* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Operational Amplifiers - Georgia Institute of Technology
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Equalization (audio) wikipedia , lookup
Phase-locked loop wikipedia , lookup
Analogue filter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
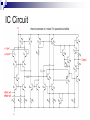
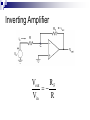
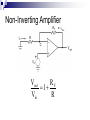
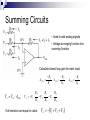
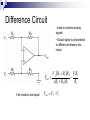
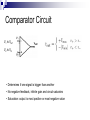
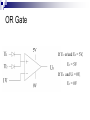
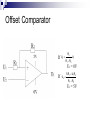
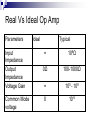
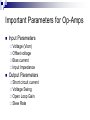
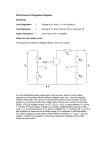
Operational Amplifiers David Lomax Azeem Meruani Gautam Jadhav What is an Op-Amp Low cost integrating circuit consisting of: Transistors Resistors Capacitors Able to amplify a signal due to an external power supply Name derives from its use to perform operations on a signal. Applications of Op-Amps Simple Amplifiers Summers Comparators Integrators Differentiators Active Filters Analog to Digital Converters Symbol for an Op-Amp +V Inverting Input Terminal Non-Inverting Input Terminal -V IC Circuit What do they really look like? Ideal Op-Amps V- IVout V+ Infinite input impedance I+ = I - = 0 Infinite gain I+ V+ = V- Zero output impedance Output voltage is independent of output current Inverting Amplifier RF iin R C Vin Vout RF Vin R iout Non-Inverting Amplifier RF iin R C Vin Vout RF 1 Vin R iout Summing Circuits • Used to add analog signals • Voltage averaging function into summing function Calculate closed loop gain for each input ACL1 Vo Vin ACLn Vo V1 Rf R1 If all resistors are equal in value: V2 Rf Rf R2 R1 V3 ACL1 Rf R2 Rf R3 Vo V1 V2 V3 ACL1 Rf R3 Difference Circuit • Used to subtract analog signals • Output signal is proportional to difference between two inputs Vout If all resistors are equal: V 2 R3 R1 R4 V1R3 ( R4 R2 ) R1 R1 Vout V2 V1 Integrating Circuit • Replace feedback resistor of inverting op-amp with capacitor • A constant input signal generates a certain rate of change in output voltage • Smoothes signals over time Differentiating Circuit • Input resistor of inverting op-amp is replaced with a capacitor • Signal processing method which accentuates noise over time • Output signal is scaled derivative of input signal Filters Low Pass Filters High Pass Filters Band Pass Filters Low Pass Filter • Used to filter out signals above a specified frequency • Example: Noise Frequency range is governed by: 1 f 2 R C Where R = R2 C = C2 High Pass Filter • Filters out frequencies below a specified frequency • Reverse locations of resistors and capacitors in a low pass filter Band Pass Filter • Created by combining a high and low pass filter • Only allows signals within frequency ranges specified by the low and high pass filters to pass Comparator Circuit V1 is Vref V2 is Vin • Determines if one signal is bigger than another • No negative feedback, infinite gain and circuit saturates • Saturation: output is most positive or most negative value OR Gate If U1 or/and U2 = 5V, U3 = 5V If U2 and U1 = 0V, U3 = 0V Offset Comparator If U2 R2 R1 R2 .U1 U3 = 0V If U2 5.R1 U1.R2 R1 R2 U3 = 5V Real Vs Ideal Op Amp Parameters Input Impedance Output Impedance Voltage Gain Common Mode voltage Ideal Typical ∞ 106Ω 0Ω 100-1000Ω ∞ 105 - 109 0 10-5 Non-Ideal Op-Amps Gain Bandwidth Falloff Frequency Slew Rate (ΔV/ΔT) Rise Time Gain Bandwidth Gain Bandwidth Product (GBP)- is the product of the open-loop gain and the bandwidth at that gain. For practical purposes the actual gain should only be 1/10 to 1/20 of the open loop gain at a given frequency to ensure that the op-amp will operate without distortion. Open and Closed Loop Response Important Parameters for Op-Amps Input Parameters Voltage (Vicm) Offset voltage Bias current Input Impedance Output Parameters Short circuit current Voltage Swing Open Loop Gain Slew Rate Where to buy Op-Amps Newark Electronics Radio Shack DigiKey Jameco References David G Alciatore & Michael B. Histand, Introduction to Mechatronics and Measurement Systems http://www.elexp.com/t_gain.htm http://allaboutelectronics.com Electronics book Questions ?