. The speed, harmonics, total harmonic distortion (THD) and power factor should be observed as these will h ...
Transistors
... Figure 3.27 Forward bias applied to a p-n junction to give a current flow. In an earlier exercise the change in resistance of a LDR in response to light was used directly to control the brightness of a LED. In low power applications this is sufficient. If higher powers are required the LDR cannot ca ...
... Figure 3.27 Forward bias applied to a p-n junction to give a current flow. In an earlier exercise the change in resistance of a LDR in response to light was used directly to control the brightness of a LED. In low power applications this is sufficient. If higher powers are required the LDR cannot ca ...
compact - Murrelektronik
... Evolution means progress. Therefore it is a perfect name for the Murrelektronik three phase power supplies. Evolution is the result of consistent development of our proven power supply products. Evolution power supplies set new standards in power supply design by providing a compact, powerful, and e ...
... Evolution means progress. Therefore it is a perfect name for the Murrelektronik three phase power supplies. Evolution is the result of consistent development of our proven power supply products. Evolution power supplies set new standards in power supply design by providing a compact, powerful, and e ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.