* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hw4-1
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Valve audio amplifier technical specification wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
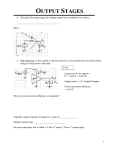
Name: ____________________________________________ Student # ________ Homework for Chapter 4-1 and 2 Questions of the Day: What is an Op-Amp, and how is it used? What is the eqivalent circuit model for an op-amp? What is negative feedback, and why is it used in OpAmp Circuits? Problems: Electrical Engineering is all about ‘what can you do to a voltage’ (or current, or resistance…). Op amp circuits let us do many different things to our voltages, currents, and resistance – such as amplifying (or reducing), comparing, adding, differencing, etc. In the next several homework assignments, we will explore several of these different types of circuits and how they are used in various applications. 1. Op amps can amplify small voltage differences. See Problem 4.8 from your Ulaby textbook. Do this problem first using the op amp model in Figure 4-4 (like the solution manual) and then repeat using the simplified ideal op amp equations in Table 4-2. You should get the same answers. 2. Op amps can be used to detect small changes in resistance. Here is an example of a Rain or Moisture sensor from1. You will be building something similar in Lab 4. Using the ideal op amp equations in Table 4-2, find an equation for the op amp output voltage for the Rain Activated Logic circuit. Although he has given you possible values of resistance and supply voltage (+6V), leave your answer as a function of the variables R1,R2,Rsensor,and Vcc, so you can use it later in the lab. Hint: The circuit you should solve looks like this: 3. Op amps can be used to amplify small differences in resistance. See the Thermistor Amplifier Circuit below. (This is often called a Comparator.) This circuit is like an inverting amplifier. The ‘nominal’ value of Vo = -R3/R2, but it will change slightly as the thermistor resistance RT changes with temperature. Solve for Vo. Treat R3 as a constant = 100kohm. Treat R1 as a constant 10kohm. Treat the thermistor as RT = R1+ΔR1 . 4. The Temperature Switch below is very similar to the Thermistor Amplifier you calculated above. Repeat your calculations for Vo for the Temperature Switch. 1 Forrest M. Mims III, ‘Science & Communication Circuits & Projects’, Master Publishing, Inc.,2007