* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
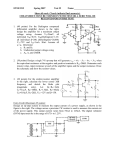
Lab #5 Overview • Activity #1 - Simulation of an Op-Amp inverting amplifier • Activity #2 - Build and Test the Op-Amp inverting amplifier • Activity #3 - Determining the Gain and Saturation of the Op-Amp inverting amplifier Simulation • Run the simulated circuit found in the class folder (Lab_5_Circuit.msm) • Notice that a negative voltage is used as the input to produce a positive output voltage • The gain is the output divided by the input Build and Test • Build and test the circuit • Measure each resistor before assembling into the circuit, so you can find the current through each resistor later Photo #1 - Power Connections on the Proto-Board Make sure there is visible wire at the terminals, so that the terminals are not clamping down on the wire insulation +15V ground At this end there will be a cut-out and/or a dot next to pin 1 ground -15V Photo #2 An example circuit layout of figure 5 on page 4 of the lab C1 R3 R1 Vin C2 1 2 8 7 3 4 6 5 R2 R6 R4 R7 Vout R5 Photo #3 - Vin Connections from the HP DC Power Supply Vin Determining Saturation • Change the input voltage until the output stops going up ( it has reached saturation) • Switching the leads on the DC power supply enable you to get positive voltages on the inputs (and negative output voltages)